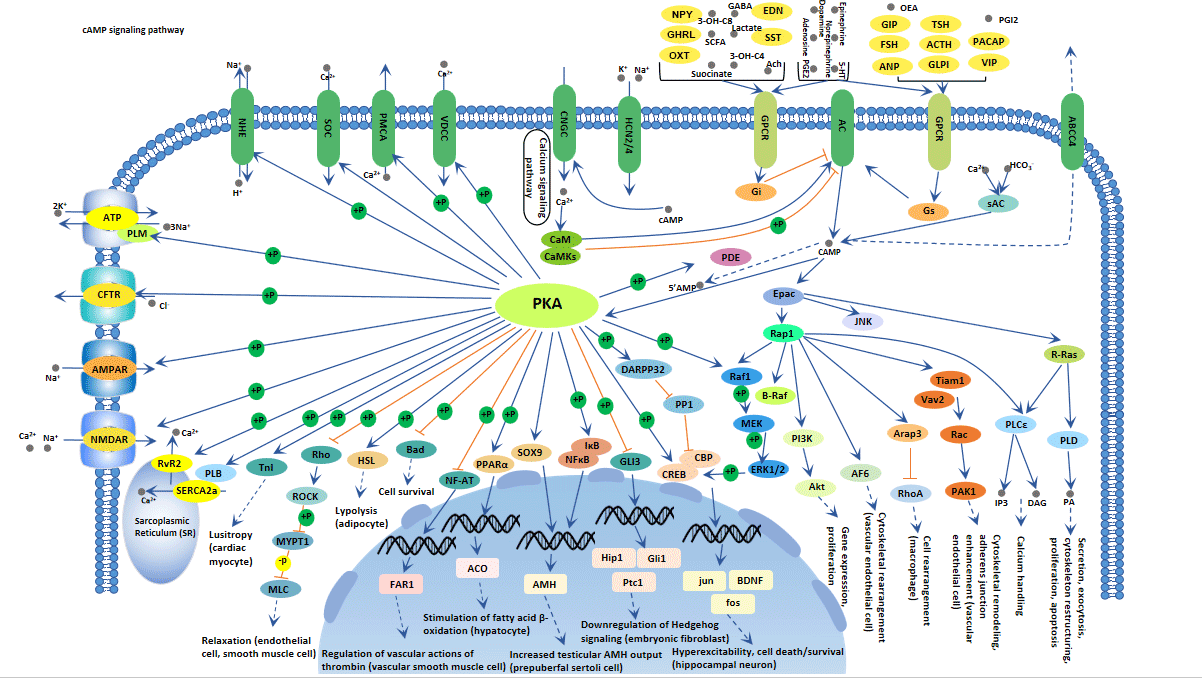
What is cAMP Signaling Pathway?
In the field of molecular biology, the cAMP signaling pathway, also known as the adenylyl cyclase pathway, is a G protein-coupled receptor-triggered signaling cascade used in cell communication. Cyclic adenosine 3’, 5’-monophosphate (cAMP) was the first second messenger to be identified and plays fundamental roles in cellular responses to many hormones and neurotransmitters.
The Critical Factor of cAMP Signaling pathway
cAMP, also known as cyclic adenosine 3,5-monophosphate, regulates pivotal physiologic processes including metabolism, secretion, calcium homeostasis, muscle contraction, cell fate, and gene transcription. cAMP is a cyclic nucleotide that serves as a vital second messenger in several signaling pathways.
The intracellular levels of cAMP are regulated by the balance between the activities of two enzymes: adenylyl cyclase (AC) and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE). Different isoforms of these enzymes are encoded by a large number of genes, which differ in their expression patterns and mechanisms of regulation, generating cell-type and stimulus-specific responses.
The Process of cAMP Signaling Pathway
As mentioned before, the level of cAMP is regulated by AC and PDE. During the process, AC is activated by a type of G-alpha, which in turn induces the conversion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) into cAMP. The stimulated adenylyl cyclase can produce numerous cAMP molecules to intensify the signal.
As the figure shows, cAMP acts directly on three main targets: protein kinase A (PKA), the exchange protein activated by cAMP (Epac), and cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channels (CNGCs). PKA modulates a number of cellular substrates via phosphorylation, including transcription factors, ion channels, transporters, exchangers, intracellular Ca2+-handling proteins, and the contractile machinery.
Epac proteins, as guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) for both Rap1 and Rap2, have a series of effector proteins, involving adaptor proteins implicated in modulation of the actin cytoskeleton, regulators of G proteins of the Rho family, and phospholipases, relay signaling downstream from Rap.





