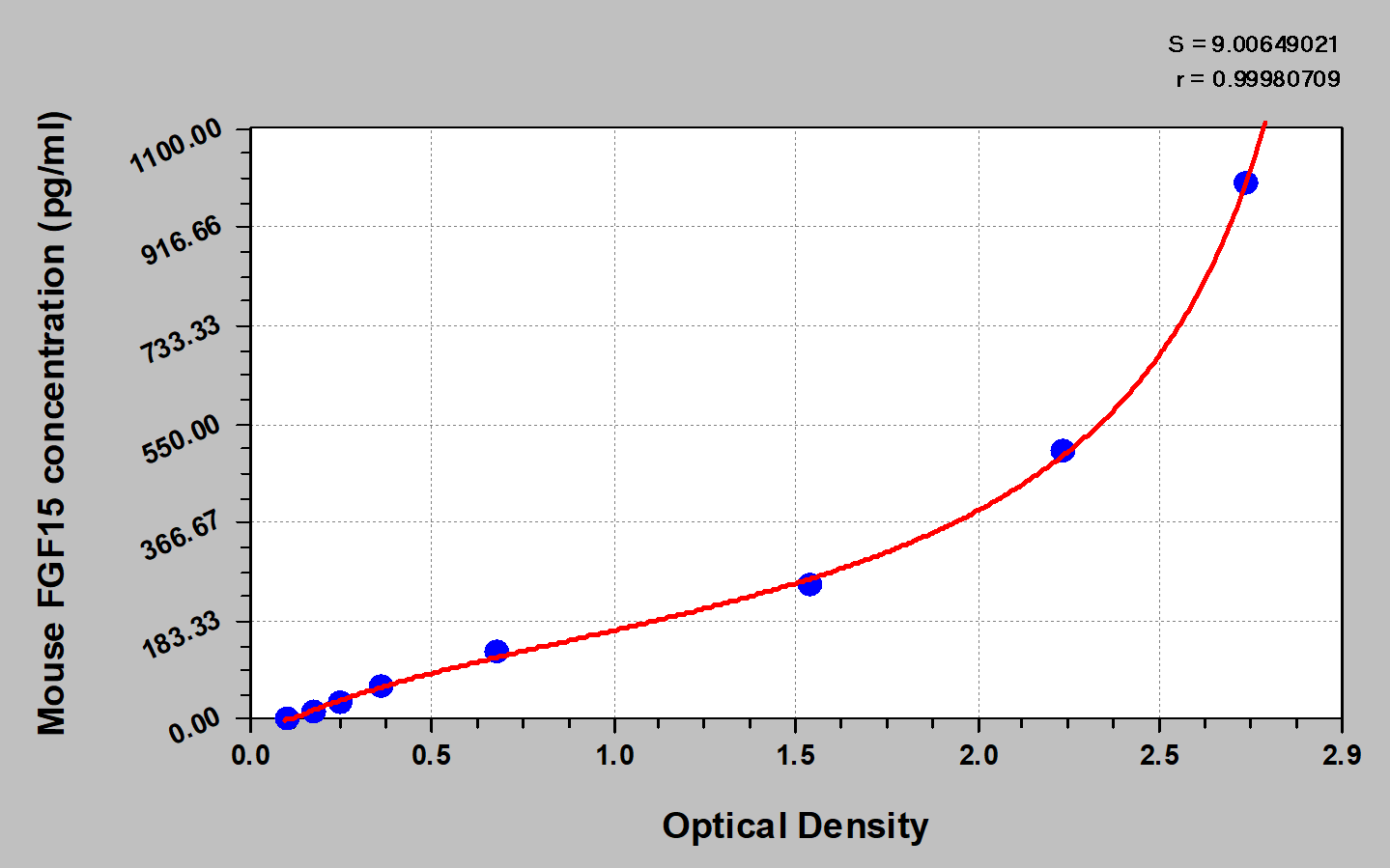
The Mouse Fibroblast growth factor 15 (FGF15) ELISA Kit is used for the quantitative detection of mouse FGF15 in many biological fluids, including serum, plasma, and tissue homogenates. The kit has high sensitivity, excellent specificity, good linearity, precision low than 10%, high recovery, good lot-to-lot consistency. Get access to more details from the product instructions.
This assay employs the Sandwich-ELISA technique, in which FGF15 in the samples or standards is sandwiched between pre-coated anti-human FGF15 and Biotin-labeled FGF15 antibody. The Ag-Ab-Ag immune complex is labeled with HRP-avidin and then develops a color reaction after the addition of the TMB substrate. The intensity of the color is positively correlated to the amount of FGF15 in the sample.
Mouse FGF15, an ortholog of human FGF19, is a bile acid (BA)-induced late fed-state gut hormone that mediates postprandial metabolic responses in the liver. It plays a key role in the bile acid-driven enterohepatic signaling. After a meal, the intestinal farnesoid X receptor (FXR) senses elevated bile acids to induce the expression of mouse FGF15. Secreted FGF15 acts on FGFR/KLB receptor complexes via repress CYP7A1 decrease BA synthesis, to stimulate glycogen synthase (GS) activity and glycogen production through inactivation of GSK3, and to inhibits gluconeogenesis by blocking the phosphorylation and activation of CREB. FGF15 thus acts after insulin in the transition from the fed to the fasted state.