Alternative Names
Apoa4 ELISA Kit; Apolipoprotein A-IV ELISA Kit; Apo-AIV ELISA Kit; ApoA-IV ELISA Kit; Apolipoprotein A4 ELISA Kit
Species
Mus musculus (Mouse)
Sample Types
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates
Detection Range
12.5 ng/mL-800 ng/mL
Detection Wavelength
450 nm
Assay Principle
quantitative
Precision
|
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8%
|
|
|
|
|
Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess.
|
|
|
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10%
|
|
|
|
|
Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess.
|
|
|
Linearity
|
To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of mouse APOA4 in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay.
|
|
|
|
Sample
|
Serum(n=4)
|
|
|
1:1
|
Average %
|
101
|
|
|
Range %
|
97-106
|
|
|
1:2
|
Average %
|
106
|
|
|
Range %
|
100-114
|
|
|
1:4
|
Average %
|
98
|
|
|
Range %
|
94-103
|
|
|
1:8
|
Average %
|
90
|
|
|
Range %
|
85-95
|
|
Recovery
|
The recovery of mouse APOA4 spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section.
|
|
|
Sample Type
|
Average % Recovery
|
Range
|
|
|
Serum (n=5)
|
96
|
91-103
|
|
|
EDTA plasma (n=4)
|
91
|
86-96
|
|
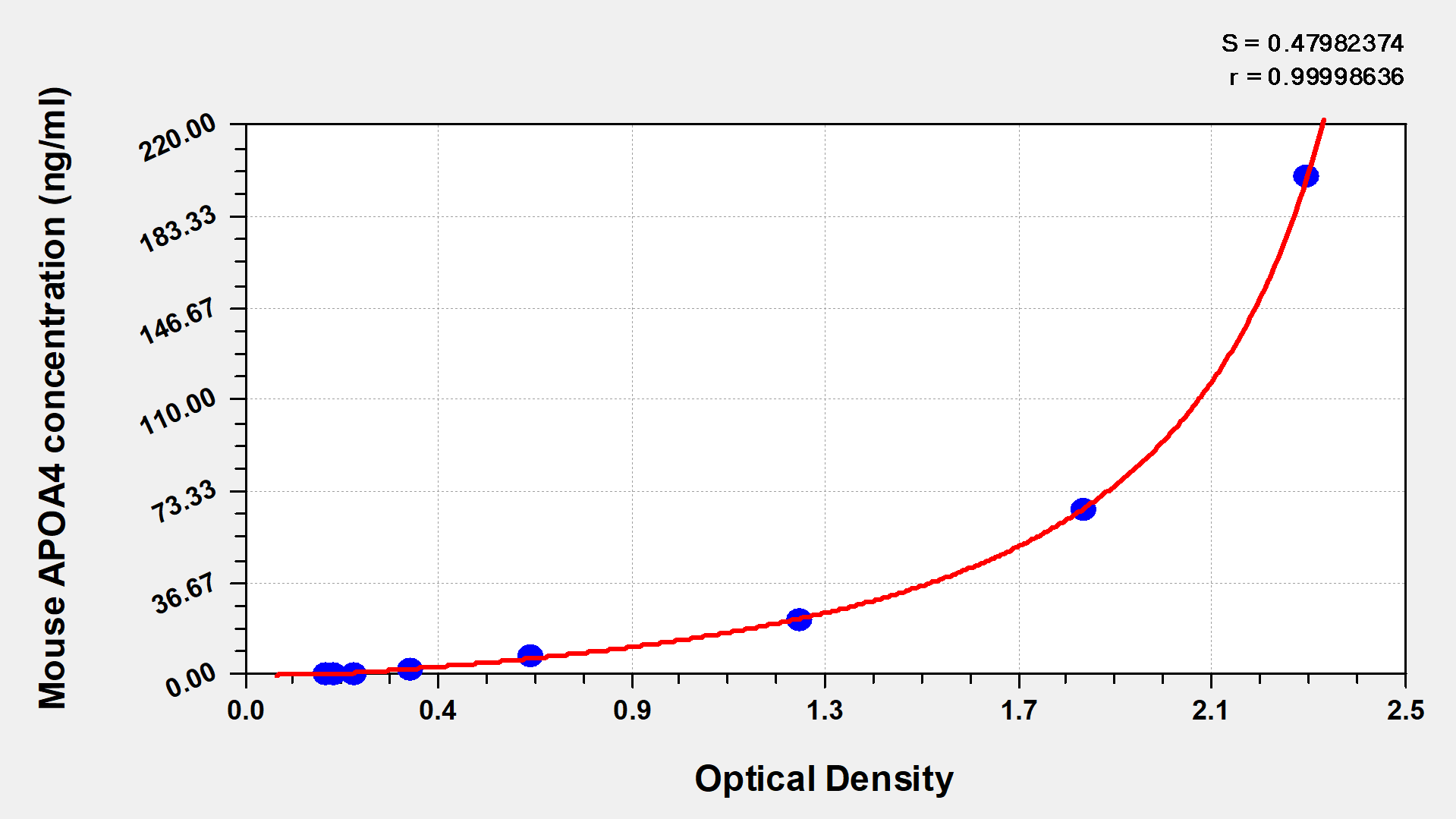
Typical Data
|
These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ng/ml
|
OD1
|
OD2
|
Average
|
Corrected
|
|
|
200
|
2.297
|
2.334
|
2.316
|
2.124
|
|
|
66.6
|
1.895
|
1.767
|
1.831
|
1.639
|
|
|
22.2
|
1.214
|
1.228
|
1.221
|
1.029
|
|
|
7.4
|
0.645
|
0.629
|
0.637
|
0.445
|
|
|
2.46
|
0.388
|
0.371
|
0.379
|
0.188
|
|
|
0.82
|
0.251
|
0.253
|
0.252
|
0.060
|
|
|
0.27
|
0.214
|
0.204
|
0.209
|
0.017
|
|
|
0
|
0.189
|
0.195
|
0.192
|
|
|
Storage
Store at 2-8°C. Please refer to protocol.
Lead Time
3-5 working days after you place the order, and it takes another 3-5 days for delivery via DHL or FedEx.






