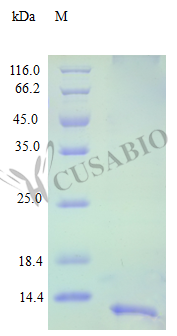
Our Recombinant Human CCL16 (C-C motif chemokine 16) is produced in E.coli, and has an expression region of 24-120aa, covering the full length of the mature protein. This product is provided in a lyophilized powder form, with a purity of >97% as determined by SDS-PAGE and HPLC. The endotoxin level is less than 1.0 EU/ug as determined by the LAL method. The recombinant CCL16 is tag-free for ease of use in various applications.
CCL16 is a chemokine that plays an important role in the trafficking and activation of leukocytes[1]. CCL16 has been implicated in various inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis[2,3]. It has been reported to have chemotactic activity for monocytes, lymphocytes, and eosinophils[4]. Additionally, CCL16 has been shown to have a potential role in angiogenesis and tumor progression[5].
Fully biologically active, the recombinant human CCL16 demonstrates a concentration range of 10-100 ng/ml in chemotaxis bioassays using human monocytes, compared to the standard.
References:
1. Mantovani, A. et al. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 2000; 21(6): 303-307.
2. Hosaka, S. et al. Predominant expression of the human LIM and SH3 domain protein, hILINCK in activated monocyte lineage. FEBS Lett. 2000; 481(2): 93-98.
3. Van Coillie, E. et al. Human monocyte chemotactic proteins-2 and -3: structural and functional comparison with MCP-1. J. Immunol. 1999; 162(7): 4349-4359.
4. Hieshima, K. et al. Molecular cloning of a novel human CC chemokine liver and activation-regulated chemokine (LARC) expressed in liver. Chemotactic activity for lymphocytes and gene localization on chromosome 2. J. Biol. Chem. 1997; 272(38): 23913-23921.
5. Müller, G. and Lipp, M. Signal transduction by the chemokine receptor CXCR5: Structural requirements for G protein activation analyzed by chimeric CXCR1/CXCR5 molecules. J. Exp. Med. 2001; 194(2): 181-192.