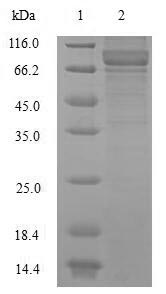
We offer five expression systems: E. coli, Yeast, Baculovirus, Mammalian cell, and Cell-Free (in vitro E.coli). Among them, yeast only has supernatant expression, and the protein expressed in the supernatant must be a soluble protein.
The E. coli, Baculovirus, Mammalian cell, and Cell-Free (in vitro E.coli) have both supernatant expression and inclusion body expression, as long as the protein expressed in the supernatant, it must be soluble, if it is the protein expressed by in the inclusion body, we will also take a variety of methods to refold it to finally ensure that all the proteins we provide are soluble.
So all the proteins we offer are soluble.