The Human soluble transferrin receptor (sTfR) ELISA kit is a sandwich immunoassay specifically designed and validated for the quantitative detection of sTfR in the serum and plasma. It is not intended for diagnostic use and only used for scientific research in humans. The kit has undergone rigorous quality control in multiple parameters, including sensitivity, specificity, precision, and inter-batch difference. Refer to the product instructions for more details.
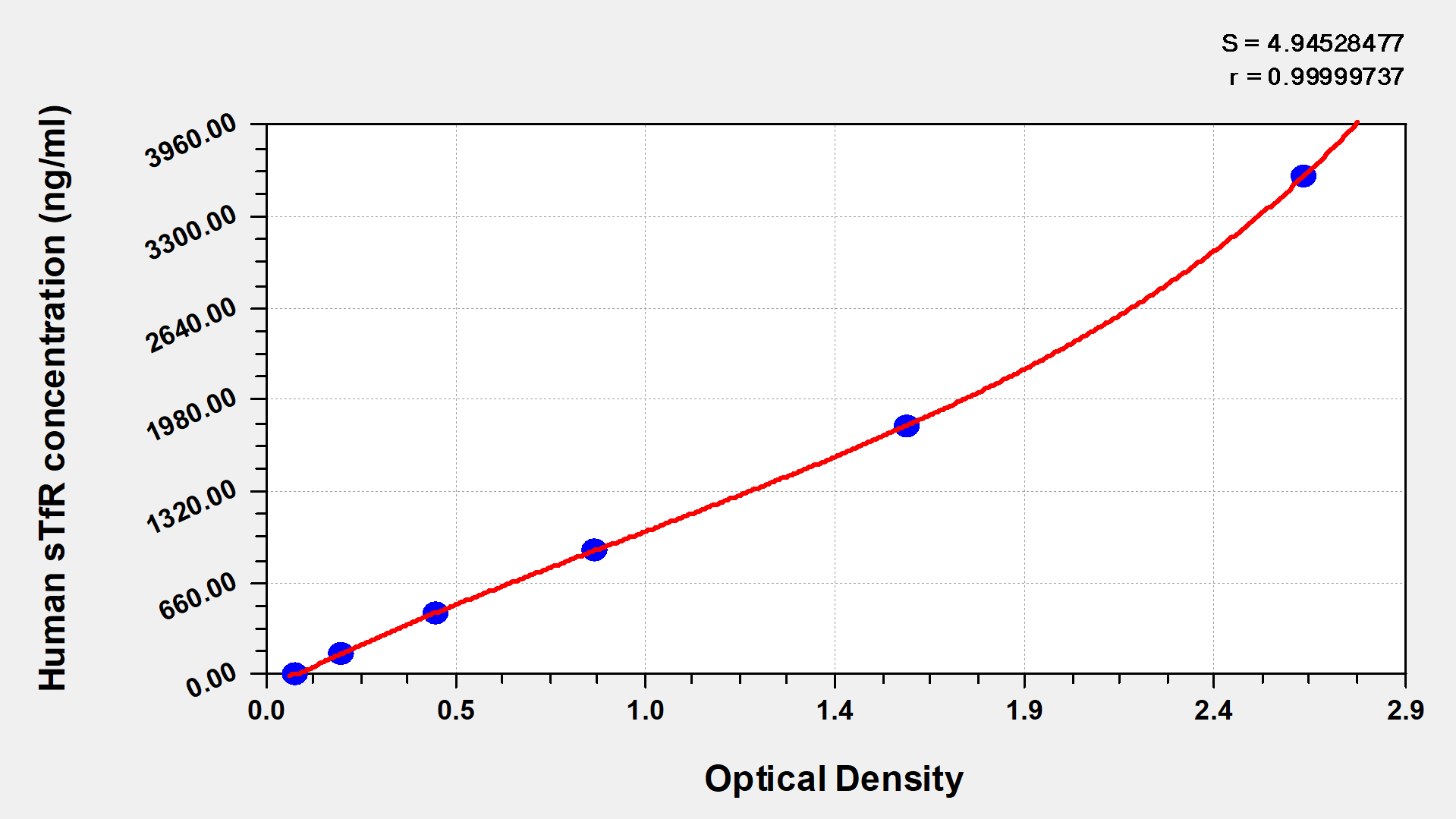
This assay employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique, in which sTfR in the samples or standards are sandwiched between pre-coated sTfR antibody and HRP-conjugated sTfR antibody. Following a wash to remove any unbound reagent, the TMB substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of sTfR bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped upon adding the stop solution, and the intensity of the color is measured at 450 nm via a microplate reader. The levels of sTfR in the samples can be determined by referring to the O.D. (optical density) of the samples to the standard curve.
sTfRs are blood proteins with increased expression in iron deficiency. It is the receptor for transferrin that binds to and carries iron to tissues and cells throughout the body. The measurement of sTfR levels can help to evaluate iron deficiency and diagnose iron-deficiency anemia. To increase sensitivity and specificity, iron status, including ferritin, TIBC, serum iron, and other relative tests are recommended to be performed along with the sTfR test.