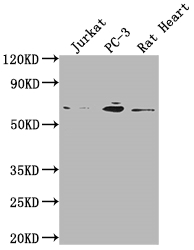
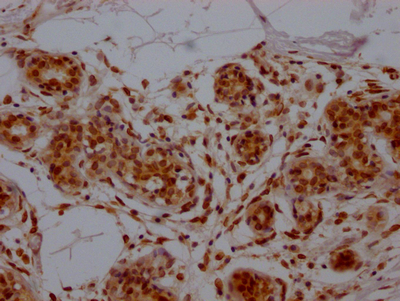
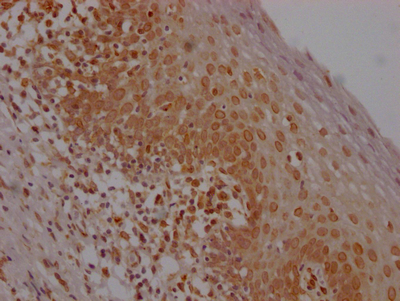
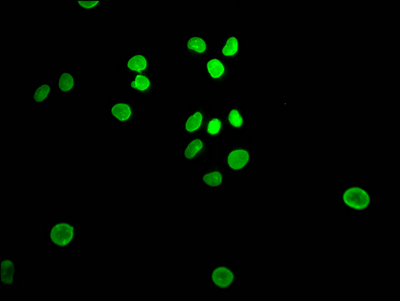
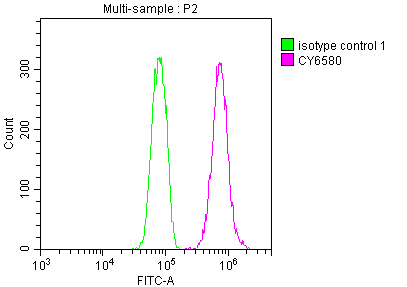
The E2F1 recombinant monoclonal antibody can be used to detect both human and rat E2F1 proteins in five assays including ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, and FC. It is produced using recombinant DNA technology. The gene that codes for the E2F1 monoclonal antibody is synthesized after sequencing the cDNA of the E2F1 antibody-producing hybridomas. The hybridomas are created by fusing myeloma cells with B cells isolated from an animal that has been immunized with a synthesized peptide derived from human E2F1. The synthesized gene is then incorporated into a vector and transfected into cells for cultivation. The resulting E2F1 recombinant monoclonal antibody is purified through affinity chromatography from the cell culture supernatant.
The E2F1 protein is a transcription factor that plays a key role in regulating the cell cycle and cell proliferation. E2F1 can activate the expression of genes required for progression through the G1/S phase transition of the cell cycle, including genes involved in DNA replication, DNA repair, and cell division. In addition, E2F1 can induce apoptosis in response to DNA damage or other stress signals. Dysregulation of E2F1 activity has been implicated in a variety of diseases, including cancer and developmental disorders.