What is VEGF Signaling Pathway?
VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) signaling pathway is a complex process in which VEGF stimulates new blood vessel formation. VEGF, also known as vascular permeability factor (VPF), is a dimer glycoprotein that binds to the VEGF receptor (VEGFR) on the surface of the cells, thereby activating intracellular tyrosine kinase and initiating a series of signaling cascades events involved in vasculogenesis and angiogenesis.
The Function of VEGF Signaling Pathway
VEGF signaling pathway plays a significant role in vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. Angiogenesis is important in various physiologic and pathologic diseases. VEGF signaling pathway performs a dual function that either beneficial or harmful for humans.
On one hand, the process of the VEGF signaling pathway helps bone formation, hematopoiesis, wound healing and development; on the other hand, it prompts the growth of tumors. According to the tumor angiogenesis of Moses Judah Folkman, when tumor size gets bigger, it will induce the formation of new blood vessels to nourish itself and sustain its existence.
The Classification of VEGF and VEGFR
In the mammals, the VEGF family includes VEGFA, VEGFB, VEGFC, VEGFD, VEGFE, and placenta growth factor (PGF). Commonly, VEGFA refers to VEGF. And there are three VEGF receptors (VEGFR): VEGFR-1, VEGFR- 2, and VEGFR-3. These receptors all belong to transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptors, including three major regions, namely the extracellular domain, transmembrane region, and intracellular carboxyl-terminal. There is now much evidence that VEGFR-2 is the major mediator of VEGF-driven responses in endothelial cells.
VEGFA: VEGF is usually referred to as VEGFA. VEGFA can bind to VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2, promoting angiogenesis, facilitating migration and mitosis of endothelial cells, increasing matrix metalloproteinase and αvβ3 activity and creating blood vessel lumen.
VEGFB: Usually, VEGFB prompts embryonic angiogenesis by binding to VEGFR-1.
VEGFC: Upon the combination with VEGFR-2 or VEGFR-3, VEGFC stimulates lymphangiogenesis.
VEGFD: VEGFD binds to VEGFR-2 or VEGFR-3 to exert its function. And it is necessary for the development of lymphatic vasculature nearby lung bronchioles.
VEGFE: VEGFE is specific for partial angiogenesis when it attaches to VEGFR-2.
PGF: One of the ligands for VEGFR-1 is PGF. PGF is important for vasculogenesis, and it is needed for angiogenesis during ischemia, inflammation, wound healing, and cancer.
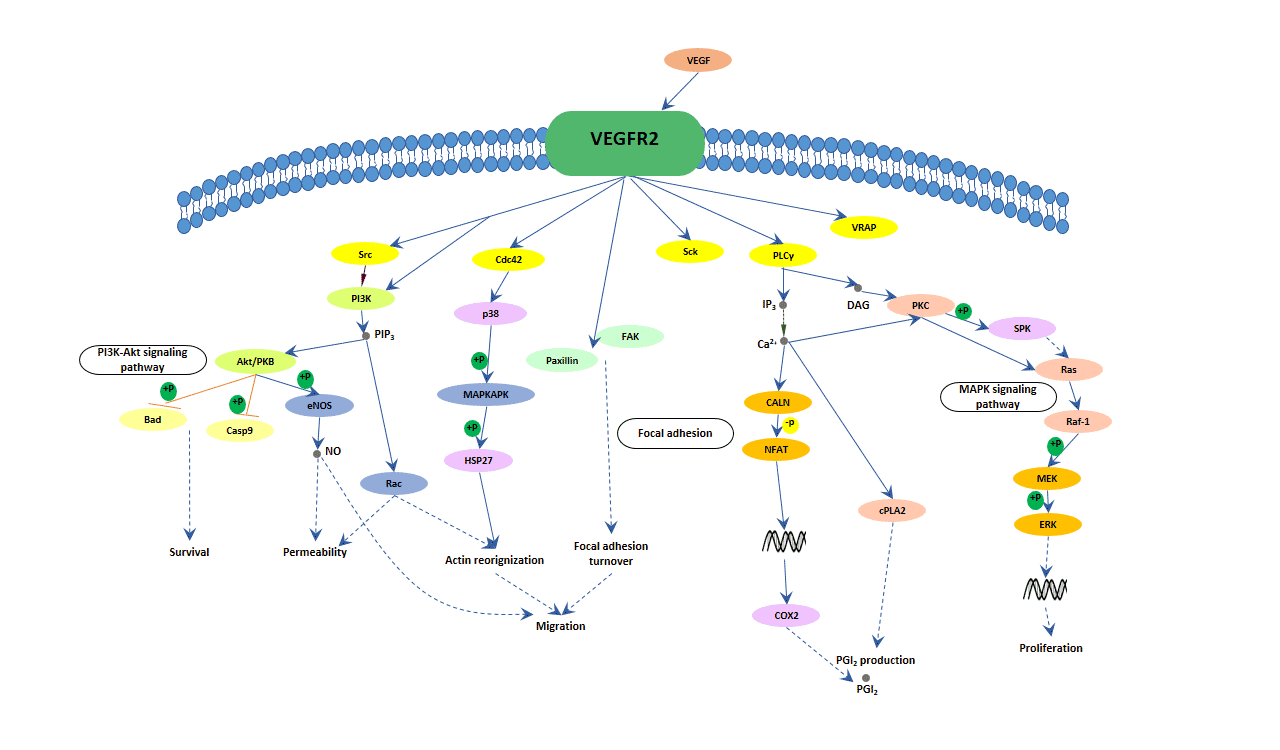
The Process of VEGF Signaling Pathway
As shown in the following picture, when a VEGF binds to its receptor, the receptor can transiently exert its kinase activity and form a complex with an intracellular tyrosine or serine/threonine kinase. And then the activated receptors result in the activation of other proteins in the signaling pathway and the production of various second messengers. Finally, these signals are transmitted into the nucleus and induce the expression of specific genes, thereby modulating proliferation, survival, migration, and permeability of vascular endothelial cells.
The binding of VEGF to VEGFR-2 leads to form receptor dimer and then activates the PLCγ (phospholipases C γ) and PKC-Raf kinase-MEK-mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, which initiates DNA synthesis to promote endothelial cell proliferation. At the same time, Src signaling is provoked to start the activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase (PI3K)-Akt pathway, which leads to increased endothelial-cell survival. The activation of the Src signaling pathway will also cause complete systemic destruction of the entire basement membrane and cell wall, resulting in increased vascular permeability. And CDC42 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling are incited. Activation of p38 MAPK further triggers actin reorganization and ultimately migration of endothelial cells.
The Diseases Associated with VEGF Signaling Pathway
The over-expression of VEGF is contributive to many diseases, such as solid tumors, breast cancer, GBM, melanoma, and hypoxic diseases. When solid tumors grow beyond a limited size, if their blood supply is insufficient, they cannot continue to grow. And then, the tumors express VEGF to promote new blood vessels formation, which facilitates self-growth and metastasis.
The Related Inhibitors
As we know from the process of the VEGF signaling pathway, the combination of the VEGF with VEGFR can initiate the occurrence of the enzymatic signaling cascades. Therefore, blocking their binding can effectively terminate the VEGF signaling pathway. VEGF inhibitors are some specific monoclonal antibodies and VEGFR inhibitors are some particular tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Existing drugs such as aflibercept bevacizumab ranibizumab and pegaptanib can inhibit VEGF and control or slow those diseases.





