| Code | CSB-E08355r |
| Size | 96T,5×96T,10×96T |
| Price | Request a Quote or Start an on-line Chat |
| Trial Size |
24T ELISA Kit Trial Size (Only USD$150/ kit) * The sample kit cost can be deducted from your subsequent orders of 96T full size kits of the same analyte at 1/5 per kit, until depleted in 6 months. Apply now |
| Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8% | ||||||
| Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess. | ||||||
| Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10% | ||||||
| Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess. | ||||||
| To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of rat VIP in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay. | ||||||
| Sample | Serum(n=4) | |||||
| 1:1 | Average % | 94 | ||||
| Range % | 90-98 | |||||
| 1:2 | Average % | 97 | ||||
| Range % | 93-101 | |||||
| 1:4 | Average % | 100 | ||||
| Range % | 97-103 | |||||
| 1:8 | Average % | 86 | ||||
| Range % | 82-92 | |||||
| The recovery of rat VIP spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section. | ||||||
| Sample Type | Average % Recovery | Range | ||||
| Serum (n=5) | 94 | 90-98 | ||||
| EDTA plasma (n=4) | 90 | 86-94 | ||||
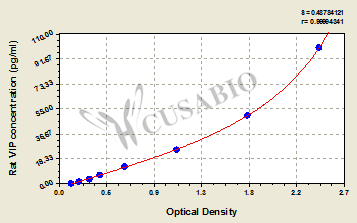
| These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Rat Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide (VIP) ELISA Kit is a highly sensitive and reliable assay for the quantification of VIP peptide in serum, plasma, and tissue homogenates from Rattus norvegicus (Rat).
VIP peptide,a neuropeptide that is widely distributed in the central and peripheral nervous systems ,is known to play a critical role in the regulation of various physiological processes, particularly in the nervous system. Our ELISA kit is designed to accurately measure the levels of VIP peptides in biological samples, making it an essential tool for researchers in the field of neuroscience.
The detection range of the kit is 1.56 pg/mL-100 pg/mL, with a sensitivity of 0.39 pg/mL, ensuring precise and accurate quantification of VIP peptides in samples. The assay time is only 1-5 hours, and the sample volume required is minimal (50-100ul), making the kit highly efficient and suitable for high-throughput experiments.
The VIP ELISA kit uses a sandwich assay principle, which involves the use of a VIP-specific antibody to capture the peptide of interest, followed by the detection of the captured VIP peptide using a second VIP-specific antibody. The detection wavelength is 450 nm, and the results are easily obtained using a microplate reader.
There are currently no reviews for this product.