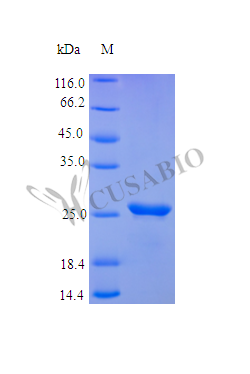
Recombinant Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23) protein is expressed in E. coli, covering the full mature protein length from amino acids 25 to 251. This product is tag-free, which appears to help maintain the native structure. Purity exceeds 95% as confirmed by SDS-PAGE, and endotoxin levels remain below 1.0 EU/μg as determined by the LAL method. The protein shows full biological activity, with an ED50 of less than 0.5 μg/ml in thymidine uptake assays, suggesting a specific activity of more than 2.0 × 10³ IU/mg.
Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23) serves as a critical regulator of phosphate and vitamin D metabolism. It plays what seems to be an essential role in maintaining phosphate homeostasis and is involved in regulating bone mineralization. FGF23 is mainly produced by osteocytes and osteoblasts. When its regulation goes awry, this can lead to disorders in mineral metabolism. This protein has become of significant interest in research focusing on metabolic bone diseases and related pathways.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
1. FGF Receptor Binding and Signaling Studies
This recombinant FGF23 is confirmed to be biologically active but requires Klotho co-expression and heparin for effective signaling. Researchers must include both Klotho (0.3 μg/ml) and heparin (10 μg/ml) in all binding and signaling assays to achieve physiological relevance. The protein is suitable for studying the unique FGF23-Klotho-FGFR signaling complex, but researchers should note that the ED₅₀ (0.5 μg/ml) is significantly higher than typical FGFs due to the ternary complex requirement. Studies should focus on α-Klotho-dependent signaling pathways rather than general FGFR activation.
2. Klotho Co-factor Dependency Research
This application is highly appropriate given the demonstrated Klotho requirement. The protein is ideal for studying FGF23-Klotho interactions, optimal co-factor ratios, and the mechanism of Klotho-dependent receptor complex formation. Researchers can systematically vary Klotho and heparin concentrations to map the cooperative interactions in FGF23 signaling. This represents the most physiologically relevant application for this protein.
3. Cell Proliferation and Metabolic Assays
While active in thymidine uptake assays, researchers should note that FGF23's primary physiological role is metabolic regulation (phosphate/calcium homeostasis) rather than proliferation. The BaF3 transfection system validates receptor engagement, but metabolic assays in kidney-derived cells or osteocytes would be more physiologically relevant. The high ED₅₀ may reflect the artificial proliferation readout rather than true potency in native metabolic signaling.
4. Heparin-Dependent Signaling Mechanism Studies
The demonstrated heparin requirement makes this protein suitable for studying glycosaminoglycan interactions in FGF23 signaling. However, researchers should distinguish between heparin's role in stabilizing FGF23-Klotho-FGFR complexes versus non-specific charge interactions. Physiological heparan sulfate proteoglycans rather than pharmaceutical heparin may provide more biologically relevant insights.
5. Antibody Development and Validation
The high-purity FGF23 serves as a good immunogen, but antibodies should be tested for their ability to block the FGF23-Klotho-FGFR ternary complex formation. Neutralization assays must include Klotho and heparin to properly validate function-blocking antibodies. The full-length nature ensures complete epitope coverage, which is particularly important for FGF23, where both N- and C-terminal domains contribute to function.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This recombinant human FGF23 is a well-characterized tool protein suitable for studying Klotho-dependent FGF23 signaling, but researchers must strictly include the required cofactors (Klotho at 0.3 μg/ml and heparin at 10 μg/ml) in all experimental systems. Prioritize applications focused on the unique FGF23-Klotho signaling axis rather than general FGFR studies. For metabolic studies, validate findings in physiologically relevant cell types (kidney proximal tubule cells, osteocytes) rather than relying solely on BaF3 proliferation data. When developing antibodies, ensure neutralization assays include the full ternary complex. The relatively high ED₅₀ reflects biological reality rather than poor activity, but researchers should optimize concentrations for their specific systems. Always include proper controls (FGF23 without Klotho, Klotho without FGF23) to demonstrate pathway specificity. For binding studies, focus on the unique α-Klotho-FGFR1c complex rather than general FGFR interactions. The E. coli expression produces non-glycosylated FGF23, which is advantageous as native FGF23 has minimal glycosylation, making this preparation highly suitable for structural and mechanistic studies.