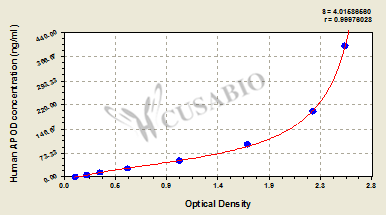
The human apolipoprotein D (APOD) ELISA Kit is used to quantitatively measure human APOD concentrations in serum, plasma, or tissue homogenates. It performs well in important characteristics, including sensitivity and specificity. This assay is based on the sandwich ELISA mechanism and enzyme-substrate chromogenic reaction. The solution color develops proportionally to the amount of APOD in the sample. And the intensity of the color can be measured at 450 nm via a microplate reader.
APOD is an atypical apolipoprotein with wide tissue distribution and has diverse different functions such as immune response, cell proliferation regulation, chemoreception, retinoid metabolism, axon growth, and proteolysis regulation. Plasma apoD is present mainly in HDL and, to a lesser extent, in VLDL. German Perdomo et al. demonstrated that APOD plays a significant role in lipid homeostasis and helps explain why genetic mutations in the APOD gene predispose at-risk individuals to developing metabolic syndrome. APOD also plays a pathophysiological role in several psychiatric disorders, particularly schizophrenia.