Immunology
Immunology is a branch of biology that covers the study of immune systems in all organisms. Although it is a branch of biology, it has broad applications in numerous disciplines of medicine, particularly in the fields of organ transplantation, oncology, rheumatology, virology, bacteriology, parasitology, psychiatry, and dermatology. Moreover, immunology contextualizes the physiological functioning of the immune system in states of both health and diseases; malfunctions of the immune system in immunological disorders. CUSABIO is always committed to immunology research, and lists several popular topics on it as follows.
1. History of Immunology Development?
Immunology is a historical subject. The development of immunology is the result of people's continuous exploration, summary and innovation in practice. It is generally believed that the development of immunology has experienced four periods: the period of empirical immunology, the period of classical immunology, the period of modern immunology and the period of modern immunology.
The period of empirical immunology refers to the period as early as the 11th century, Chinese medical scientists creatively invented the human vaccinia vaccine in practice, that is, to prevent smallpox by artificial mild infection. The period of classical immunology was from the 18th century to the middle of the 20th century. During this period, people's understanding of the immune function from the observation of human phenomena into the period of scientific experiments. The period of modern immunology is from the middle of the 20th century to the 1960s. In this period, people broke through the shackled theory of anti-infection immune template, and had a more comprehensive understanding of the immune response of organisms. The period of modern immunology is from the 1960s to the present. During this period, to confirm the status of lymph cell line in the immune response, illuminates the immunoglobulin, molecular structure and function of the immune system.
2. What is Immune System?
The immune system is a network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against attacks by “foreign” invaders. These are primarily microbes (germs)—tiny, infection-causing organisms such as bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi. The organs of the immune system are positioned throughout the body (Figure 1). They are called lymphoid organs because they are home to lymphocytes, small white blood cells that are the key players in the immune system.
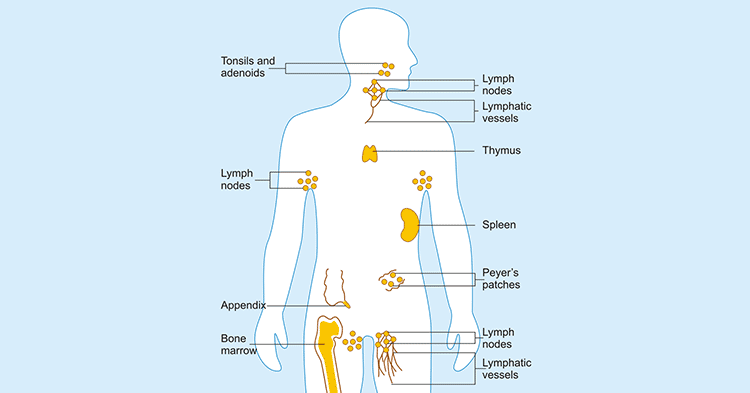
Figure 1. The organs of the immune system in the body
*this picture is derived from https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/organs-of-the-immune-system
Bone marrow is the soft tissue in the hollow center of bones. It is the ultimate source of all blood cells, including white blood cells destined to become immune cells. The thymus is an organ that lies behind the breastbone; lymphocytes known as T lymphocytes, mature in the thymus. Lymphocytes can travel throughout the body using the blood vessels. Small, bean-shaped lymph nodes are laced along the lymphatic vessels, with clusters in the neck, armpits, abdomen, and groin. Immune cells and foreign particles enter the lymph nodes via incoming lymphatic vessels or the lymph nodes' tiny blood vessels. The spleen is a flattened organ at the upper left of the abdomen. Like the lymph nodes, the spleen contains specialized compartments where immune cells gather and work.
Featured Products
CUSABIO has been committed to developing and expanding in the field of immunology. Here, we list part of products which are popular with customer as follows:
● Featured Proteins Related to Immunology
● Featured Antibodies Related to Immunology

