| Code | CSB-E12703r |
| Size | 96T,5×96T,10×96T |
| Price | Request a Quote or Start an on-line Chat |
| Trial Size |
24T ELISA Kit Trial Size (Only USD$150/ kit) * The sample kit cost can be deducted from your subsequent orders of 96T full size kits of the same analyte at 1/5 per kit, until depleted in 6 months. Apply now |
| Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8% | ||||||
| Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess. | ||||||
| Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10% | ||||||
| Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess. | ||||||
| To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of rat CXCR4 in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay. | ||||||
| Sample | Serum(n=4) | |||||
| 1:1 | Average % | 92 | ||||
| Range % | 86-95 | |||||
| 1:2 | Average % | 103 | ||||
| Range % | 97-106 | |||||
| 1:4 | Average % | 93 | ||||
| Range % | 85-96 | |||||
| 1:8 | Average % | 97 | ||||
| Range % | 91-100 | |||||
| The recovery of rat CXCR4 spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section. | ||||||
| Sample Type | Average % Recovery | Range | ||||
| Serum (n=5) | 95 | 89-98 | ||||
| EDTA plasma (n=4) | 96 | 92-99 | ||||
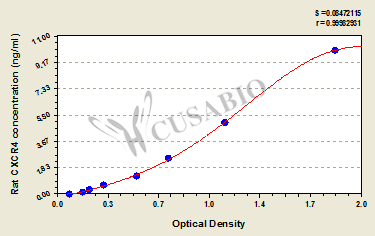
| These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The rat CXCR4 ELISA Kit is used to quantitatively measure rat CXCR4 levels in serum, plasma, cell culture supernates, or tissue homogenates. It performs well in important characteristics, including sensitivity and specificity. This assay is based on the sandwich ELISA mechanism and enzyme-substrate chromogenic reaction. The solution color develops proportionally to the amount of CXCR4 in the sample. And the intensity of the color can be measured at 450 nm via a microplate reader.
CXCR4 binds to SDF-1, transducing a cascade downstream signaling including PI3K/AKT, mTOR, and NF-κB pathways that eventually regulate cell survival, proliferation, chemotaxis, apoptosis and differentiation, and enhance angiogenesis in targeted diseases. CXCR4 plays a pivotal role in both physiological processes such as germ cell development, neurogenesis, vascular formation, and cardiogenesis and pathological processes such as muscle regeneration and vascular formation. Upregulation of CXCR4 can be found during injury, hypoxia, stress, and vascular tissue damage.
There are currently no reviews for this product.
STRING: 10116.ENSRNOP00000005143
UniGene: Rn.44431