The rat COX-2 ELISA Kit quantitates rat COX-2 levels in serum, plasma, and tissue homogenates. COX-2 (PTGS2) is the key rate-limiting enzyme needed for the synthesis of prostanoids, including PGE2, PGD2, PGF2a, PGI2, and TAX2, from an essential fatty acid arachidonic acid (AA). It is constitutively expressed in certain cell groups of the brain and inducibly expressed in response to inflammatory reactions. In the central nervous system (CNS), COX-2 affects memory, sensory integration, and autonomic modulation. COX-2 overexpression is mainly linked to inflammation, apoptosis inhibition, uncontrolled cell proliferation, growth, metastasis, neovascularization, and angiogenesis finally resulting in cancer. COX-2 is often expressed in many malignant tumors and is associated with occurrence, progression, and prognosis.
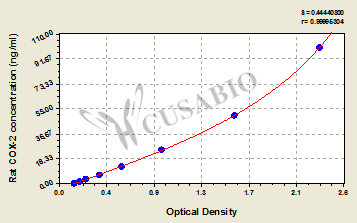
This kit employs the sandwich-ELISA mechanism in conjugation with COX-2 antibody-COX-2 antigen-specific binding as well as HRP-TMB chromogenic reaction to measure the concentration of COX-2 in the samples. The kit is characterized by high sensitivity, strong specificity, good linearity, high recovery, and a precision of less than 10%.