| Code | CSB-E08040r |
| Size | 96T,5×96T,10×96T |
| Price | Request a Quote or Start an on-line Chat |
| Trial Size |
24T ELISA Kit Trial Size (Only USD$150/ kit) * The sample kit cost can be deducted from your subsequent orders of 96T full size kits of the same analyte at 1/5 per kit, until depleted in 6 months. Apply now |
| Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<15% | ||||||
| Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess. | ||||||
| Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<15% | ||||||
| Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess. | ||||||
| To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of rat TRH in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay. | ||||||
| Sample | Serum(n=4) | |||||
| 1:1 | Average % | 100 | ||||
| Range % | 96-104 | |||||
| 1:2 | Average % | 92 | ||||
| Range % | 88-95 | |||||
| 1:4 | Average % | 93 | ||||
| Range % | 87-96 | |||||
| 1:8 | Average % | 101 | ||||
| Range % | 97-105 | |||||
| The recovery of rat TRH spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section. | ||||||
| Sample Type | Average % Recovery | Range | ||||
| Serum (n=5) | 95 | 89-99 | ||||
| EDTA plasma (n=4) | 97 | 93-102 | ||||
| These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
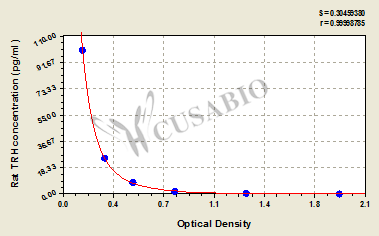
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Rat Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH) ELISA Kit is a highly sensitive and accurate assay for the detection and quantification of TRH in serum, plasma, and tissue homogenates from the Rat species.
TRH is a peptide hormone that plays a vital role in regulating the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the pituitary gland. Abnormalities in TRH levels have been linked to a variety of neurological and psychiatric disorders, as well as endocrine system dysfunction. Thyroid hormone-releasing hormone is the first messenger signal in the brain in many of the actions that control thyroid hormone production.Our TRH ELISA Kit offers a simple and efficient means of measuring TRH levels in biological samples, with a detection range of 0.5 pg/mL to 100 pg/mL and a sensitivity of 0.25 pg/mL.
The assay principle of our TRH ELISA Kit is based on the competitive method. During the assay process, a TRH-specific antibody is added to the coated wells, along with a biotinylated TRH standard and the sample. The biotinylated TRH competes with the TRH in the sample for binding to the antibody, resulting in a decreased signal. The signal is then detected using streptavidin-HRP and a chromogenic substrate, producing a colorimetric signal that is inversely proportional to the TRH concentration.
This TRH ELISA Kit offers a quick assay time of 1-5 hours, with a sample volume of 50-100ul and a detection wavelength of 450 nm. It is suitable for use in signal transduction and endocrine system research and has been cited in more than 2 publications.
There are currently no reviews for this product.