Recombinant Protein Resources
What is Recombinant Protein?
Recombinant proteins are proteins that are produced through genetic engineering techniques by introducing exogenous genes into host cells and utilizing the host cell's machinery for protein synthesis. This revolutionary technology has transformed the way proteins are produced, allowing researchers to produce large quantities of proteins with specific structures and functions.
In basic research, recombinant proteins are used for functional studies, structural research, immunology research, gene regulation studies, and disease research, among others. They provide researchers with tools to understand protein function and interactions, thereby advancing the fields of cell and molecular biology. In addition to basic research, recombinant proteins have broad applications in fields such as drug discovery, biotechnology, and diagnostics.
CUSABIO 5 Protein Expression Systems
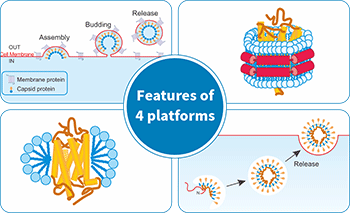
CUSABIO 4 Protein Expression Platforms
How to Prepare Recombinant Proteins?
The preparation of recombinant proteins involves several steps:
● Gene Cloning: Gene cloning is the process of inserting the target gene into an expression vector. Researchers can choose various cloning techniques such as restriction enzyme cloning, PCR amplification, or Gateway cloning to generate the DNA sequence of the target gene.
● Expression System Selection: Selecting an appropriate expression system is crucial for recombinant protein production. Commonly used expression systems include bacteria (such as Escherichia coli), yeast, insect cells, and mammalian cells. Each system has its advantages and limitations, and the choice depends on the specific requirements of the protein.
In addition to the commonly used four expression systems, CUSABIO has also established a cell-free expression system and virus-like particles (VLPs), detergent and Nanodisc technology platforms for membrane proteins expression, as well as nanoparticle technology for small molecular weight protein expression. These platforms enable CUSABIO to provide risk-free protein customization services to its customers.
● Transformation and Expression: After constructing the expression plasmid containing the target gene, it is introduced into the host cells. The cells are then cultured under optimized conditions to induce protein expression. This may involve the addition of specific inducers or adjusting the growth temperature.
● Protein Purification: Once the protein is expressed, it needs to be purified from the host cell lysate or culture medium. Protein purification techniques such as affinity chromatography, ion exchange chromatography, size exclusion chromatography, or protein-specific purification methods can be employed to isolate and purify the target protein.
Guides, Tips and Tools for Research with Recombinant Proteins
Please don't forget to explore the left navigation for a wide range of resources, including guides, tips, tools, and technical articles. (If you're visiting this page on your cell phone, you'll find the navigation at the end of the page.)
The guides provide in-depth knowledge on expression systems, purification techniques, and protein characterization. Discover practical insights and recommendations in our tips section, helping you optimize protein expression and troubleshoot challenges. Additionally, we offer handy calculators, databases, and more to simplify your research process.
Except for to guides, tips, and tools, the left navigation also features technical articles covering various topics related to recombinant proteins. These articles provide valuable insights and guidance to support your research endeavors.
If you have any questions or need further assistance, our team of experts is always ready to help. Enjoy exploring and conducting impactful research!