The Secret Life of Brain
Everyone seems familiar and also unfamiliar with his brain on the neck. Why A is so smart? Why B is a bit dull? Why C's reaction is so quick? How does your brain control your movements? Why the things we see are not the facts? The gray mud paste-like substance creates a complete inner world with emotions, memories, ideas and desires for us. Everything we see, touch, hear and feel is produced by the secret life of this substance, which is still not fully understood.
Consciousness of the brain is the basis of all human activity. The people's lives would be seriously threatened if the activity of the brain was in disorder or stopped. Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a common brain disease in old people, and is characterized by the progressive memory loss and cognitive dysfunction. Currently the cause of Alzheimer's disease is not still very clear, but the generation and aggregation of Aβ (β-amyloid) has been considered as one of the important factors. A recent study has found that Aβ has the same "positive role" as antimicrobial peptides - to protect the brain against the invasion of pathogens.
So what is Aβ?
Let's talk about how magical Aβ is – not only to protect the brain but also to deprive 350 million people of consciousness around the world.
To understand Aβ, we start from its precursor protein APP.
APP is the abbreviation of Amyloid Precursor Protein. Human APP gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 21, which contains at least 18 exons. APP is widely distributed, the mRNAs and proteins of which are expressed in the brain, thymus, heart, muscle, lung, kidney, adipose tissue, liver, spleen, skin, intestinal tract, and other tissues[1]. APP belongs to the transmembrane glycoproteinⅠand the molecular weight of APP is about 110-130kD, with a large outer membrane (amino-terminal) domain and a small cytoplasmic tail (intracellular carboxy-terminal)[1]. The extracellular portion of APP is composed of two sub-domains (E1 and E2), and the cytoplasmic domain is called E3 domain[2].
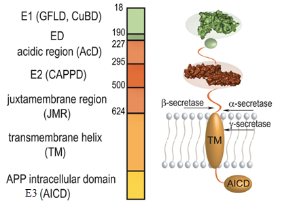
Figure 1: The multi-domain structure of the amyloid precursor protein (Image cited from: Coburger I et al.Analysis of the overall structure of the multi-domain amyloid precursor protein)
Aβ is produced by the protease cleavage of APP protein. There are two pathways in the transmembrane secretion process, which are the non-amyloid pathway that does not produce Aβ and the amyloid pathway that produces Aβ. In the first pathway, the proteolysis and secretion of APP must be catalyzed by the α-secretase, which can produce and release the soluble α-APPs into the extracellular environment, and keep the α-CTF or APP C83 (C-terminal fragment, CTF). C83 can be further cut by γ-secretase, subsequently producing the intracellular AICD and p3 peptides that cannot aggregate[3]. Because the structure of Aβ is destroyed and without neurotoxicity, this process is known as non-amyloid protein-producing pathway and it is the dominant metabolic pathway under normal circumstances.
Aβ is generated via the amyloid protein-producing pathway. First of all, APP is secreted from the N-terminal region of Aβ catalyzed by the β-secretase, producing soluble N-terminal fragments β-APPs and Aβ membrane associated C-terminal fragment (βCTF), then continue to be cleaved by γ-secretase, producing AICD and a series of Aβ that vary in length (39 ~ 43 amino acids)[4]. The imbalance between production and clearance of Aβ can lead to the abnormal deposition of Aβ in the brain cortex, which leads to synaptic dysfunction and neuronal degeneration.
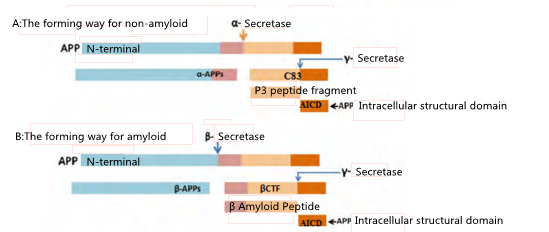
Figure 2: The metabolic pathways of APP (Image cited from: Zhang and Song. Alzheimer's Research & Therapy)
What is the relationship between Aβ and AD?
Senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles are important pathological features of AD. The main composition of senile plaques is Aβ and neurofibrillary tangles are mainly composed of hyperphosphorylated Tau protein.
Since the pathogenesis of AD is very complex, there is no clear explanation about the pathogenesis of the disease and many theories are in the hypothesis stage. Among these hypotheses, the Aβ hypothesis is the dominant one[5]. The hypothesis states that Aβ is the initial factor of AD induction. Aβ is cleaved and produced by β- and γ- secretase. Large amounts of generation, aggregation and deposition of Aβ not only have direct toxic effects on neurons, but also induce brain inflammation and highly phosphorylated Tau protein, therefore resulting in a large number of neuronal death, which is followed by neuronal loss and neurofibrillary tangles, thus leading to AD progression and aggravation[6]. In recent years, pharmaceutical companies have aimed Aβ as a target to be cleared. Drug development targeting Aβ formation, accumulation and clearance is the focus of drug research nowadays.
While everyone was busy removing Aβ, a paper published on the journal of Science Translational Medicine has shown that the well-known toxic Aβ might have some "secret activities" in the brain - protecting the brain against the invasion of pathogens. The researchers have found that Aβ can defend against microbial infection as antimicrobial peptides, and that for some microorganisms Aβ has the antibacterial effect which is over 100 times stronger than penicillin. Thus, maybe Aβ do not need to be completely eliminated.
Humans are becoming more and more powerful. Cusabio, as a good partner of life science research, manufactures and provides APP recombinant proteins, polyclonal antibodies and monoclonal antibodies.
1. Rat Amyloid beta A4 protein(APP) ELISA kit (product code: CSB-EL001950RA)
2. Rabbit anti-Human APP Polyclonal antibody (product code: CSB-PA001950OJ01HU)
3. APP Monoclonal Antibody (product code: CSB-MA0019501A0m)
4. Recombinant Dog Amyloid beta A4 protein(APP) (product code: CSB-YP634665DO)
5. Recombinant Sheep Amyloid beta A4 protein(APP) (product code: CSB-YP634684SH)
6. Recombinant Rabbit Amyloid beta A4 protein(APP) (product code: CSB-YP635706RB)
7. Recombinant Pig Amyloid beta A4 protein(APP) (product code: CSB-YP001950PI1)
8. Recombinant Mouse Amyloid beta A4 protein(App) (product code: CSB-YP001950MO1)
9. Recombinant Human Amyloid beta A4 protein(APP) (product code: CSB-CF001950HU)
10. Recombinant Rat Amyloid beta A4 protein(App) (product code: CSB-YP001950RA1)
11. Recombinant Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque) Amyloid beta A4 protein(APP) (product code: CSB-YP001950MOW)
12. Recombinant Bovine Amyloid beta A4 protein(APP) (product code: CSB-YP631695BO)
References:
[1]Nalivaeva NN, Turner AJ. The amyloid precursor protein: A biochemical enigma in brain development, function and disease. FEBS Lett, 2013, 587, 2046-2054.
[2]Coburger I, Dahms SO, Roeser D, et al. Analysis of the overall structure of the multi-domain amyloid precursor protein (APP). PloS One, 2013, 8, e8 1926.
[3]Zhang YW, Thompson R, Zhang H, et al. APP processing in Alzheimer's disease. Mol Brain, 2011, 4:3.
[4]Sastre M, Steiner H, Fuchs K, et al. Presenilin-dependent gamma-secretes processing of beta-amyloid precursor protein at a site corresponding to the S3 cleavage of Notch. EMBO Rep, 2001, 2:835-41.
[5]Kaur J, Adya R, Tan BK, et al. Identification of chemerin receptor (ChemR23) in human endothelial cells: chemerin-induced endothelial angiogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2010, 391:1762-1768.
[6]Le Y, Gong W, Tiffany HL, Tumanov A, et al. Amyloid (beta) 42 activates a G-protein-coupled chemoattractant receptor, FPR-like-1. J Neurosci, 2001, 21:RC123.
Cite this article
CUSABIO team. The Secret Life of Brain. https://www.cusabio.com/c-19731.html






Comments
Leave a Comment