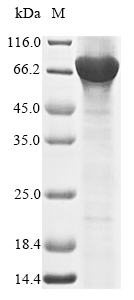
Amino acids 1-518 constitute the expression domain of recombinant Human RORC. The expected molecular weight for the RORC protein is calculated to be 74.2 kDa. Expression of this RORC protein is conducted in e.coli. The RORC coding gene included the N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO tag, which simplifies the detection and purification processes of the recombinant RORC protein in following stages of expression and purification.
The nuclear receptor ROR-gamma (RORC) is a transcription factor that belongs to the retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor (ROR) family. RORC plays a pivotal role in immune regulation, specifically in the development and function of Th17 cells. Th17 cells are involved in inflammatory responses and host defense against pathogens. RORC orchestrates the expression of genes associated with Th17 cell differentiation and function, including the production of IL-17, a key cytokine in the Th17-mediated immune response. Additionally, RORC has been implicated in various autoimmune diseases, making it a potential therapeutic target for conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel diseases. Understanding the molecular mechanisms controlled by RORC is crucial for deciphering its role in immune regulation and developing targeted therapies.