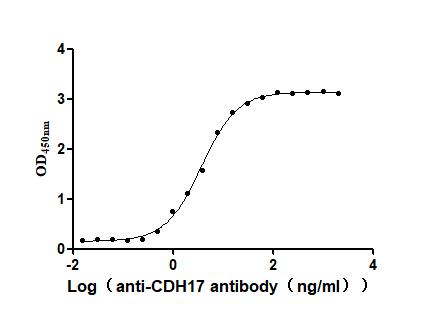
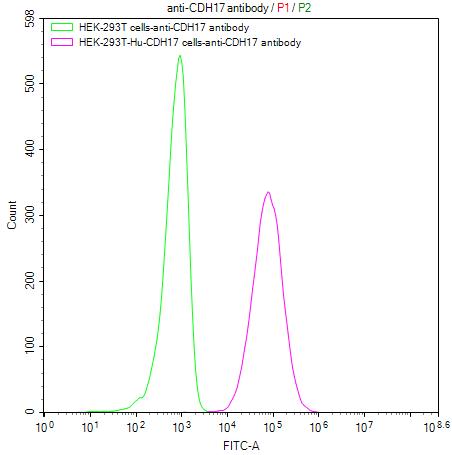
The gene is isolated from the B cells produced by immunizing the animal with the recombinant human CDH17 protein and then cloned into a plasmid vector. The recombinant vector is introduced into host cell lines. The transfected cells are cultured to allow antibody expression. The CDH17 recombinant monoclonal antibody is purified from the cell lysate through affinity chromatography. It can be reacted with human CDH17 protein in the ELISA and FC applications.
CDH17 is primarily expressed in embryonic and adult intestinal epithelial cells, as well as in some pancreatic duct epithelial cells but is almost absent in liver cells, esophageal epithelial cells, and gastric mucosa in healthy individuals. Acting as a functional Ca2+-dependent cell adhesion molecule, CDH17 exerts its adhesive function by directly interacting with the cellular cytoskeleton. Structural abnormalities and functional disruptions of CDH17 can lead to decreased cell-cell adhesion among tumor cells, resulting in loose tissue structure that is prone to detachment or deformation, thereby promoting tumor invasion and metastasis. Research has confirmed elevated expression levels of CDH17 in various human malignancies. Consequently, CDH17 can serve as a new objective indicator reflecting solid cancer's biological behavior and could potentially become a novel target for solid cancer treatment. Currently, clinical progress in CDH17-targeted drugs is limited, with most drugs in the preclinical stages. Therefore, the preparation of CDH17 protein could facilitate the development and research of CDH17-targeted clinical drugs.