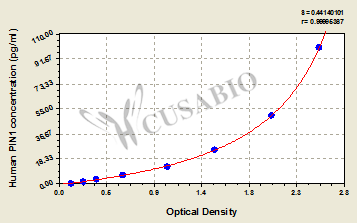
This human PIN1 ELISA kit employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique to measure the levels of human PIN1 in multiple samples, including serum, plasma, urine, or tissue homogenates. It also uses the enzyme-substrate chromogenic reaction to visualize and analyze the analyte levels through the color intensity. The intensity of the colored product is in direct proportion to the PIN1 levels in the sample and is measured at 450 nm through a microplate reader.
PIN1 specifically binds and isomerizes the phosphorylated serine/threonine–proline motif, which leads to the alteration of protein structure, function, and stability. The altered structure and function of these phosphorylated proteins regulated by PIN1 are closely related to cancer development. PIN1 participates in cellular processes such as the cell cycle, the folding of newly synthesized proteins, responses to DNA damage and stress, and immune responses. PIN1 is highly expressed in human cancers, including prostate cancer, breast cancer, and oral squamous carcinomas. PIN1 drives tumor progression and is negatively associated with clinical outcomes in patients with cancer.