How does DT3C protein work in an ADC internalization assay?
The efficiency of antibody internalization is key to designing effective antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). For the cytotoxic drug to reach and destroy tumor cells, the antibody must first be internalized by the target cell. Without this step, the drug cannot be released where it's needed.
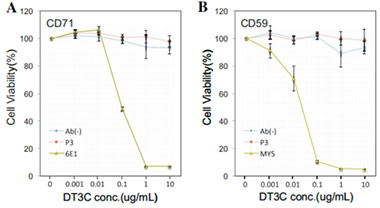
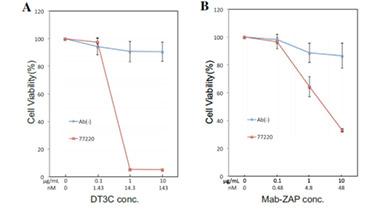
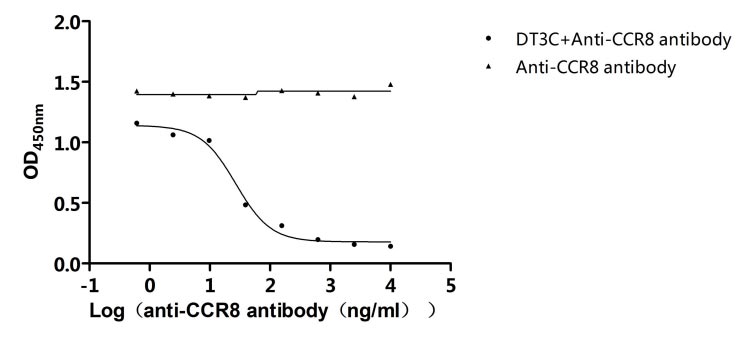
DT3C protein is a reliable tool for measuring how well antibodies are internalized. It helps researchers evaluate the internalization efficiency of antibodies in target cells, making it easier to identify those with strong binding and efficient internalization. These high-performing antibodies can be used in ADCs to improve drug targeting and safety.
To see why DT3C works, we need to explore its structural and functional features.
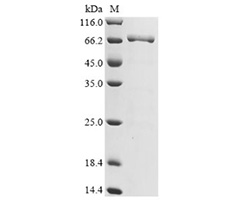
DT3C protein is a recombinant fusion protein that consists of a diphtheria toxin (DT) protein lacking the receptor-binding domain (only catalytic and translocation domains) but containing the C1, C2, and C3 domains (IgG-binding domain) of Streptococcus protein G (3C). It is characterized by low toxicity and high affinity with antibodies.
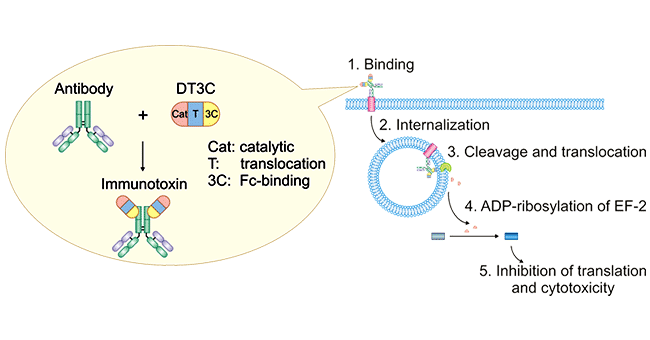
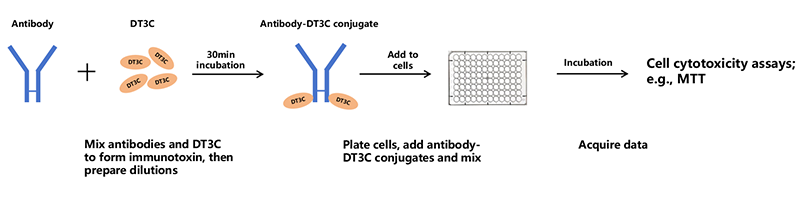
Figure 1. Mechanism of antibody: DT3C-induced cytotoxicity
DT3C's unique structure enables its role in mAb-DT3C conjugates, which mimic ADC behavior in vitro.
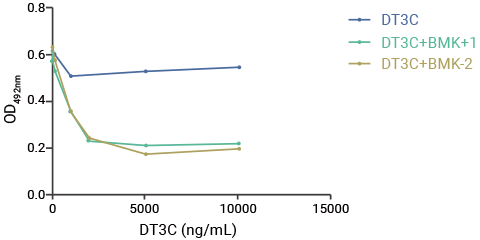
A mAb-DT3C conjugate, which functions in vitro similarly to an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), can kill cancer cells or reduce the viability of cancer cells only when the mAb being tested is internalized by the target cells through antibody-antigen interactions.
After the mAb-DT3C conjugate recognizes and binds to cell surface antigens, the mAb-DT3C-antigen complex is internalized into the cell via endocytosis. In the cell, the translocated terminus of DT3C is cleaved by the cellular furin protease, and the catalytic domain of DT3C is released into the cytoplasm, leading to ADP ribosylation of EF-2, subsequent blockade of the protein translation machinery, and ultimate cytotoxicity.
Therefore, the internalization efficiency of antibodies can be evaluated according to the cell-killing situation.
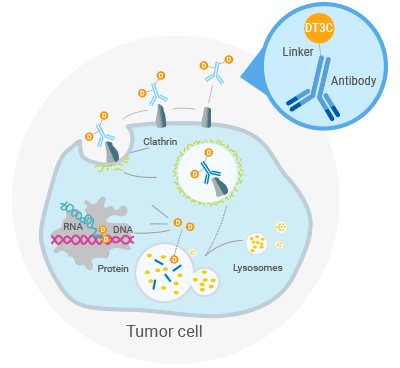
Figure 2. DT3C-Induced Cell Killing Mechanism