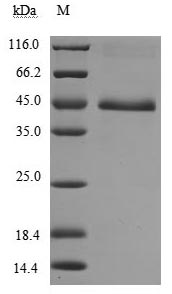
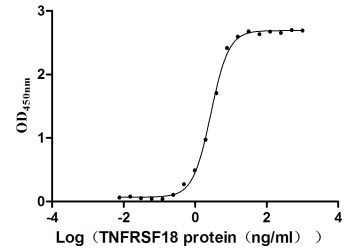
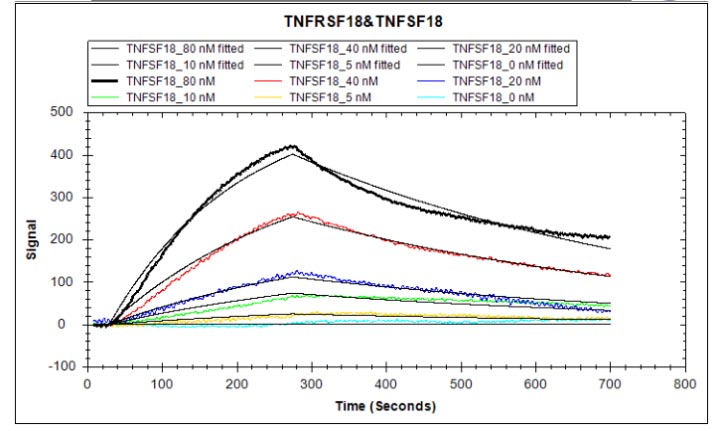
The recombinant human TNFRSF18 protein is expressed in mammalian cells from a plasmid containing the gene of interest. The gene of interest corresponds to the 26-162aa of the human TNFRSF18 and is fused with a C-terminal hFc-tag gene. Its purity is over 90% as confirmed by SDS-PAGE, and its endotoxin content is less than 1.0 EU/μg as measured by the LAL method. Its biological activity is proven via ELISA and LSPR assay. In a functional ELISA, this human TNFRSF18 protein binds to the TNFSF18 (CSB-MP891791HU), with the EC50 of 2.565 to 2.940 ng/ml. In an LSPR assay, it binds to the human TNFSF18 protein (CSB-MP891791HU) with an affinity constant of 38.5 nM.
Human TNFRSF18 (GITR) is a crucial component of the immune system, particularly in regulating T-cell responses. As a member of the TNFR superfamily, TNFRSF18 plays a significant role in modulating immune responses, especially within the tumor microenvironment (TME) [1][2][3]. TNFRSF18 is predominantly expressed on Tregs and other activated immune cells, where its expression is upregulated in the TME. This upregulation is positively correlated with the immunosuppressive functions of Tregs, suggesting that TNFRSF18 may facilitate the maintenance of immune tolerance in cancer [1][4].
In the context of cancer, TNFRSF18 has been implicated in various malignancies. In multiple myeloma, TNFRSF18 expression is silenced due to promoter methylation, leading to enhanced tumor proliferation. Restoration of TNFRSF18 expression in deficient myeloma cells has been shown to inhibit cell growth and induce apoptosis, highlighting its potential as a tumor suppressor [5][6]. Additionally, TNFRSF18 has been identified as a marker for specific Treg subtypes, such as FOXP3+IL10+ Tr1 cells, which are associated with immunosuppressive environments in tumors [1][4].
The signaling pathways activated by TNFRSF18 involve various adaptor proteins, including TNF Receptor Associated Factors (TRAFs), which mediate downstream signaling through pathways such as NF-κB and MAPK [2][6]. These pathways are critical for regulating cell survival, proliferation, and apoptosis, further emphasizing the importance of TNFRSF18 in immune regulation and tumor biology [2][6][7].
References:
[1] Z. Liu. Multi-omics profiling identifies aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 as a critical mediator in the crosstalk between treg-mediated immunosuppression microenvironment and hepatocellular carcinoma, International Journal of Biological Sciences, vol. 20, no. 7, p. 2763-2778, 2024. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.93075
[2] E. Vanamee and D. Faustman. Structural principles of tumor necrosis factor superfamily signaling, Science Signaling, vol. 11, no. 511, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.aao4910
[3] S. Ronchetti, M. Petrillo, L. Cari, G. Migliorati, G. Nocentini, & C. Riccardi. Glucocorticoid-induced tumour necrosis factor receptor-related protein: a key marker of functional regulatory t cells, Journal of Immunology Research, vol. 2015, p. 1-17, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/171520
[4] J. Li, X. Zhang, L. Yao, & K. Hu. The bioinformatics and experimental analysis of the novel roles of virus infection-associated gene cdc20 for prognosis and immune infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma, Aging, vol. 14, no. 10, p. 4513-4529, 2022. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204093
[5] D. Xiong. Tumor intrinsic immunity related proteins may be novel tumor suppressors in some types of cancer, Scientific Reports, vol. 9, no. 1, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-47382-3
[6] J. Li, N. Liu, L. Tang, B. Yan, X. Chen, J. Zhang, et al. The relationship between traf6 and tumors, Cancer Cell International, vol. 20, no. 1, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-01517-z
[7] H. Shen, L. Li, S. Yang, D. Wang, S. Zhou, X. Chen, et al. Regulatory role of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 in breast cancer by activating the protein kinase b/glycogen synthase kinase 3β signaling pathway, Molecular Medicine Reports, vol. 16, no. 2, p. 2269-2273, 2017. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6782