Essential reading|Ranking No.1 Impact Factor (IF244.59) Superb Periodical CA-2018 Latest Global Cancer Statistics
A CANCER JOURNAL FOR CLINICIANS(CA,IF=244.59)is a summarized Academic periodicals which is directed by American Cancer Society and performs peer review. The papers cover cancer diagnosis, treatment and prevention.
The main feature of this periodical isReview Articles with 2-5 papers every issue. For CA, cancer statistic is the flagship review. According to iNature,the average number of citations per such article reached 15,000, making a huge impact in the oncology field.
On September 12, 2018, the Journal of Clinicians Cancer ( the official journal of the American Cancer Society who is with the World's #1 impact factor ), published online the 2018 edition of Global Cancer (GLOBOCAN) Statistical Report from the headquarters in Lyon (France) of International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) in the World Health Organization's (WHO) and headquarters in Atlanta of the American Cancer Society.(The previous edition was published in 2012). The 2018 edition estimated the incidence and death of 36 cancers in 185 countries by the whole 32 pages.
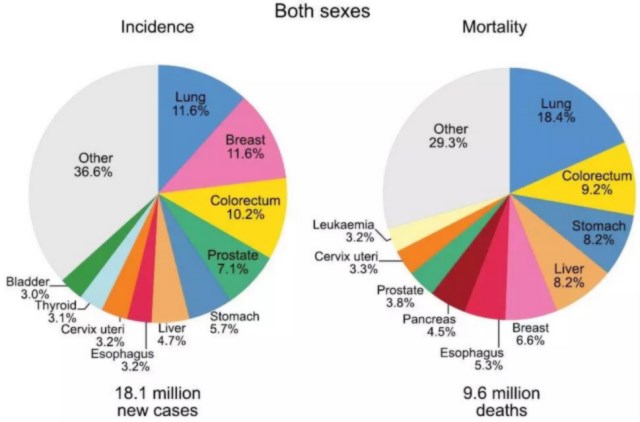
According to data, the global burden of cancer continues to grow, with 18.1 million new cancer cases and 9.6 million deaths expected in 2018 (17 million and 9.5 million, respectively, after excluding non-melanoma skin cancers).

Asia is the hardest hit for cancer
According to comprehensive data, nearly 50% of new cases and more than 50% of cancer deaths in the world are expected to occur in Asia in 2018, partly because nearly 60% of the global population is located in Asia.
Although Europe accounts for merely 9 percent of the world's population, the number of cancer cases and cancer deaths in Europe is not low, respectively at 23.4% and 20.3%, globally.
The America accounts for 13.3 percent of the global population, with the number of onset and death of 21% and 14.4%, respectively.
Compared with the rest of the world, the proportion of cancer deaths in Asia and Africa (57.3% and 7.3% respectively) is higher than that of incidence (48.4% and 5.8%, respectively). The main reason is that cancer types with poor prognosis and high mortality rates are high in these areas, and in many countries the opportunities for timely diagnosis and treatment are elusive.
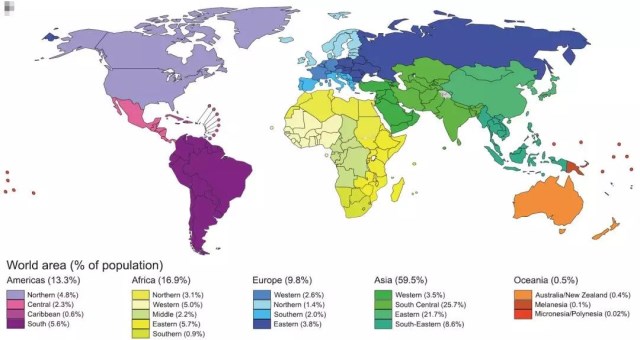
▲Percentage of global area and population
-
Lung cancer has become the number one killer
-
The proportions of various cancers that account for the incidence and death of all cancers are as follows:
-
Both sexes:lung cancer (11.6%) and death rate (18.4%) were highest, followed by female breast cancer (11.6%), prostate cancer (7.1%), colorectal cancer (6.1%), colorectal cancer (9.2%), gastric cancer (8.2%) and liver cancer (8.2%).
-
Men:lung cancer had the highest incidence rate (31.5%) and death rate (27.1%), followed by prostate cancer (29.3%), colorectal cancer (23.1%), liver cancer (12.7%) and stomach cancer (11.7%).
-
Women:the incidence of breast cancer (46.3%) and death rate (13.0%) is the highest, followed by colorectal cancer (15.7%), lung cancer (14.6%), cervical cancer (13.1%), lung cancer (11.2%), colorectal cancer (7.0%) and cervical cancer (6.9%).
Overall, the top 10 cancer types account for more than 65 percent of new cancer cases and deaths.
Breast cancer is the most common among women, accounting for 24.2% of the total number of cancer cases in women, about 1/4 of all new cancer cases worldwide, including breast cancer; The GLOBOCAN database incorporates all the data from 185 countries, with breast cancer being the most common in 154 countries.
Lung cancer is the leading cause of death for both men and women. It is noteworthy that lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death for women in 28 countries. The highest incidence of lung cancer among women is found in North America, Northern and Western Europe (especially Denmark and the Netherlands), China, Australia and New Zealand, with Hungary topping the list.
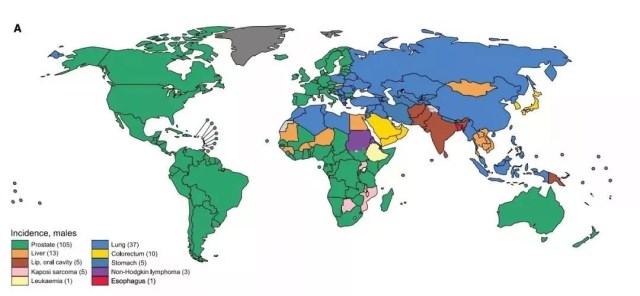
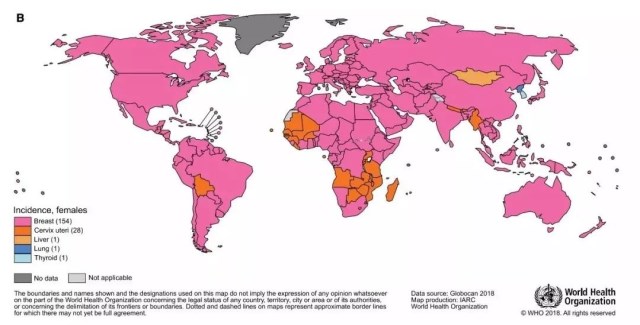
▲2018 most common types of cancer in the world (A) male (B) female
Relative to the level of socio-economic development
Global cancer morbidity and mortality rates are growing rapidly. The reasons are complex, but it reflects population ageing and growth, as well as the prevalence and distribution of major risk factors for cancer, some are related to socio-economic development.
With rapid population growth and ageing in many countries, cancer is becoming a major cause of death, partly reflecting a significant decline in stroke and coronary heart disease mortality relative to cancer.
By comparing the heat maps of graphs A and B, we can see that the location of cancer as a cause of premature death reflects the level of national social and economic development.
According to the Spanish national newspaper reported(September 12,) the WHO International Center for Cancer Research published a new global report that the world's new cancer cases in the past six years increased by 28% and cancer has become a measure of socio-economic development is an important indicator.
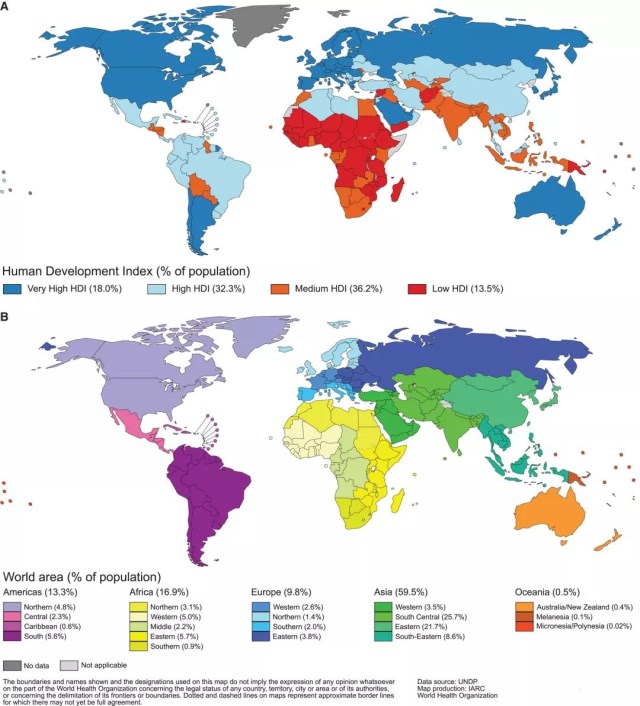
▲Global Heat Map Presentation (A) 4 level HDI-Human development Index and (B) 20 regions of the world
The causes of cancer are changing
For many cancers, in countries with a high level of human Development Index (Human development Index, HDI), the total incidence of multiple cancers is often 2-3 times higher in low-or medium-HDI countries.
Rafael Marcos, a Spanish epidemiology expert, noted that developed countries have a longer life expectancy and a higher incidence of cancer, while less developed countries have a relatively low incidence of cancer, and more people die from infectious diseases.
However, the difference in mortality between the two regions is small. On one hand, the incidence of some of the poorer cancers in low HDI countries is very high. On the other hand, the access to timely diagnosis and effective treatment is relatively difficult.
Cancer transformation is most pronounced in emerging economies, where the increase in disease is similar to that of common types of cancers. One recurrent observation is that some of the causes of cancer linked to poverty and infection previously is being linked to lifestyle-related problems.
The causes of cancer are changing
For many cancers, in countries with a high level of human Development Index (Human development Index, HDI), the total incidence of multiple cancers is often 2-3 times higher in low-or medium-HDI countries.
Rafael Marcos, a Spanish epidemiology expert, noted that developed countries have a longer life expectancy and a higher incidence of cancer, while less developed countries have a relatively low incidence of cancer, and more people die from infectious diseases.
However, the difference in mortality between the two regions is small. On one hand, the incidence of some of the poorer cancers in low HDI countries is very high. On the other hand, the access to timely diagnosis and effective treatment is relatively difficult.
Cancer transformation is most pronounced in emerging economies, where the increase in disease is similar to that of common types of cancers. One recurrent observation is that some of the causes of cancer linked to poverty and infection previously is being linked to lifestyle-related problems.
We are delighted to see a decline in cancer mortality. Let us pay a tribute to researchers working on the frontline of cancer!
At the same time, Wuhan Huamei Biotech, as a collection of scientific research, production and sales of biological high-tech enterprises, provides high-quality scientific research reagents for scientific research friends, but also hopes to rely on their own innovative strength to become a leader in the field of biomedical excellence!
Cusabio has carefully selected the tumor markers related quality products for you to help your research career!
A list of related tumor markers corresponding to the type of cancer and some related products is shown below:
Reference source:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.3322/caac.21492
Picture source:
CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians
Cite this article
CUSABIO team. Essential reading|Ranking No.1 Impact Factor (IF244.59) Superb Periodical CA-2018 Latest Global Cancer Statistics. https://www.cusabio.com/c-20723.html










Comments
Leave a Comment