Efficient Universal CAR Detection Reagent: Anti-CAR Linker Antibody
CAR-T therapy is an immunotherapy in which T cells of patients are genetically engineered to express specific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR), thereby enhancing their ability to recognize and attack cancer cells. The therapy has shown surprising efficacy in some malignancies, particularly in some refractory hematological cancers.
Click to view the complete introduction to CAR-T cell therapy >>
CAR Generates "Everything": From CAR-T to CAR-X
With a deeper understanding of the immune system, the application scope of CAR technology is continuously expanding, and the development of novel CAR cell therapies is becoming a hot topic. These include CAR-NK, CAR-M, CAR-Treg, and CAR-γδ. Compared to the potential adverse effects and limitations in treating solid tumors associated with CAR-T therapy, these new CAR cell therapies offer distinct advantages, infusing new vitality into the development of immunotherapies.
Basic Structure of CAR
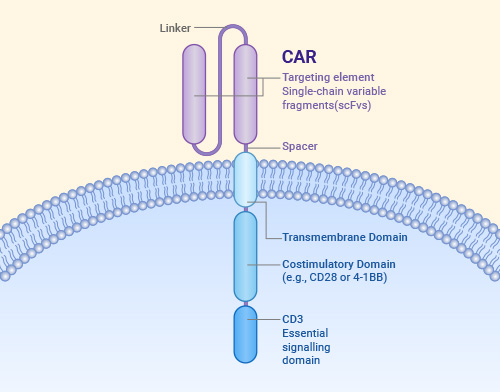
Whether it is CAR-T, CAR-NK, or CAR-M, they all share a similar CAR structure. The CAR structure primarily consists of three parts: the extracellular domain, the transmembrane domain, and the intracellular domain.
- Extracellular Domain: This is typically a single-chain variable fragment (scFv), which is formed by connecting the variable heavy chain (VH) and variable light chain (VL) of an antibody with a linker. The scFv is responsible for recognizing tumor antigens. A hinge region connects the scFv to the transmembrane domain, providing flexibility to overcome spatial hindrance and allowing the scFv to access the target epitope.
- Transmembrane Domain: Its primary function is to ensure that the CAR is stably embedded in the cell membrane.
- Intracellular Domain: This includes co-stimulatory domains and signaling domains, which activate and enhance the immune cell response.
Structural elements of a chimeric antigen receptor(CAR)
Rodríguez-Lobato LG, et al. Front Oncol. 2020.
Why Perform CAR Detection?
Currently, as more and more CAR-based cell therapies enter clinical research stages, the detection of CAR expression has become a critical aspect of drug quality control. This directly impacts treatment outcomes, and relevant regulations have set clear requirements for CAR positivity testing.
Therefore, to ensure strict control over all stages—from early research phases involving CAR cell preparation and functional testing, through CMC phases for cell quality and purity assessment, to clinical testing phases for in vivo cell monitoring and PK (Pharmacokinetics) studies—it is crucial to develop accurate, simple, and universal CAR positivity detection reagents.
Comparison of Existing CAR Detection Methods
Common CAR detection methods include anti-human (or mouse) IgG F(ab')2 polyclonal antibodies, anti-idiotypic antibodies, and Protein L. While each method has its advantages, they also have some limitations. For example, they often require the development of specific antibodies for each CAR, which can be costly, and they can only be used to detect known antigens*.
| Detection Method |
Detection Mechanism |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Anti-human F(ab')2 pAb and Anti-mouse F(ab')2 pAb |
Binds to IgG F(ab')2 fragments |
- Low cost, easy to obtain, high stability;
- Has some universality, can detect different CARs.
|
- Low specificity, may cross-react with other IgG-like substances;
- Batch-to-batch consistency is difficult to maintain, results may vary by batch.
|
| Anti-idiotypic antibodies |
Specifically binds to the antigen-binding region of scFv
|
- High specificity, targets the unique antigen-binding region of CAR;
- High sensitivity, low background noise.
|
- High cost, usually requires customization;
- Different antibodies need to be designed for different CARs, poor universality.
|
| rh-protein |
Specifically binds to the antigen-binding region of scFv |
- High specificity, targets the unique antigen-binding region of CAR;
- High sensitivity, low background noise.
|
- High cost, requires purchasing and validating specific rh-proteins;
- Can only be used to detect known antigens, poor universality.
|
| Protein L |
Binds to antibody kappa light chains |
- Low cost, has some universality, can detect CARs targeting different antigens.
|
- Poor specificity, low sensitivity, prone to false-positive results.
|
Our Products
Linker-specific mAbs |
Detect CAR linker |
- High specificity, targets the linker sequence of CAR;
- Can detect most CARs;
- Low cost, easy to use.
|
- The CAR structure must include a linker sequence.
|
*Linker-specific monoclonal antibodies present a simple and reliable detection method for scFv-based CAR NK cells. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024.
Linker-Specific mAb Products from CUSABIO
Since most CAR constructs contain single-chain variable fragments (scFvs) with either Whitlow or G4S linkers, the Whitlow linker (GSTSGSGKPGSGEGSTKG) is primarily used in CAR constructs targeting hematological malignancies, such as CD19 CAR [1], while the G4S linker (glycine4-serine) is commonly used in CARs targeting solid tumor antigens, such as HER2 and CEA [2]. Developing specific monoclonal antibodies against these two linkers allows for the detection of a wide range of CARs.
Based on this technical background, CUSABIO now introduces a new set of highly efficient and broadly applicable CAR positivity detection tools—Anti-Whitlow Linker Antibody and Anti-G4S Linker Antibody.
● Product List
● Product Features
High Specificity
- Specific Binding to Linkers: Specifically recognizes linker sequences, avoiding non-specific binding to other regions of the CAR.
- Avoids False Positives: Since linker-specific mAbs do not bind to IgG or other proteins in serum, they do not produce false positive results.
Broad Applicability
- Suitable for Most CARs: Most CARs contain Whitlow or G4S linkers, making these antibodies highly versatile.
- Not Restricted by Antigen Specificity: Does not target specific antigen-binding regions, allowing the detection of CARs with different antigens.
Easy to Use
- Direct Use in Flow Cytometry: No complex experimental steps required; simple and easy to standardize.
- Compatible with Other Methods: Can be used in combination with other detection methods (such as rh-proteins) to improve the specificity and sensitivity of the detection.
● Product Data
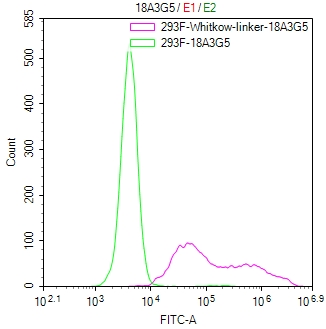
The Binding Activity of Whitlow linker with Anti-Whitlow linker antibody.
(Code:
CSB-MA234468A0m)
Untransfected HEK-293F cells (green line) and transfected scFv-based Anti-CD19 CAR containing a Whitlow/218 linker stable cells (red line) were stained with anti-Whitlow linker antibody (2µg/1*106), washed and then followed by FITC-conjugated anti-Mouse IgG Fc antibody and analyzed with flow cytometry.
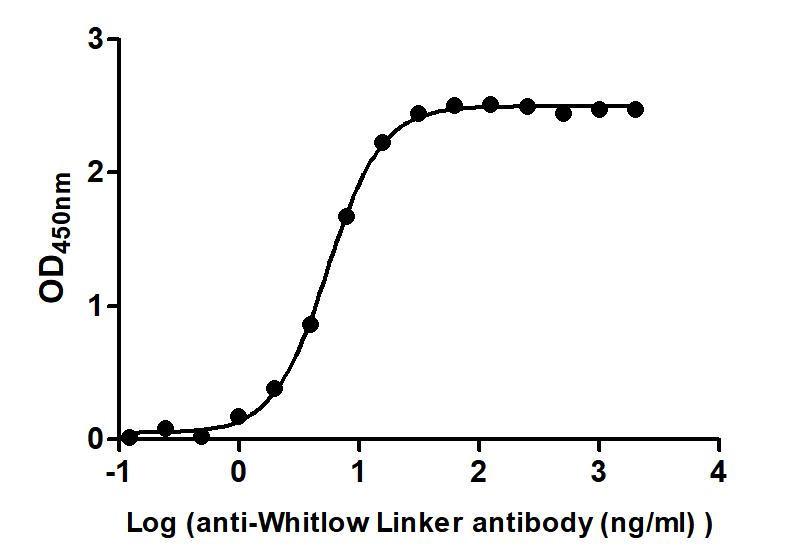
The Binding Activity of Whitlow linker with Anti-Whitlow linker antibody.
(Code:
CSB-MA234468A0m)
Immobilized scFv-based Anti-CD19 CAR recombinant antibody at 2 μg/mL can bind Anti-Whitlow linker antibody. The EC50 is 5.147 to 5.761 ng/mL.
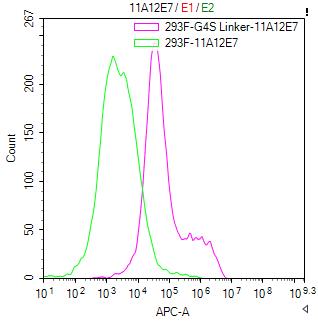
The Binding Activity of G4S linker with Anti-G4S linker antibody.
(Code:
CSB-MA186062I1m)
Untransfected HEK-293F cells (green line) and transfected scFv-based Anti-CD19 CAR containing a G4S linker stable cells (red line) were stained with anti-G4S linker antibody (2µg/1*106), washed and then followed by APC-conjugated anti-Mouse IgG Fc antibody and analyzed with flow cytometry.
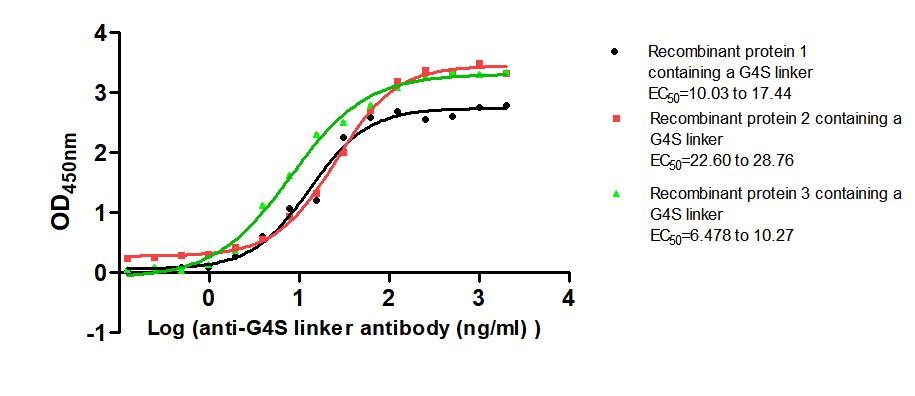
The Binding Activity of G4S linker with Anti-G4S linker antibody.
(Code:
CSB-MA186062I2m)
Immobilized Three recombinant proteins containing G4S linker at 2 μg/mL can bind Anti-G4S linker antibody. The EC50 is 10.03 to 17.44 ng/mL, 22.60 to 28.76 ng/mL and 6.478 to 10.27 ng/mL.
References
[1] B-cell depletion and remissions of malignancy along with cytokine-associated toxicity in a clinical trial of anti-CD19 chimeric-antigen-receptor-transduced T cells. Blood. 2012.
[2] CAR-T cell potency: from structural elements to vector backbone components. Biomark Res. 2022.