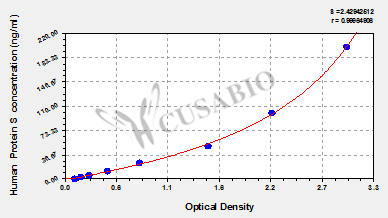
The human Protein S ELISA kit offers a robust and sensitive tool for quantifying Protein S levels in various human samples, including serum, plasma, and tissue homogenates. It provides a detection range of 3.12 ng/mL to 200 ng/mL with a sensitivity of 0.78 ng/mL. The assay principle is based on a sandwich method, utilizing a detection wavelength of 450 nm. The assay time ranges from 1 to 5 hours, requiring a sample volume of 50-100 µl. The kit's sensitivity and wide detection range make it suitable for various experimental applications. The sandwich assay principle ensures precise measurement of Protein S, contributing to the kit's reliability. The use of this ELISA kit can aid in studying conditions such as diabetes and obesity, where Protein S levels are significantly altered and correlated with metabolic markers [1].
References:
[1] L. Scheffler, A. Crane, H. Heyne, A. Tönjes, D. Schleinitz, C. Ihlinget al., "Widely used commercial elisa does not detect precursor of haptoglobin2, but recognizes properdin as a potential second member of the zonulin family", Frontiers in Endocrinology, vol. 9, 2018. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00022