Cardiovascular Diseases Research
The cardiovascular system, also known as circulatory system, consists of the heart, which is a muscular pumping device, and blood vessels (including arteries, veins and capillaries). It is an organ system that is responsible for transporting nutrients (such as amino acids and electrolytes) and oxygen to the tissues of the body and removing carbon dioxide and other wastes from them.
The cardiovascular system includes the pulmonary circulation and the systemic circulation. The pulmonary circulation transports deoxygenated blood away from the right side of the heart to the lungs and returns oxygenated blood to the left side of the heart. The systemic circulation transports highly oxygenated blood from the left side of the heart to the rest of the tissues of the body (with the exception of the heart and lungs). Systemic circulation returns deoxygenated blood to the right side of the heart (Figure 1).
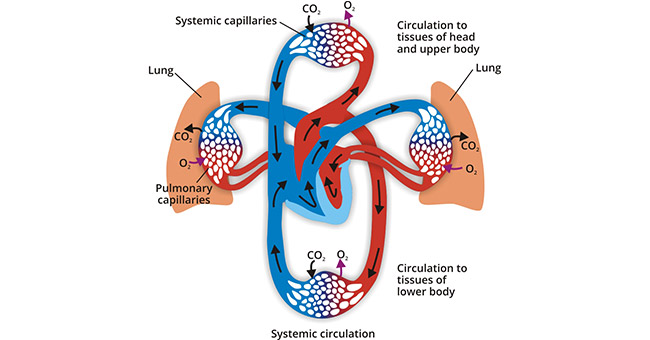
Figure 1. The diagram of cardiovascular system
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) refer to a group of disorders of the heart and blood vessels, including atherosclerosis, cardiac arrhythmias, cardiomyopathy, heart failure, hypertension, coronary diseases, coagulative disorders, and more. CUSABIO has been committed to developing and expanding the featured area (including cardiovascular, cancer, immunology, signal transduction, neuroscience, epigenetics etc.), where we have the most comprehensive products and the strongest cooperation channels. To learn more about the related products, please click on a research area.
The Common Cardiovascular Diseases
Atherosclerosis is a narrowing of the arteries that can significantly reduce the blood supply to vital organs. It is the main cause of coronary heart disease, cerebral infarction, and peripheral vascular disease. In atherosclerosis, the arteries are narrowed when fatty deposits called plaques build up inside. Plaques typically contain cholesterol from low-density lipoproteins (LDL), smooth-muscle cells and fibrous tissue, and sometimes calcium.
Coronary Artery Disease is also called CAD. It develops when the major blood vessels that supply your heart with blood, oxygen and nutrients (coronary arteries) become damaged or diseased. CAD causes by a buildup of plaque in your coronary arteries, the blood vessels that bring oxygen-rich blood to your heart.
Heart attack, also called myocardial infarction, occurs when the flow of blood to the heart is blocked. It most often causes by a build-up of fat, cholesterol and other substances, which form a plaque in the arteries that feed the heart (coronary arteries).
Stroke is usually divided into ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke. An ischemic stroke is the most common type of stroke, which occurs when a blood vessel that feeds the brain gets blocked, usually from a blood clot. A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel within the brain bursts. This is most often caused by uncontrolled hypertension (high blood pressure).
Popular Recombinant Proteins for Cardiovascular Diseases Research