The Superb Journal CA(IF=244.59) Once Again Released an Article -Speed Reading on American Cancer Data
A CANCER JOURNAL FOR CLINICIANS (CA,
IF=244.59), is a review, peer-reviewed academic journal sponsored by the
American Cancer Society, covering cancer diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Its impact factor has been at the forefront of SCI's annual release of JCR.
On September 12, 2018, CA published the
latest global cancer morbidity and mortality statistics, assessing 36 cancer
morbidity and mortality rates in 185 countries.
On January 8, 2019, CA issued a new
article, "Cancer Statistics, 2019" was released, focusing on the data
changes of the incidence, mortality, etc. of various types of tumors since 1991
with the development of human medicine. The whole report includes 28 pages, in
which the incidence of cancer in recent years (by 2015) and the mortality rate
(by 2016) in the United States were collated. It also predicted the estimated
number of new cases and deaths of cancer in the 2019.
The data
shows that in the 25 years from 1991-2016, the overall US cancer mortality rate
has dropped by 27%, equivalent to a decrease in the number of cancer deaths of
about 2.62 million. The report predicts that there will be 1,762,500 new cancer
cases in the United States in 2019, and 406,800 deaths due to cancer.
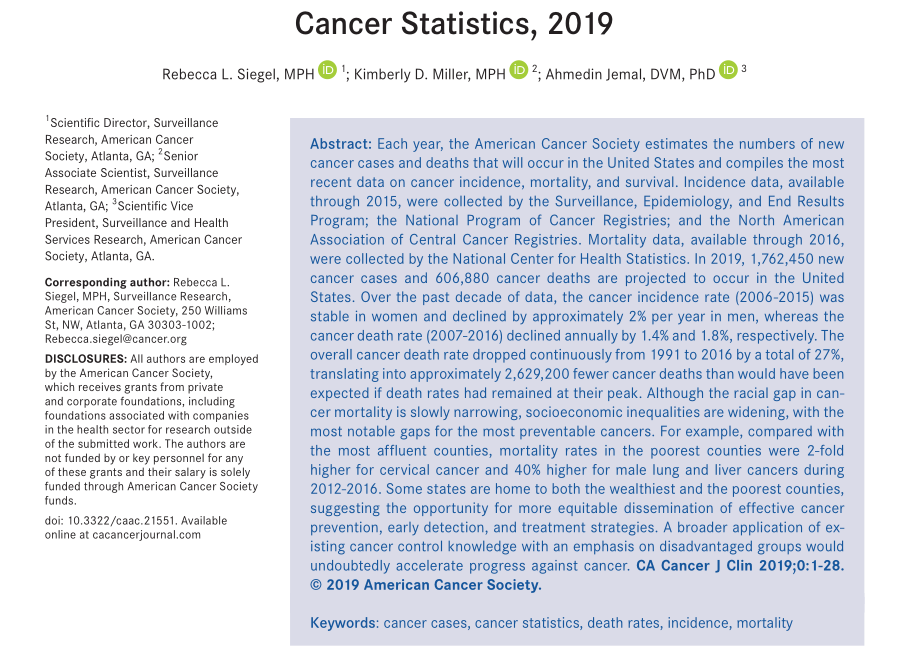
1. It
is estimated that 4,800 people are diagnosed with cancer every day
According to comprehensive data, it is
estimated that the number of new cancers in the United States in 2019 is about
1,762,400, which is equivalent to 4,800 people diagnosed with cancer every day.
It is estimated that 606,880 people will die of cancer, which is equivalent to
nearly 1,700 deaths per day from cancer.
The
top three male cases account for 42% of new cases:
Prostate cancer:20%
Lung
cancer:13%
Colorectal cancer:9%
The
top three male deaths account for 33% of deaths:
Lung cancer:24%
Prostate cancer:10%
Colorectal cancer:9%
The
top three female new cases account for 51% of new cases:
Mammary cancer:30%
Lung cancer:13%
Colorectal cancer:8%
The
top three female deaths account for 46% of deaths:
Lung cancer:23%
Mammary cancer:15%
Colorectal cancer:8%
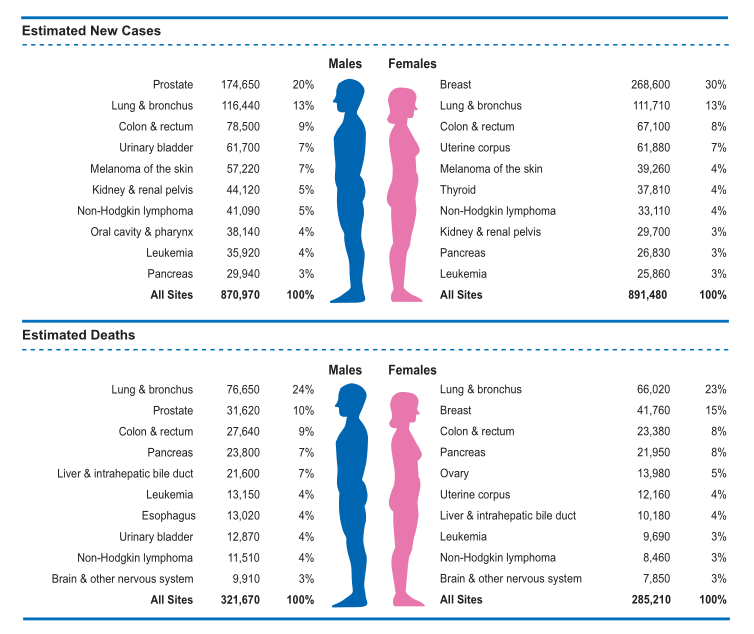
▲Predicted
number of new tumors and new deaths in the United States in 2019
2.
The overall incidence of cancer is decreasing year by year
With the control of cancer risk factors and
changes in medical practice, the overall incidence of cancer is decreasing year
by year.
In the past decade of 2006-2015, the
incidence of male cancer decreased by about 2% per year; in the past five years
from 2011 to 2015, the incidence of male lung cancer and colorectal cancer
accelerated at a rate of 3% per year, and prostate cancer declined. The rate
reached 7% due to the promotion of prostate specific antigen (PSA) screening
technology.
The
overall incidence of cancer in women tends to be stable. Although the incidence
of lung cancer and colorectal cancer declines, the incidence of other common
cancers is stable or rising.
The
decline in cancer mortality over the past two decades has been mainly due to
the reduction in the number of smokers and the early detection of clinical
tumors and the progress of cancer treatment, mainly reflected in four types of
cancer: lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer and colorectal cancer.
The
incidence of melanoma, liver cancer, thyroid cancer, uterine cancer, and
pancreatic cancer continues to rise, especially in liver cancer, and both men
and women are growing faster.
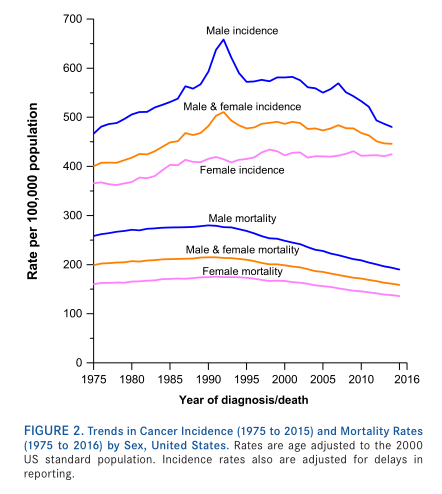
▲Trends
in the incidence of cancer in men and women in the United States from 1975 to
2015
3. The cancer survival rate is increasing
Since the mid-1970s, in addition to
cervical and uterine tumors, the 5-year survival rate of almost all common
types of cancer has increased.
For all stages of cancer, according to the
5-year survival rate of cancer, prostate cancer has the highest 5-year survival
rate (98%), followed by skin melanoma (92%) and female breast cancer (90%). Due
to the limitations in diagnostic techniques, most cancer cases such as lung
cancer and pancreatic cancer are diagnosed at an advanced stage. The 5-year
survival rate of pancreatic cancer is the lowest (9%), followed by liver cancer
(18%), esophageal cancer (19%), and lung cancer (19%).
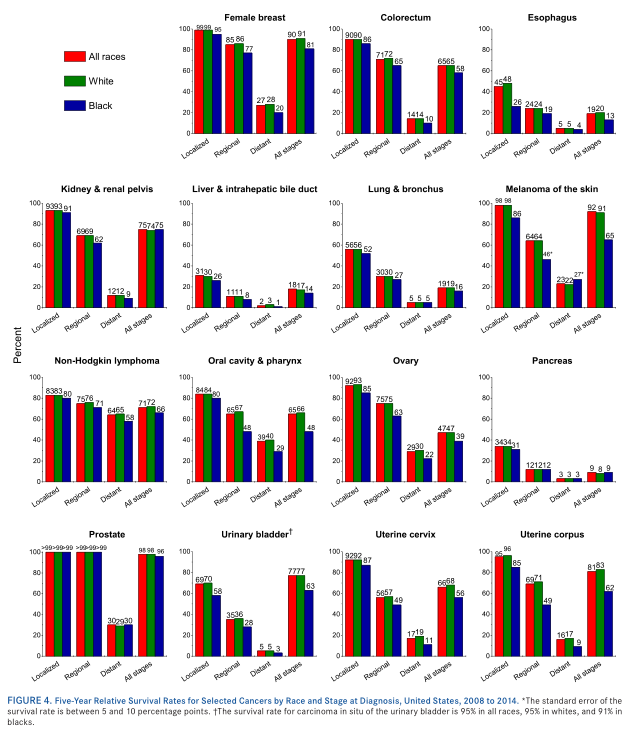
▲5-year
relative survival rate of cancer at different stages of different races in the
United States, (2008-2014)
4. The trend of cancer mortality
Compared with the incidence or survival
rate, cancer mortality can better reflect the progress of fighting cancer.
From 1991 to 2016, the overall cancer death
rate fell by 27% (215.1/100,000 people vs. 156.0/100,000 people), which is
equivalent to a reduction of about 2.6 million deaths.
The decline in cancer mortality is mainly
attributable to the steady decline in smoking and early diagnosis and treatment
progress, which is reflected in the rapid decline in lung cancer, breast
cancer, prostate cancer and colon cancer mortality.
Prostate cancer mortality experienced a
steep decline (4% per year), thanks to PSA screening and treatment progress.
For liver cancer, pancreatic cancer,
uterine tumors, and brain and other nervous system tumors, soft tissue tumors
(including the heart), HPV-related oral and pharyngeal cancers, mortality
increased in 2012-2016.
Cervical cancer remains the second leading
cause of cancer death in women between the ages of 20 and 39, with 9 deaths per
week at this age. This finding underscores the need to increase HPV vaccination
among adolescents and to adhere to screening guidelines among young women.
5. The incidence of cancer varies due to the gap
between rich and poor
By comparing the overall cancer mortality
rate in the poorest and most affluent regions of the United States during
2012-2016, it was found that the overall cancer mortality rate in the poorest
regions was about 20% higher than in the richest regions.
This shows that there are differences in
cancer mortality rates in different socioeconomic status areas, and the biggest
difference is reflected in the majority of cancer-preventable mortality rates.
For example, the mortality rate of cervical cancer in women in poor areas is
twice that of rich areas, and the mortality rate of male lung cancer and liver
cancer is 40% higher.
This is mainly related to the high
prevalence of bad behavior in poor areas, such as higher smoking rates and
obesity rates. In addition, early screening is less popular, cancer is diagnosed
later, and the best treatment accessibility also affects cancer mortality.
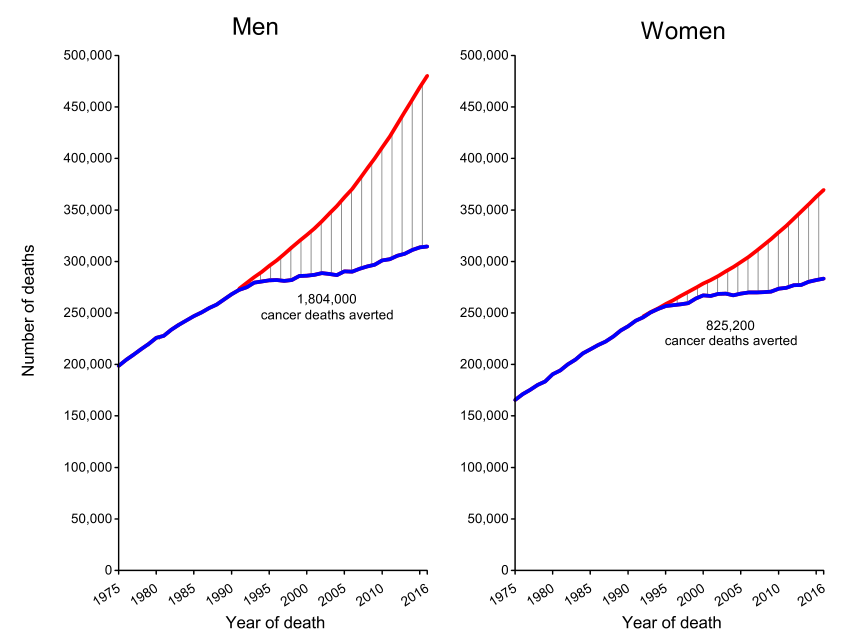
6. Children and adolescent cancer
Total cancer mortality in children and
adolescents has fallen by 65% for 45 years.
In addition to accidents, cancer is the
second leading cause of death among children in the United States (1-14 years).
In 2019, it is estimated that 1,060 children in this age group will be
diagnosed with cancer, of which 1,190 will die. Leukemia accounts for nearly
one-third (28%) of all childhood cancers, followed by brain and other
neurological tumors (26%). The distribution of cancer in adolescents (15 to 19
years old) is different from that of children, with lymphoma being the most
common.
Since 1975, the overall cancer incidence
among children and adolescents has increased slightly by 0.7% per year.
However, the mortality rate has continued to decline over the same period, a
total of 65% (65% for children and 61% for adolescents).
7. The decline in cancer mortality is attributed to 3
points
●Smoking is reduced stably
Since 1964, the United States has begun to
widely publicize the dangers of cigarettes and called on the American people to
smoke less. Thirty years later, the incidence of lung cancer in the United
States has slowly declined.
●Early cancer screening
In the case of breast cancer, since the
American people have a regular awareness of breast cancer screening, 80% of
breast cancer can be found early. Since 1990, the United States has been screening
for colorectal cancer, breast cancer, and prostate cancer. In 25 years, breast
cancer mortality has decreased by 39%, prostate cancer has decreased by 53%,
and female colorectal cancer has decreased by 44%. Colorectal cancer was
reduced by 47%. It can be seen that carrying out targeted anti-cancer physical
examination is an important measure to reduce cancer mortality.
●Medical technology innovation
The highly developed medical industry in
the United States has driven innovation in medical technology, and new medical
technologies and tools have emerged in the United States, particularly in drug
discovery and research and development.
On the road to treating cancer, we still
have a long way to go, but the exciting thing is that cancer mortality is decreasing!
As a bio-tech enterprise integrated with scientific research, production and
sales, CUSABIO TECHNOLOGY LLC provides high-quality scientific research
reagents for scientific research friends, and hopes to become a leading
biomedical leader with its own innovative strength!
Cite this article
CUSABIO team. The Superb Journal CA(IF=244.59) Once Again Released an Article -Speed Reading on American Cancer Data. https://www.cusabio.com/c-20816.html










I am no sure where you’re getting your information, but great topic. I needs to spend some time learning much more or understanding more. Thanks for great information I was looking for this info for my mission.