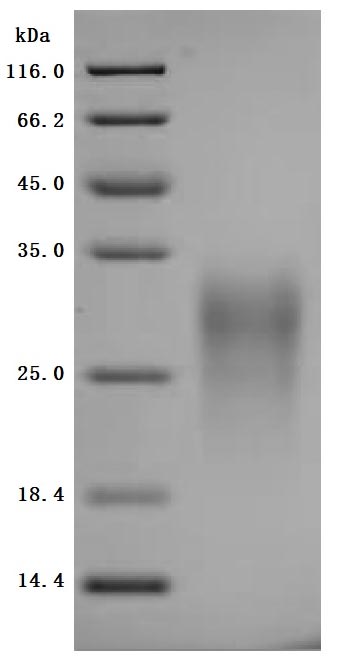
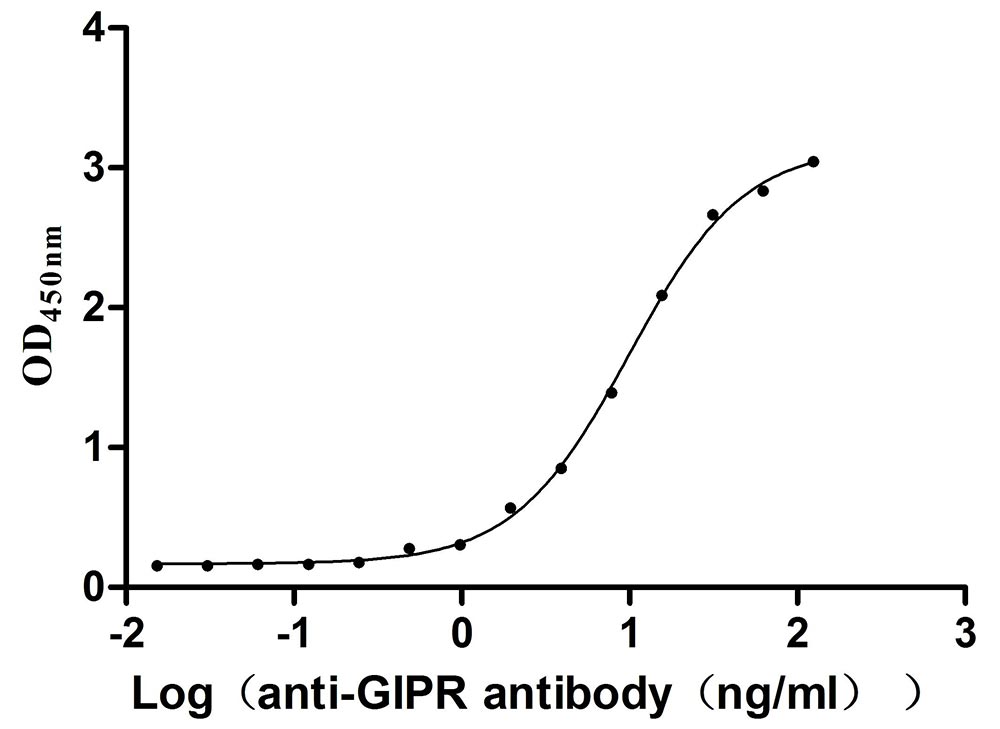
The gene sequence encoding amino acids 19 to 134 of the mouse gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr) is combined with a 10xHis-tag gene sequence at its C-terminus and then integrated into a plasmid vector. This recombinant vector is introduced into mammalian cells, and the cells that have been transfected are carefully selected and cultured to facilitate the expression of the protein. The recombinant mouse Gipr protein is isolated from the cell lysate. This protein's purity surpasses 95%, as determined using SDS-PAGE analysis, and its endotoxin content is less than 1.0 EU/μg as assessed by the LAL method. The functional capacity of the protein is affirmed through a functional ELISA test. When immobilized at a concentration of 2 μg/mL, the mouse Gipr protein effectively binds with the anti-Mouse Gipr recombinant antibody (CSB-RA009438MA1MO), with an EC50 of ranging from 8.622 to 11.36 ng/ml.
Gipr has a widespread distribution in the body, being expressed in organs like the pancreas, stomach, small intestine, adipose tissue, heart, and brain tissue, where many cells directly or indirectly control body weight. Activating the GIP-Gipr signaling pathway not only stimulates the secretion of insulin and glucagon-like peptide-1 but also promotes the proliferation and survival of pancreatic β-cells, playing a significant role in blood glucose regulation. The Gipr gene polymorphism is associated with elevated BMI and increased visceral fat content in the body. The mouse Gipr shares about 83% homology with the human Gipr, with relatively similar structure and function. Developing drugs to treat obesity is one of the most promising directions currently. Most of these processes require validation in preclinical mouse animal models, making the preparation of active mouse Gipr protein essential. Therefore, preparing the mouse Gipr contributes to the development of drugs with cross-species reactivity and further aid in clinical drug research and development.