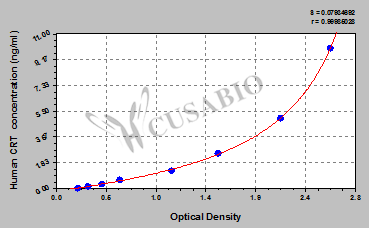
The product CSB-E09787h is a ready-to-use microwell, strip plate ELISA Kit for quantitatively detecting the amount of the Calreticulin (CRT/CALR) in human serum, plasma, urine, or tissue homogenates. This assay kit was designed and optimized for Tags & Cell Markers-related research in humans. It has undergone rigorous quality control in multiple parameters, including sensitivity, specificity, precision, linearity, recovery, and inter-batch difference. Refer to the product instructions for more details. This assay employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique, in which CRT in the samples or standards are sandwiched between pre-coated CRT antibody and Biotin-conjugated CRT antibody. HRP-avidin is then added into the wells. Following a wash to remove any unbound reagent, the TMB substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of CRT bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped upon adding the stop solution, and the intensity of the color is measured at 450 nm via a microplate reader. The levels of CRT in the samples can be determined by referring to the O.D. (optical density) of the samples to the standard curve.
CRT, also called CALR, is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) chaperone protein involved in conformation-dependent molecular sorting of newly synthesized proteins (known as quality control (QC)). Within the ER, CALR normally binds misfolded proteins and retains them for ER-associated degradation (ERAD). Outside of the ER, CALR also participates in a variety of biological processes, including antigen processing and presentation for the adaptive immune response, cell adhesion/migration, cell proliferation, and immunogenic cell death. In the nucleus, CALR regulates gene expression and influences cell proliferation by suppressing interactions between retinoic acid receptor and its DNA response elements.