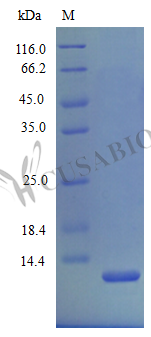
Recombinant Mouse C-X-C motif chemokine 2 protein (Cxcl2) is produced in E. coli and covers the full length of the mature protein from amino acids 28-100. This tag-free protein achieves a purity level of over 97% as determined by SDS-PAGE. The protein appears to maintain full biological activity, as established through a chemotaxis bioassay using human neutrophils, with effective concentrations ranging from 1.0-10 ng/ml. Endotoxin levels remain below 1.0 EU/µg, verified by the LAL method.
C-X-C motif chemokine 2 (Cxcl2) is a chemokine that likely plays a key role in neutrophil chemotaxis and immune response. As part of the CXC chemokine family, it may be crucial for recruiting immune cells to inflammation or injury sites. Researchers often examine Cxcl2 for its role in inflammatory processes and its potential relevance across various fields, including immunology and cell signaling pathways.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
1. Neutrophil Chemotaxis Assays
This recombinant mouse Cxcl2 is confirmed to be biologically active in human neutrophil chemotaxis (1.0-10 ng/ml) and suitable as a positive control in migration studies. However, researchers should validate cross-reactivity in mouse-specific systems despite the demonstrated human neutrophil activity, as species-specific receptor affinity differences may exist. The high purity and low endotoxin ensure minimal interference in primary cell assays.
2. Inflammatory Response Modeling in Cell Culture
The protein is appropriate for inflammatory signaling studies, but researchers should note that the demonstrated activity is in human neutrophils, not mouse cells. Dose optimization is recommended for different cell types, as receptor expression and signaling thresholds may vary. The confirmed bioactivity supports its use in CXCR2-mediated pathway activation studies.
3. Antibody Development and Validation
This high-purity Cxcl2 serves as a good antigen for antibody development. However, antibodies generated against this E. coli-expressed protein should be validated for recognition of native, mammalian-produced Cxcl2, as differences in post-translational modifications may affect antibody binding in some applications. The cross-species activity suggests conserved epitopes are present.
4. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
The biologically active Cxcl2 is suitable for CXCR2 interaction studies, but the cross-species activity suggests binding characteristics may differ between mouse and human receptors. Researchers should specify the receptor species used in binding assays and interpret kinetics data in the context of potential species-specific variations.
5. Comparative Species Studies
The demonstrated activity on human neutrophils makes this protein particularly valuable for cross-species comparative studies. Researchers can directly compare mouse vs. human Cxcl2 functionality using the same assay system. However, the E. coli expression system produces a non-glycosylated protein, which may affect direct comparison with mammalian-expressed chemokines in structural studies.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This recombinant mouse Cxcl2 is a well-characterized reagent with demonstrated cross-species bioactivity, making it suitable for the proposed applications. For immediate use, employ it in the 1.0-10 ng/ml range for neutrophil chemotaxis studies, noting the unusual but valuable human-mouse cross-reactivity. When developing antibodies, validate cross-reactivity with native mouse Cxcl2 from inflammatory sources. For signaling studies, the protein reliably activates CXCR2 pathways, but researchers should confirm response kinetics in their specific cell models. The cross-species activity enables unique comparative studies, but researchers should acknowledge the E. coli expression limitations when making structural comparisons. Always include appropriate species-matched controls and validate key findings in physiologically relevant systems.