Full Product Name
Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) MTTP Polyclonal antibody
Alternative Names
ABL antibody; Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (large polypeptide 88kDa) antibody; Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein 88kD antibody; Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein antibody; Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein large subunit antibody; MTP antibody; MTP large subunit antibody; MTP_HUMAN antibody; MTTP antibody; Transfer RNA, mitochondrial, proline antibody; tRNA-Pro, mitochondrial antibody
Immunogen
Recombinant Human Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein large subunit protein (19-151AA)
Immunogen Species
Homo sapiens (Human)
Conjugate
Non-conjugated
The MTTP Antibody (Product code: CSB-PA015209LA01HU) is Non-conjugated. For MTTP Antibody with conjugates, please check the following table.
Available Conjugates
| Conjugate |
Product Code |
Product Name |
Application |
| HRP |
CSB-PA015209LB01HU |
MTTP Antibody, HRP conjugated |
ELISA |
| FITC |
CSB-PA015209LC01HU |
MTTP Antibody, FITC conjugated |
|
| Biotin |
CSB-PA015209LD01HU |
MTTP Antibody, Biotin conjugated |
ELISA |
Purification Method
>95%, Protein G purified
Concentration
It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
Buffer
Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, PH 7.4
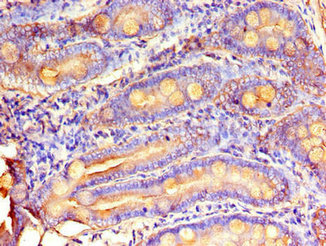
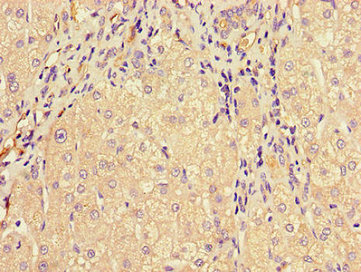
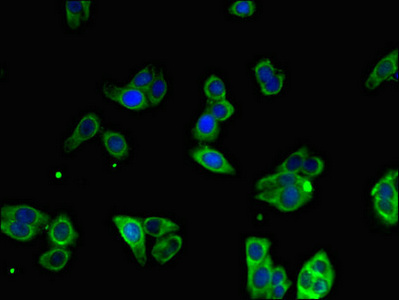
Tested Applications
ELISA, IHC, IF
Recommended Dilution
| Application |
Recommended Dilution |
| IHC |
1:20-1:200 |
| IF |
1:50-1:200 |
Storage
Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
Lead Time
Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
Usage
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.