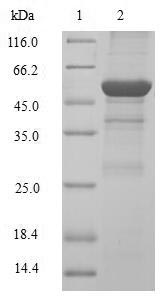
Recombinant Human G1/S-specific cyclin-D2 (CCND2) is produced using an E.coli expression system and spans the complete protein sequence from amino acids 1 to 289. The protein carries an N-terminal GST tag to help with purification and detection. SDS-PAGE verification shows a purity level exceeding 90%, which appears to make this preparation suitable for research applications. This product is intended for research use only.
Cyclin-D2 plays a crucial role in cell cycle regulation, particularly in controlling the progression through the G1/S phase transition. It works by interacting with cyclin-dependent kinases to influence how cells proliferate. This regulatory function likely makes cyclin-D2 an important target for studying cell division and cancer research, potentially offering insights into cell cycle control mechanisms and therapeutic approaches.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Based on the provided information, the recombinant Human CCND2 is expressed in E. coli, a prokaryotic system that is generally unsuitable for producing functional eukaryotic cell cycle regulators. CCND2 requires precise folding and specific post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation) for its biological activity in binding CDK partners and regulating G1/S transition. The presence of large fusion tags (N-terminal MBP and C-terminal 6xHis-Avi) significantly increases the likelihood of improper folding or steric hindrance of functional domains. While the protein is full-length (1-289aa), the E. coli expression system cannot provide the eukaryotic chaperones and modification machinery necessary for correct cyclin folding.
1. GST Pull-Down Assays for Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
The protein contains MBP and His-Avi tags, not a GST tag. The description is fundamentally flawed as it references an incorrect tag system. Even with the correct tags (MBP/His-Avi), if CCND2 is misfolded (as expected in E. coli), it will not interact authentically with CDK partners. Pull-down assays would likely yield non-physiological results. This application should not be pursued without folding validation.
2. Antibody Development and Validation
This application is appropriate. The recombinant CCND2 can serve as an immunogen for generating antibodies that recognize linear epitopes. The high purity (>85%) supports immunization protocols. However, if misfolded, antibodies may not recognize conformational epitopes of native CCND2 in cells. It should be noted that antibody validation against endogenous CCND2 is essential.
3. In Vitro Binding Assays with CDK Partners
This application is highly problematic without activity verification. CCND2 must be correctly folded to form functional complexes with CDKs. If misfolded, binding studies (SPR, ITC) will yield inaccurate kinetics and affinities. The large MBP tag may sterically hinder CDK binding even if the cyclin domain is folded. This application requires prior validation of CDK binding capability.
4. Biochemical Characterization and Stability Studies
This application is appropriate and should be prioritized. Biophysical techniques (thermal stability, etc.) can assess the protein's folding state and aggregation propensity. These studies are valuable for characterizing the recombinant product itself, regardless of biological activity.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This recombinant CCND2 is most suitable for antibody development and biochemical characterization studies. Due to the high probability of misfolding in E. coli (particularly for a protein requiring precise conformation for partner binding), functional applications like CDK interaction studies should be avoided without extensive validation. Recommended first steps: 1) Perform biophysical characterization (size exclusion chromatography, circular dichroism) to assess folding; 2) If possible, test binding to known CDK partners with positive controls; 3) For antibody production, use the protein as immunogen but validate resulting antibodies against native CCND2 from mammalian cells. Given the limitations of E. coli expression for this complex eukaryotic protein, consider alternative expression systems (e.g., insect or mammalian cells) for functional studies.