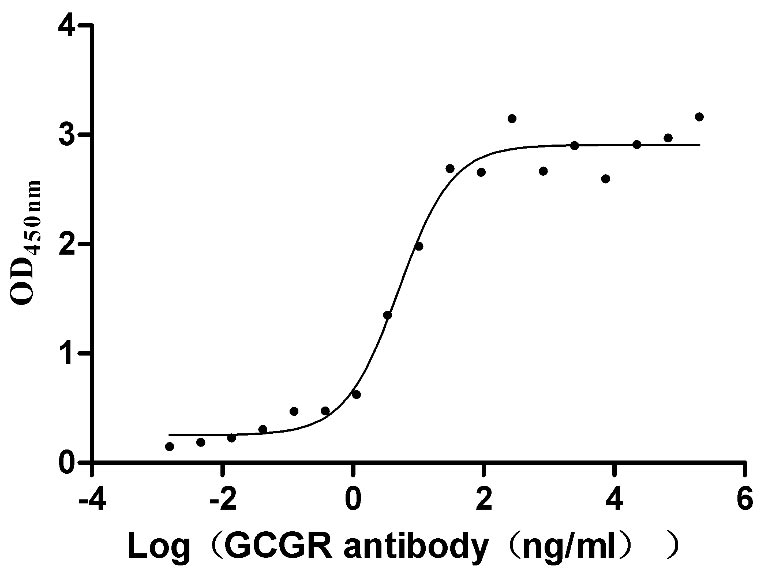
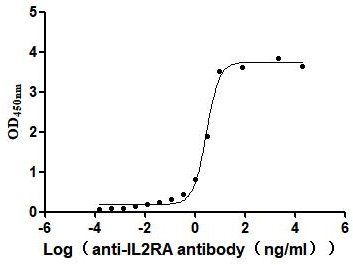
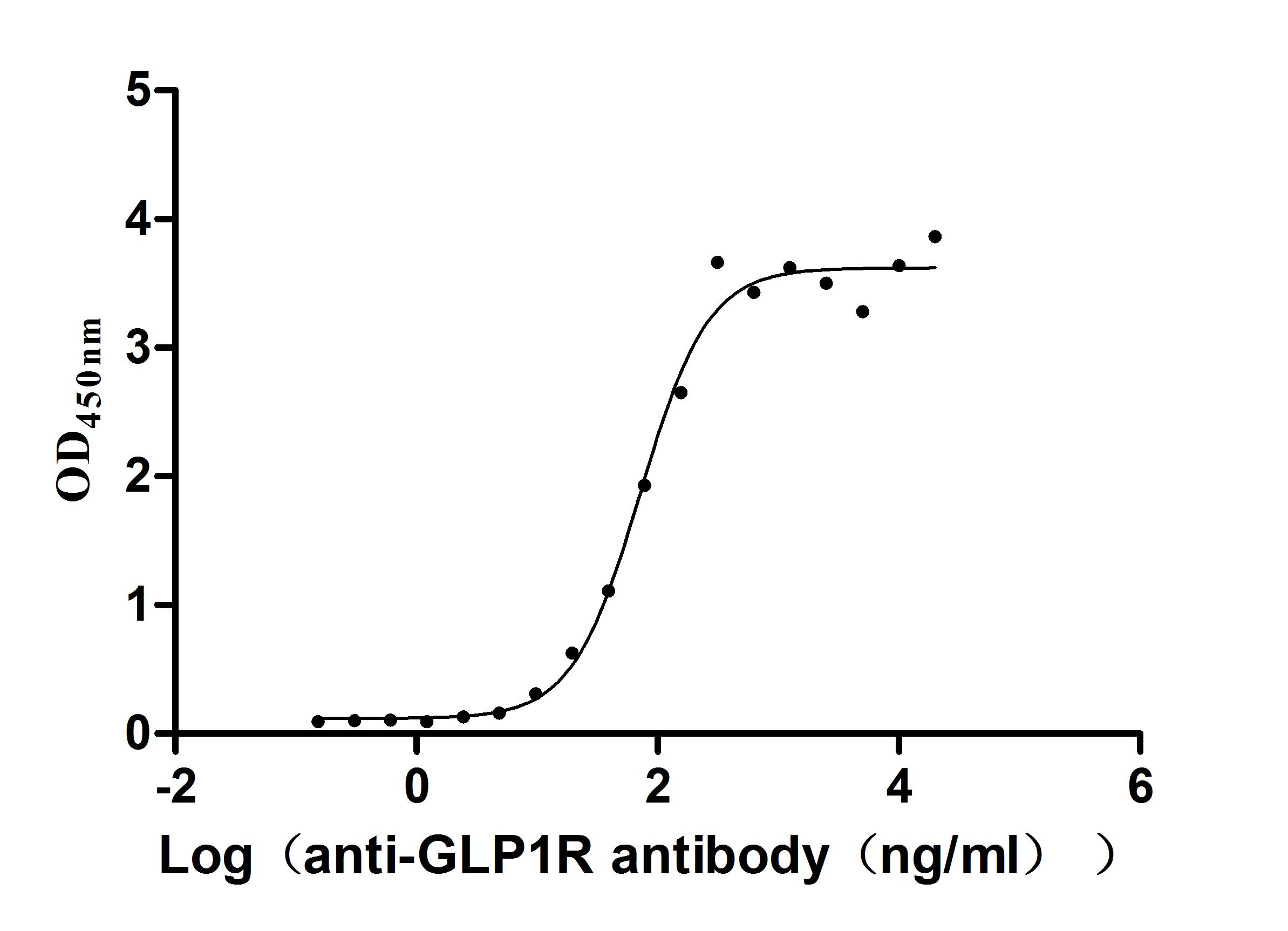
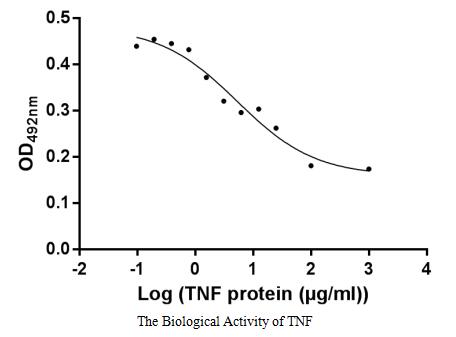
Autoimmune Diseases (AD) are a group of chronic diseases caused by the body's immune system mistakenly attacking its own tissues and organs, and have become the second most common disease area after tumours globally, with their incidence on the rise.
Its pathogenesis mainly involves the destruction of immune tolerance, resulting in auto-reactive T or B lymphocytes attacking normal or degenerated tissues and organs. This destruction can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetic susceptibility, environmental factors, and imbalances in immune regulation.
There is a wide variety of autoimmune diseases, and the most common ones, classified according to system, include:
- Connective tissue diseases: rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis and scleroderma, ect.
- Neuromuscular diseases: multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis and demyelinating lesions, ect.
- Endocrine diseases: primary adrenocortical atrophy, chronic thyroiditis, type 1 diabetes mellitus, and hyperthyroidism, ect.
- Digestive system diseases: chronic non-specific ulcerative colitis, chronic active hepatitis, pernicious anaemia and atrophic gastritis, ect.
- Diseases of the urinary system: autoimmune glomerulonephritis, ect.
- Diseases of the haematological system: autoimmune haemolysis, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura and idiopathic leucopenia, ect.
Symptoms of autoimmune diseases are mainly related to the specific site or tissue system of the disease. For example, patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) may present with fever, alopecia, arthralgia, mouth ulcers and facial erythema, while patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) may present with joint damage, dysfunction, and deformities of the joints.
There are various treatment options for autoimmune diseases, including hormone therapy, immunosuppressants, anti-inflammatory drugs, and biologics such as infliximab and tocilizumab. In recent years, CAR-T cell therapy has also made significant progress in the treatment of certain autoimmune diseases.
Popular Autoimmune Diseases and Drug Discovery Target Proteins
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic systemic autoimmune disease that mainly affects the joints. Its clinical manifestations are symmetrical, multi-joint swelling, pain, deformity, often involving the hands, wrists, knees and other joints, and in advanced stages can lead to joint ankylosis and loss of function.
There is a wide range of therapeutic drugs for RA, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, anti-rheumatic drugs, immunosuppressants, etc. In recent years, biological agents such as TNF-α inhibitors and IL-6 receptor inhibitors have achieved significant efficacy in the treatment of RA, and the pipeline of investigational monoclonal antibody drugs has reached 299. In addition, small molecule targeted drugs such as Jakinib analogues have also shown great promise in the treatment of RA.
● Popular Research Targets:
● Featured Products:
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
SLE is an autoimmune disease that involves multiple systems and organs, and is characterised by the production of autoantibodies against the nuclear components of the cells, leading to diverse clinical manifestations. Common symptoms include fever, rash, arthralgia, mouth ulcers, hair loss, etc. It may also involve the kidneys, heart, lungs and other vital organs.
Currently, drug development for SLE indications is very active worldwide, with a large number of drugs in various preclinical and clinical stages. Among them, drugs targeting CD19, BTK and other targets have made significant progress. For example, antagonists targeting TLR7/8 such as Enpatoran and Afimetoran have entered clinical phase II studies aimed at evaluating their efficacy and safety in SLE patients.
● Popular Research Targets:
● Featured Products:
Sjogren syndrome (SS)
Dry syndrome is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease mainly characterised by hypofunction of the lacrimal and salivary glands. Its clinical manifestations include dryness of the mouth and eyes, and it can also involve the lungs, kidneys, blood and other systems to cause corresponding symptoms.
At present, the therapeutic drugs for dry syndrome mainly include immunosuppressants, artificial tears, artificial saliva and other symptomatic therapeutic drugs. In recent years, with the in-depth study of the pathogenesis of SS, some new therapeutic targets such as BAFF, APRIL, etc. have gradually entered the research field.
● Popular Research Targets:
● Featured Products:
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease characterised by inflammatory demyelinating lesions of the white matter of the central nervous system. The most commonly affected areas of the disease include periventricular white matter, optic nerves, spinal cord, brainstem, and cerebellum, and common symptoms include fatigue, muscle weakness, vision problems, and balance difficulties.
Treatment strategies for MS include disease-modifying therapies and symptomatic drugs, which slow disease progression and relieve symptoms by modulating the immune response, suppressing inflammation, and protecting nerve cells, among other mechanisms. Some new MS therapeutic targets discovered in recent years, such as the JAK-STAT signalling pathway, S1PR5, SIRPA, etc., provide new directions for treatment.
● Popular Research Targets:
● Featured Products:
Myasthenia Gravis (MG)
Myasthenia gravis is a neuromuscular disorder characterised by muscle weakness and fatigue that worsens especially with activity. It is caused by impaired signalling at the neuromuscular junction and is usually associated with autoantibodies attacking the acetylcholine receptor (AChR), resulting in the inability of muscles to contract properly.
Therapeutic targets for myasthenia gravis focus on the immune system and the neuromuscular junction. These include therapies targeting B cells, such as rituximab (Eculizumab), which selectively removes B cells; inhibitors targeting complement C5 activation, such as eculizumab and zilucoplan, which inhibit complement activation and reduce inflammatory damage; and drugs targeting the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), such as exemplifymod, which rapidly depletes pathological IgG antibodies.
● Popular Research Targets:
● Featured Products:
Systemic Sclerosis (SSc)
Systemic sclerosis, also known as scleroderma, is a systemic autoimmune disease characterised by inflammation, degeneration, thickening and fibrosis of the skin leading to sclerosis and atrophy. It is characterised by fibroplasia of the skin and onion skin-like changes in the blood vessels, which ultimately lead to sclerosis of the skin, ischaemia of the blood vessels, and possible involvement of internal organs such as the heart, lungs, gastrointestinal tract and kidneys.
Therapeutic targets for scleroderma focus on alleviating the fibrotic process in the skin and internal organs, modulating the abnormal response of the immune system, and protecting damaged nerves. For example, by inhibiting the proliferation of fibroblasts and collagen synthesis to stop or reverse the fibrosis of the skin and internal organs; by regulating the immune response to reduce the production of autoantibodies, thereby reducing the inflammatory response and immunopathological damage; and by protecting and repairing damaged nerves through neurotrophic and supportive functions. In addition, with the in-depth study of the pathogenesis of scleroderma, new therapeutic targets such as the STING pathway are gradually being discovered, providing more possibilities for the treatment of scleroderma.
● Popular Research Targets:
● Featured Products:
Dermatomyositis (DM)
Dermatomyositis is a complex autoimmune connective tissue disease characterised by involvement of the skin and transverse muscles, which may be accompanied by multiple skin lesions and involvement of multiple organs. Its clinical manifestations include symmetrical weakness of the limb-girdle, neck and pharyngeal muscles, as well as purplish-red spots on the eyelids, purplish-red papules, oedema and fever.
Therapeutic targets for dermatomyositis revolve around modulating aberrant immune responses and reducing inflammation, including targeted therapy against T cells, B cells and inflammatory mediators such as cytokines and chemokines, as well as inhibition of overactivation of the complement system and key signalling pathways, such as JAK/STAT and NF-κB.
● Popular Research Targets:
● Featured Products:
Psoriasis
Psoriasis, commonly known as 'psoriasis', is a common chronic inflammatory recurrent skin disease, which is characterised by erythematous, scaly patches, often accompanied by intense itching, a long course of the disease and easy to recur, and is classified as one of the most serious non-communicable diseases by the World Health Organisation.
In recent years, research on therapeutic drugs for psoriasis has progressed rapidly, especially the emergence of biologics and small molecule-targeted drugs, which have brought new therapeutic options for psoriasis patients. Biological agents, such as TNF-α inhibitors, IL-17A inhibitors, IL-12/23 inhibitors, etc., have achieved precise treatment of psoriasis by targeting specific inflammatory mediators or receptors. Meanwhile, small molecule targeted drugs such as PDE-4 inhibitors and JAK inhibitors are also showing good efficacy and safety in development.
● Popular Research Targets:
● Featured Products:
Crohn's Disease (CD)
Crohn's disease is a chronic, inflammatory bowel disease whose pathogenesis may be related to a variety of factors such as genetics, immunity, and intestinal microecology. The disease can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, commonly at the end of the ileum, and the lesions are segmental or jumping in distribution. Clinical manifestations include abdominal pain, diarrhoea, weight loss, intestinal obstruction and other symptoms, and in severe cases, it may also affect the joints, skin, liver and other organs.
The therapeutic targets of Crohn's disease mainly focus on inhibiting the inflammatory response, regulating the immune response and blocking the fibrosis process. In recent years, with the rapid development of biological agents, such as TNF-α antagonists, IL-12/23 inhibitors and other new biotherapeutic drugs have been gradually applied to the treatment of Crohn's disease, and achieved significant efficacy.
● Popular Research Targets:
● Featured Products:
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM)
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is an autoimmune disease induced by a combination of genetic susceptibility and environmental factors. It is characterised by destruction of pancreatic β-cells, leading to an absolute deficiency in insulin secretion, which in turn causes an increase in blood glucose.
T1DM usually develops in childhood or adolescence, but may also develop in the newborn and early adulthood. Its main symptoms include polydipsia, polyphagia, polyuria and weight loss, which may lead to acute complications such as diabetic ketoacidosis in severe cases.
Therapeutic strategies for T1DM are currently focused on immunomodulation, especially targeting the regulation of T and B cell activation, such as using anti-CD3 monoclonal antibodies, drugs such as alfacalcip, abatacept to inhibit T cell activation, as well as anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies, such as rituximab, to target B cells and reduce their attack on pancreatic islet β-cells. There is also interest in the role of some cytokines such as TNF-α in the disease process, and drugs targeting these cytokines such as golimumab are being tried for therapeutic use.
● Popular Research Targets:
● Featured Products:
Ulcerative Colitis (UC)
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic non-specific inflammatory bowel disease, mainly affecting the mucosa and submucosa of the colon and rectum, manifesting as recurrent diarrhoea, abdominal pain, blood in the stools, etc. It is generally believed to be associated with a variety of factors such as intestinal immune imbalance, genetic factors, environmental factors and psychoneurological factors.
The current therapeutic target of ulcerative colitis focuses on inflammation regulation and the restoration of intestinal immune balance, not only through the inhibition of pro-inflammatory factors to reduce inflammation, but also through the regulation of macrophage and other immune cells to restore the immune homeostasis, such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-10, and through the effective inhibition of their activities by the specific antibody or receptor antagonist, significantly alleviate the symptoms of inflammation.
● Popular Research Targets:
● Featured Products:
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF)
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic, progressive, fibrotic interstitial lung disease with lesions mainly confined to the lungs, prevalent in the middle-aged and elderly population, and with an etiology related to immune-inflammatory injury.
The characteristic histopathological change of IPF is generalised interstitial pneumonia, which is characterised by fibrosis of lung tissue and honeycomb lung changes, leading to a sustained decline in lung function, and ultimately death may occur due to respiratory failure.
In response to the pathogenesis of IPF, researchers have identified several potential therapeutic targets. For example, the development of targeted drugs against cytokines and their signalling pathways that promote the fibrotic process, such as TGF-β and CTGF; the design of specific inhibitors against key cell types in the process of pulmonary fibrosis, such as fibroblasts, immune cells, etc.; and the development of intervention strategies against key molecular events in the process of pulmonary fibrosis, such as production and degradation of extracellular matrix, apoptosis and proliferation. and development of intervention strategies for key molecular events in lung fibrosis, such as extracellular matrix production and degradation, apoptosis and proliferation.
● Popular Research Targets:
● Featured Products:
Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)
Interstitial lung disease is a disease with diffuse parenchymal and alveolar inflammation and interstitial fibrosis as the basic pathological changes, which often leads to symptoms such as coughing, shortness of breath, dyspnoea, and may cause respiratory failure and pulmonary heart disease.
Currently, glucocorticosteroids, immunosuppressants and antifibrotic drugs are widely used to improve the symptoms and slow down the progression of interstitial lung diseases. Especially for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), the introduction of drugs such as nintedanib has effectively slowed down the rate of decline in lung function and reduced the risk of acute exacerbation or death by inhibiting targets such as PDGFRα/β, FGFR1-3, and VEGFR1-3. In addition, JAK inhibitors (JAKi) targeting the JAK-STAT signalling pathway have also demonstrated potential therapeutic efficacy in clinical trials and are expected to provide new therapeutic options for ILD patients.
● Popular Research Targets:
● Featured Products:
Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT)
Chronic thyroiditis is a common autoimmune thyroid disease, which is characterised by infiltration of lymphocytes or plasma cells in the thyroid tissue, interstitial fibrosis, and degenerative destruction of the thyroid follicular epithelial cells, ultimately leading to hypothyroidism in most patients.
Currently, pharmacological treatment of chronic thyroiditis (Hashimoto's thyroiditis) focuses on replacement therapy for hypothyroidism. Levothyroxine (L-T4), a commonly used replacement therapy, is effective in reducing the symptoms of goiter, but there is no evidence that it prevents the progression of the disease. In addition, some patients with HT with IgG4-related disease manifestations respond well to early glucocorticoid therapy, which reduces immune damage, delays the fibrotic process and improves thyroid function.
● Popular Research Targets:
● Featured Products:
Autoimmune Glomerulonephritis (Autoimmune GN)
Autoimmune glomerulonephritis is a kidney disease caused by dysfunction of the immune system, characterised by the deposition of immune complexes in the glomeruli, leading to glomerular damage and inflammatory response. This condition can further lead to clinical manifestations such as haematuria, proteinuria, oedema and hypertension.
Drug development for autoimmune glomerulonephritis has focused on the complement system (e.g., Ipecopam targets the complement bypass pathway), B-cell immune pathways (tetraciprazole, aceciprazole targeting BLyS and APRIL), effector T-cells (ustekinumab inhibits T-cell activation), and macrophages (potential target CXCL4). Significant progress has been made in the development of these targeted agents, which are expected to lead to more effective treatments for patients.
● Popular Research Targets:
● Featured Products:
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA)
Autoimmune haemolytic anaemia is a type of haemolytic anaemia caused by a disorder in the regulation of the body's immune function. The disease is primarily triggered by the production of autoantibodies and/or complement adsorbed on the surface of red blood cells, which accelerates red blood cell destruction through antigen-antibody reactions.
Therapeutic strategies for AIHA focus on B-cells and antibody production (e.g. rituximab targeting the CD20 antigen to reduce antibody production), the complement system (e.g. sultirizumab inhibition of C1s to block complement activation), and T-cells and immune responses (e.g. cyclosporine A regulates immune responses by inhibiting T-cells). In addition, emerging drugs such as PI3K inhibitors and futatinib are in clinical trials.
● Popular Research Targets:
● Featured Products:
Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is an autoimmune haemorrhagic disease characterized by thrombocytopenia, normal or increased bone marrow megakaryocytes with impaired maturation, which is mostly associated with increased platelet destruction due to dysfunction of the body's immune system.
Drug development for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is mainly in two directions: first, immunomodulatory targets, such as splenic tyrosine kinase (SYK), which reduces platelet destruction by autoimmune reactions through inhibition of its activity; and second, thrombopoietic targets, such as recombinant human thrombopoietin (rhTPO), which is designed to promote the proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow megakaryocytes in order to increase platelet count.
● Popular Research Targets:
● Featured Products:


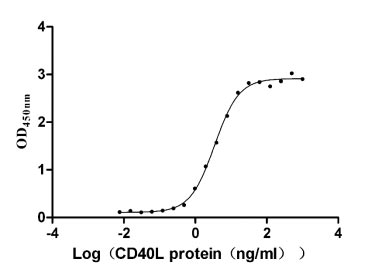
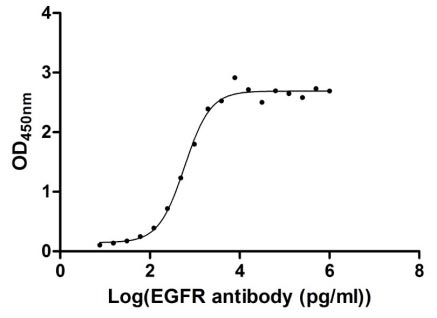
-AC1.jpg)
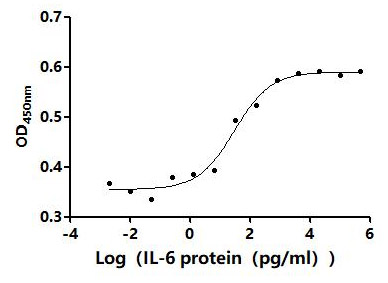
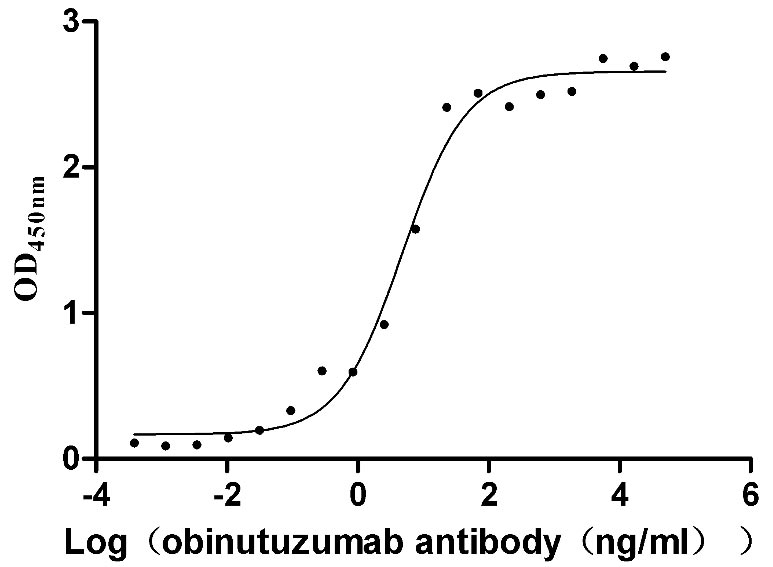
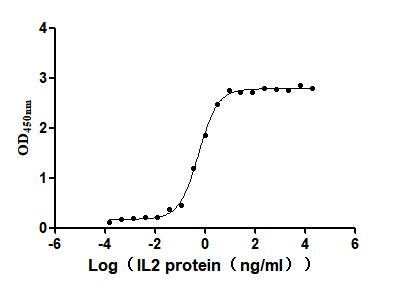
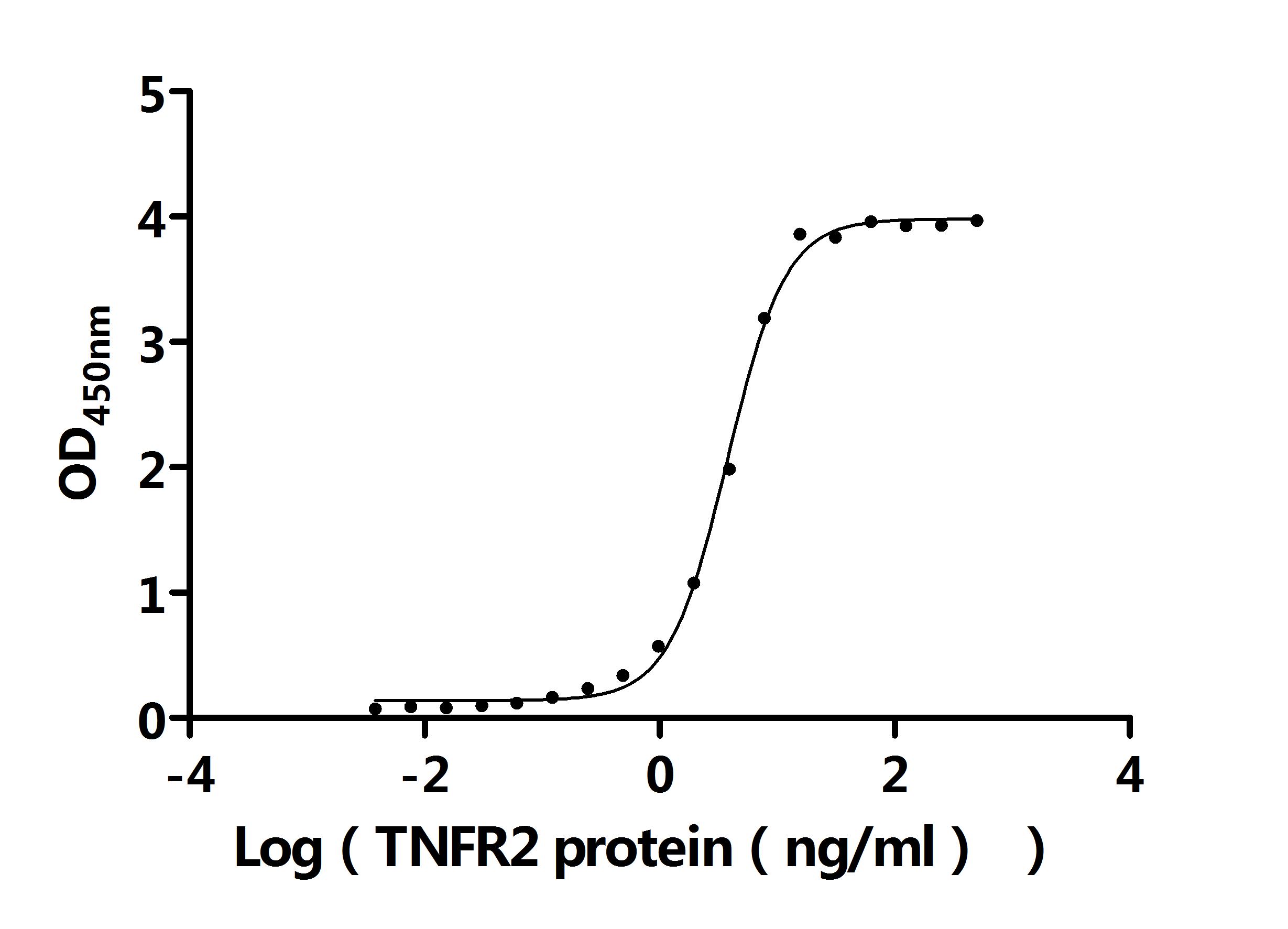
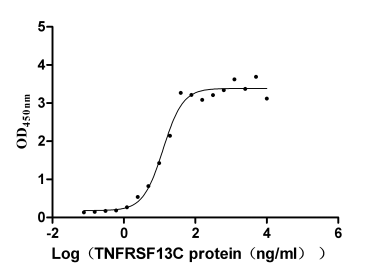
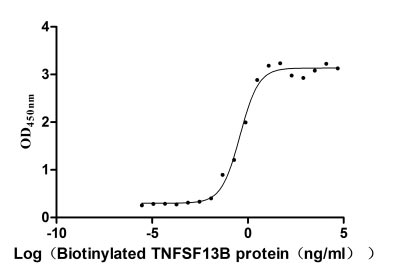
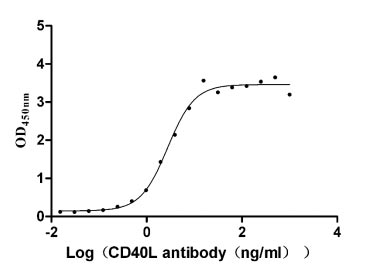
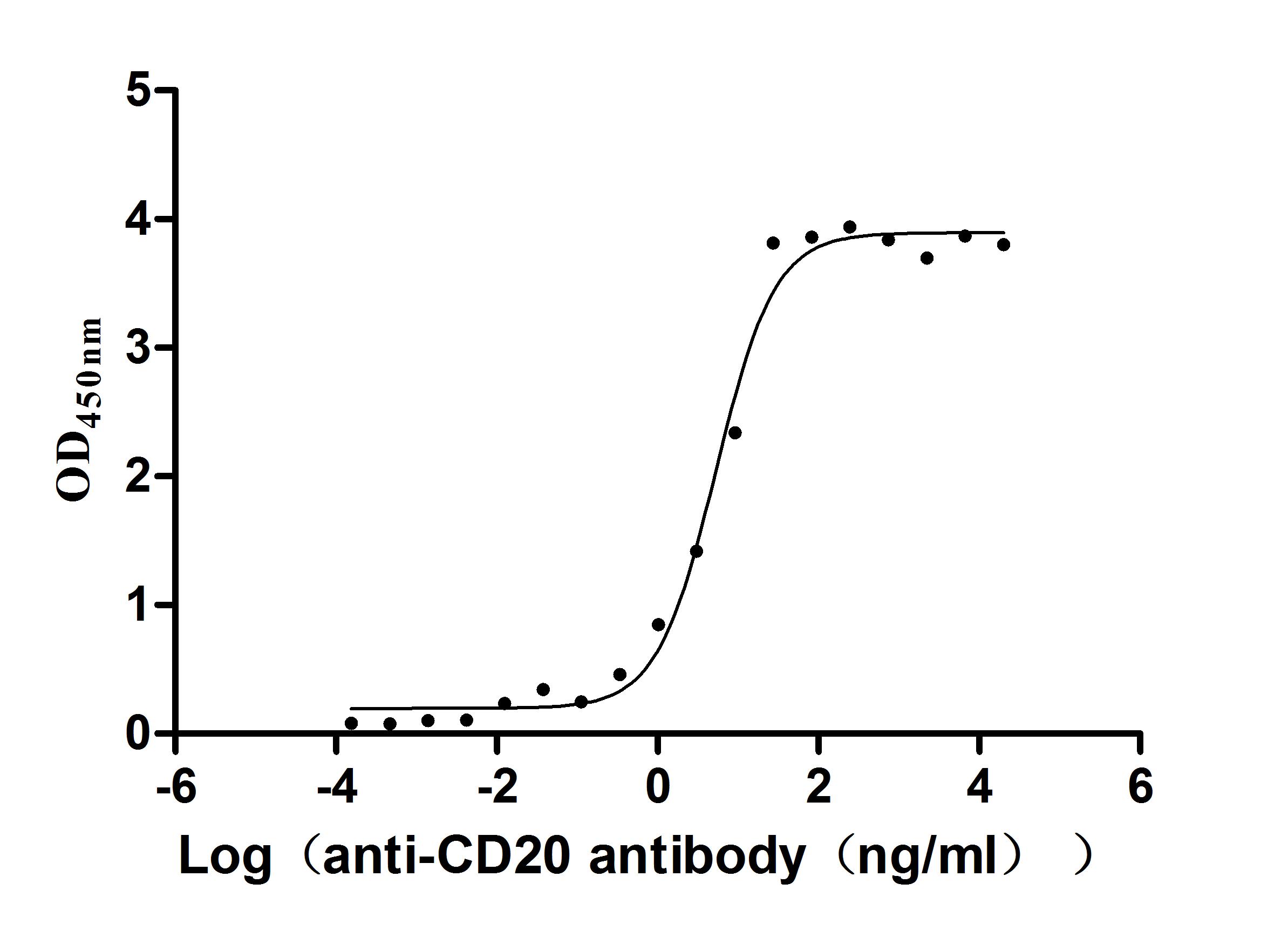
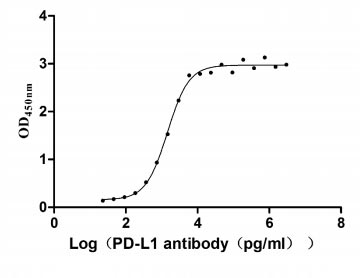
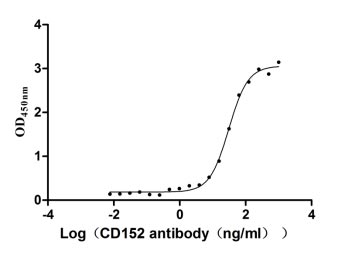
-AC1.jpg)