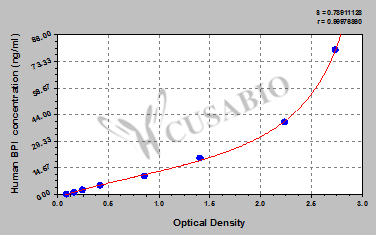
The human bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein (BPI) ELISA Kit is used to quantitatively measure human BPI concentrations in serum, plasma, or cell culture supernates. It performs well in important characteristics, including sensitivity and specificity. This assay is based on the sandwich ELISA mechanism and enzyme-substrate chromogenic reaction. The solution color develops proportionally to the amount of BPI in the sample. And the intensity of the color can be measured at 450 nm via a microplate reader.
BPI, a neutrophil-derived protein, is the natural antagonist of LBP since the interaction of BPI with its ligand LPS is strong enough to prohibit the LPS-dependent stimulation of immune cells. In the context of Gram-negative infection, BPI neutralizes the endotoxic activity of lipopolysaccharides, and thus inhibits hyperactivation. BPI functions as an immune-enhancing pattern recognition molecule in Gram-positive infections. In addition to acting as an LPS-neutralizing protein, BPI also has other functions such as inhibition of endothelial cell growth and dendritic cell maturation or being an anti-angiogenic, chemoattractant, or opsonization agent.