What is Cancer?
Cancer is the name for a group of more than 100 diseases, such as brain cancer, gastrointestinal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer etc. Cancer can develop anywhere in the body. The figure 1 shows the main distribution of cancers in human. It starts when cells divide uncontrollably and crowd out normal cells. Cancer often has the ability to spread into surrounding tissues, even throughout your body. Cancer is the second-leading cause of death in the world. But survival rates are improving for many types of cancer, thanks to improvements in cancer screening and cancer treatment.
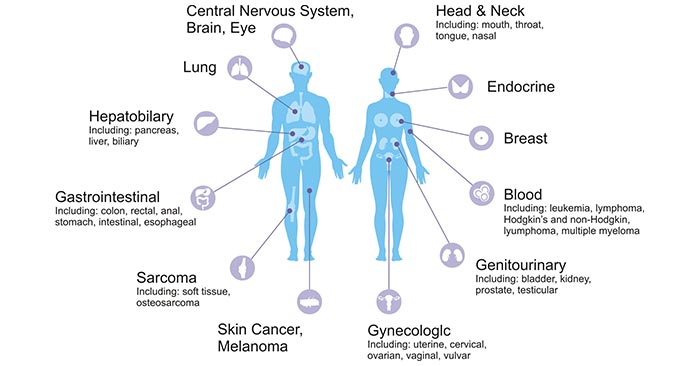
Figure 1. The distribution of cancers in human
Cancer is caused by mutations in the DNA (also called gene). These mutations mainly include single-base mutations, indels, increased copy numbers of large fragments of the genome, and translocations. In this page, we collect the targets information of 16 most common cancer and hope them give some assistance in your research.
Most Common Cancers
- Breast cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the breast. Breast cancer cells usually form a tumor that can often be seen on an x-ray or felt as a lump. Breast cancer occurs almost entirely in women, and is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in American women, but men can get breast cancer, too.
- Lung cancer, also called primary bronchogenic carcinoma, is a type of cancer that originates in the bronchi and alveoli. It is the leading cause of cancer deaths in both men and women in the U.S. and worldwide.
- Gastric cancer, also known as stomach cancer, begins when cancer cells form in the inner lining of your stomach. It ranks fourth after lung cancer, breast cancer and intestinal cancer, and usually grows slowly over many years.
- Prostate cancer starts when cells in the prostate gland (a gland found only in males) start to grow out of control. It is the most common cancer and the second leading cause of cancer death among men in the United States. Similar to stomach cancer, prostate cancer also usually grows very slowly.
- Colorectal cancer, also called colon cancer, is a type of cancer that begins in the final part of the digestive tract (also called colon). Colorectal cancer typically affects older adults, though it can happen at any age.
- Pancreatic cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the tissues of pancreas - an organ behind the lower part of the stomach. Pancreas is to releases enzymes to aid digestion and hormones. It is a critical organ in regulating blood sugar. Pancreatic cancer typically spreads rapidly to nearby organs.
- Ovarian cancer refers to the cancerous changes that occur in the ovaries- a female reproductive organ that produce eggs. Ovarian cancer is a common female reproductive system tumor with a high incidence, second only to cervical cancer and endometrial cancer.
- Endometrial cancer also called uterine cancer, starts in the layer of cells that form the lining (endometrium) of the uterus - a hollow, pear-shaped pelvic organ where fetal development occurs. Endometrial cancer affects mainly post-menopausal women. The mean age of women diagnosed with endometrial cancer is 61 years
- Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix-the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. This cancer can affect the deeper tissues of their cervix and may spread to other parts of their body, often the lungs, liver, bladder, vagina, and rectum.
- Melanoma, usually referred to as malignant melanoma, is a highly malignant tumor derived from melanocytes which control the pigment in your skin. Melanoma occurs mostly in the skin, but also in the mucous membrane and viscera.
- Thyroid cancer starts in the cells of the thyroid. Thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of your neck, and produces hormones which regulate heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature and weight. Thyroid cancer is relatively uncommon compared to other cancers. In the United States, it’s the tenth most common type of cancer.
- Hepatocellular carcinoma, also called liver cancer, refers to cancer that originates in the liver, which is distinguished from "secondary" liver cancer that spreads from other organs to the liver. Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common type of liver cancer in adults. It is usually diagnosed in people aged 50 or older.
- Bladder cancer refers to a malignant tumor that occurs on the cells of bladder - a hollow muscular organ in your lower abdomen that stores urine. Bladder cancer is a common malignancy in women and is the fourth most common malignancy in men. Men's risk is 3-4 times that of women.
- Multiple myeloma is a malignant plasma-cell disorder that accounts for approximately 1% of neoplastic diseases and 10% of all hematologic cancer. It is characterized by clonal proliferation of malignant plasma cells in the bone marrow microenvironment, monoclonal protein in the blood or urine, and associated organ dysfunction.
- Leukemia is a malignant clonal disease of hematopoietic stem cells. Leukemia cells in the clone will stop at different stages of cell development due to uncontrolled proliferation, differentiation failure, and obstructed apoptosis.
- Non-hodgkin's lymphoma is cancer that originates in your lymphatic system - a network spread throughout your body. Non-hodgkin's lymphoma most often affects adults, but children can get it too. It is one of the most common cancers in the United States, accounting for about 4% of all cancers.
CUSABIO Featured Products Related to Cancer
● Protein Products
● Antibody Products


