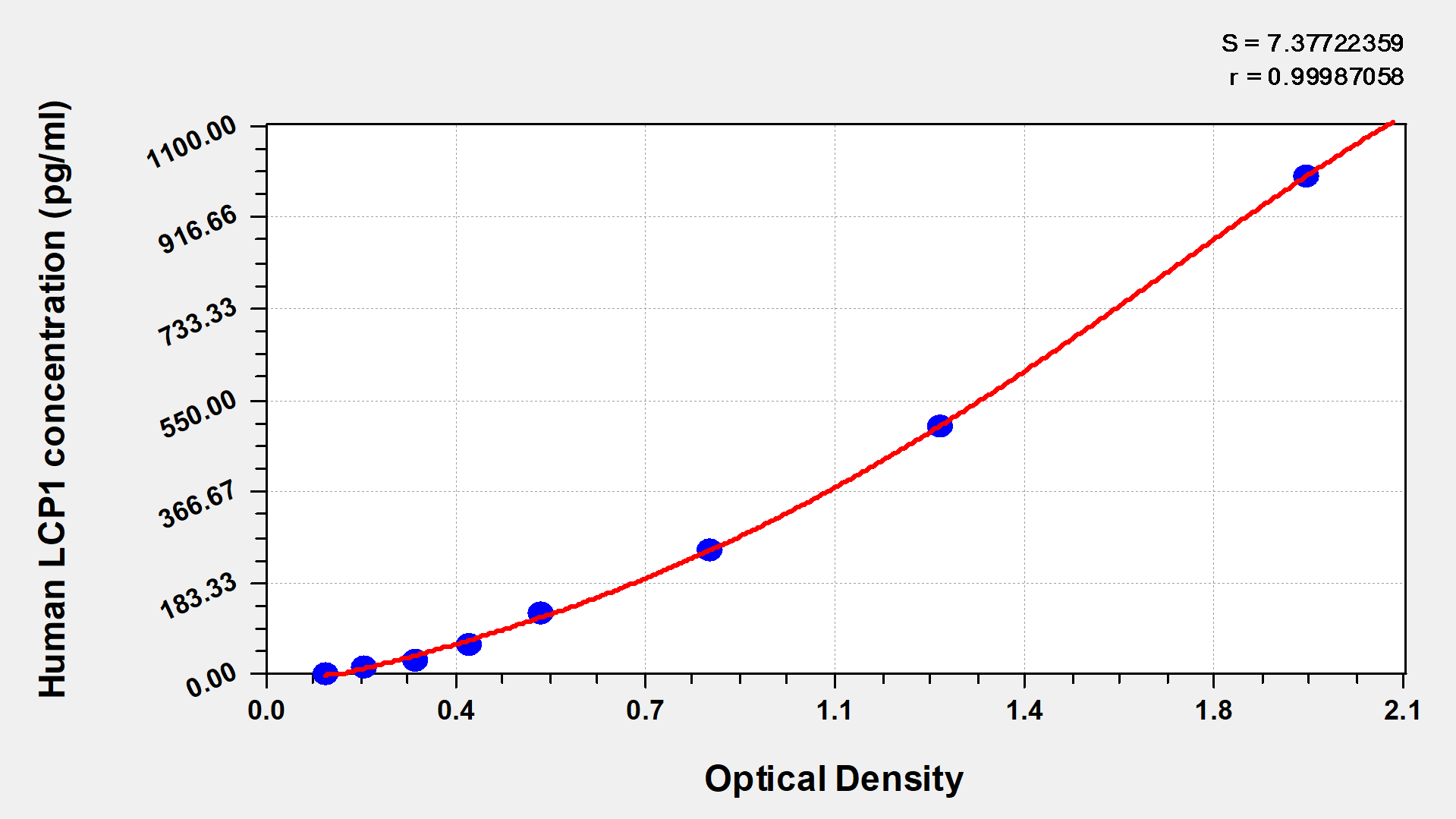
CUSABIO's human plastin-2 (LCP1) ELISA kit is an in vitro enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantitatively measuring human LCP1 in serum, plasma, or tissue homogenates. This assay uses the sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique in combination with the enzyme-substrate chromogenic reaction to quantify the analyte in the sample. The color develops positively to the amount of LCP1 in samples. The color intensity is measured at 450 nm via a microplate reader.
LCP1, alternatively referred to as LPL, is a Ca2+- and actin-binding protein expressed exclusively in myeloid lineage cells, including macrophages and lymphocytes. LPL plays an important role in macrophage functions such as host defense against bacterial infections. LPL is known to be required for T cell activation and motility. It is also involved in osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption. Its phosphorylation promotes the formation of sealing rings in osteoclasts in the early phase via the actin-bundling process, and its inhibition leads to substantially compromised bone resorption in vitro. Abnormal expression of LPL has been found in multiple nonhematopoietic cancer cells. Overexpression of LPL is associated with cancer invasion and metastasis.