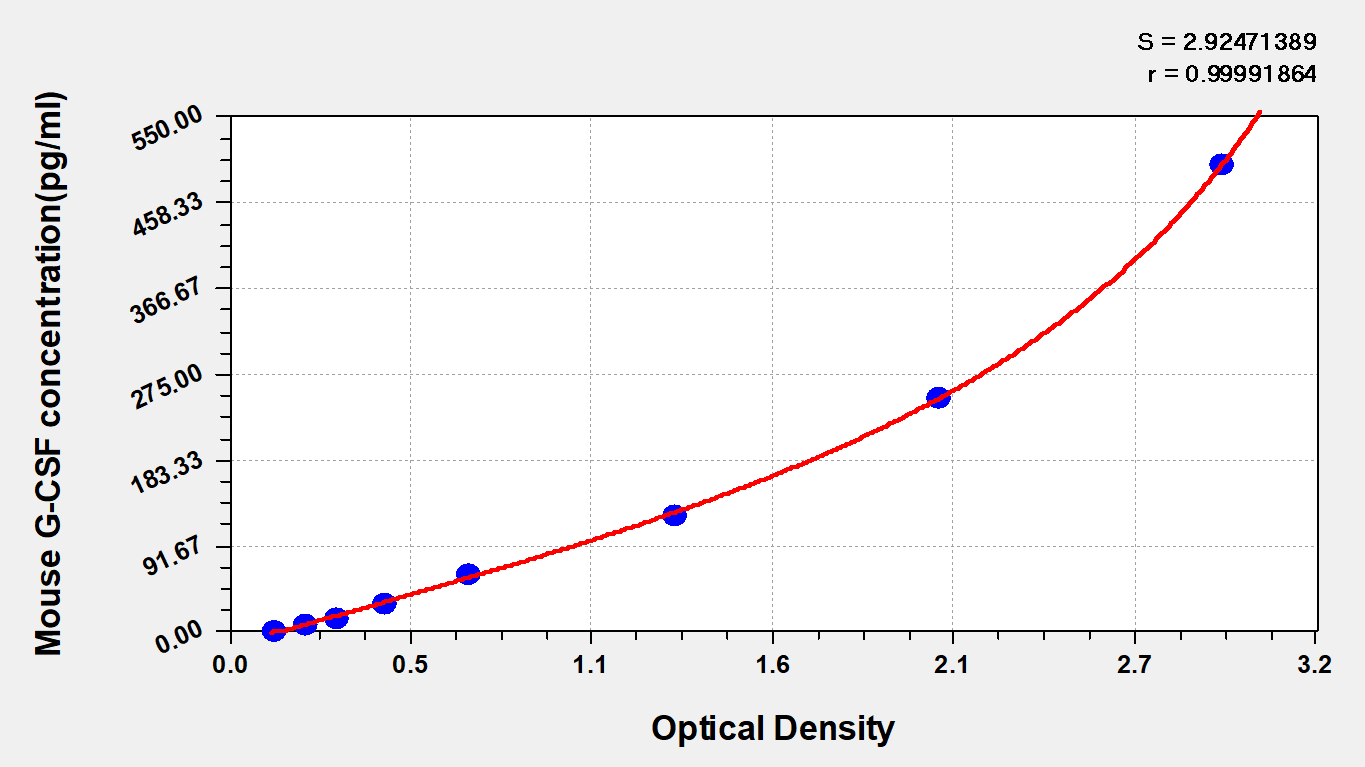
CUSABIO's mouse G-CSF ELISA kit is an in vitro enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the quantitative measurement of mouse G-CSF in serum, plasma, or tissue homogenates. This assay uses the sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique in combination with the enzyme-substrate chromogenic reaction to quantify the analyte in the sample. The color develops positively to the amount of G-CSF in samples. The color intensity is measured at 450 nm via a microplate reader.
G-CSF (CSF3), specific for granulocytes, is a cytokine used clinically for promoting the production and release of bone marrow-derived hematopoietic stem cells and granulocytes. CSF3 and its receptor CSF3R regulate granulopoiesis, neutrophil function, and hematopoietic stem cell mobilization. It also increases the production and release of neutrophils and modulates the differentiation, lifespan, and effector functions of mature neutrophils. CSF3 is currently used to treat neutropenia and to mobilize hematopoietic stem cells for transplantation. Studies have found that CSF3 plays an important role in cancer progression. CSF3 is upregulated in different types of cancer cells, such as lung cancer, gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, invasive bladder carcinoma, glioma, and breast cancer.