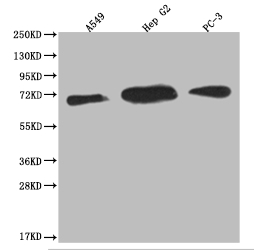
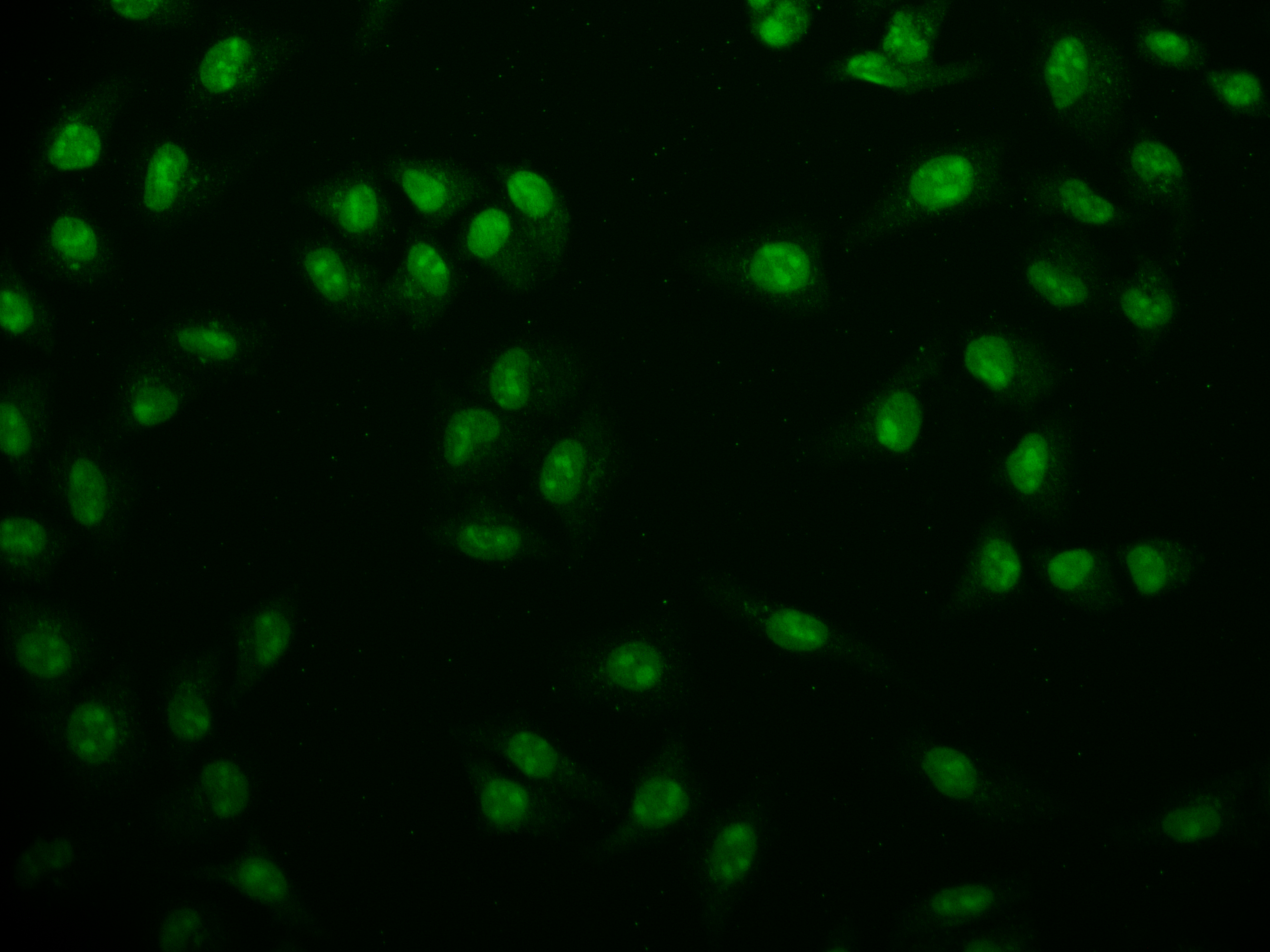
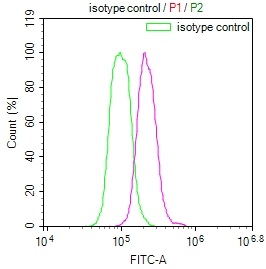
Producing the USP22 recombinant monoclonal antibody requires a series of intricate procedures. First, the USP22 monoclonal antibody is harvested, and its gene sequence is analyzed. Then, a vector carrying the USP22 monoclonal antibody gene is constructed and transfected into a host cell line for culture. During USP22 monoclonal antibody production, a synthesized peptide based on human USP22 is used as an immunogen. The USP22 recombinant monoclonal antibody is purified through affinity chromatography and analyzed for specificity using ELISA, WB, IF, and FC applications. It only reacts with human USP22 protein.
USP22 is a deubiquitinating enzyme that removes ubiquitin from target proteins. It is a component of the SAGA and ATAC histone acetyltransferase complexes, where it regulates gene expression by deubiquitinating histones and other proteins. USP22 has been implicated in various cellular processes, including DNA damage repair, cell cycle progression, and stem cell differentiation. Dysregulation of USP22 has been linked to cancer development and progression.