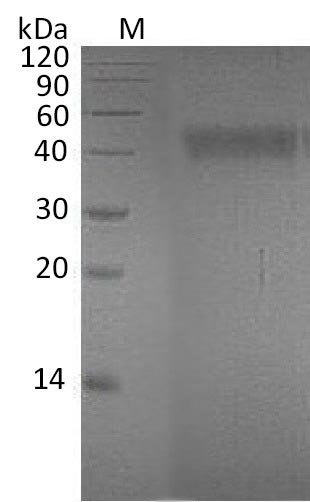
Recombinant Human Ephrin-A4 (EFNA4) is produced using a mammalian cell expression system and covers amino acid region 26-171. The partial protein carries a C-terminal 6xHis-Fc tag, which makes purification and detection more straightforward. SDS-PAGE analysis confirms purity levels exceeding 95%. The protein shows biological activity - functional ELISA testing reveals a binding ED50 of 1.5190 ug/ml to Human EphA7-His. Endotoxin levels stay below 1.0 EU/μg.
Ephrin-A4 appears to play an important role in cell signaling, especially during development. As part of the ephrin family, it works with Eph receptors to enable cell-to-cell communication. This interaction seems critical for several pathways that affect how cells stick together, move around, and organize into tissues. These functions make Ephrin-A4 an interesting target for scientists studying how cells develop and communicate.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
1. Eph-Ephrin Signaling Pathway Studies
This recombinant EFNA4 is confirmed to bind EphA7 (ED₅₀ 1.5190 μg/ml) but has important limitations for signaling studies. The C-terminal Fc tag creates an artificial dimer that may cause non-physiological receptor clustering, potentially amplifying signaling beyond natural monomeric ephrin levels. The partial sequence (26-171aa) lacks the GPI-anchor domain critical for membrane anchoring and proper spatial organization in physiological Eph-ephrin signaling. Researchers should validate key signaling findings with full-length, membrane-anchored EFNA4.
2. Receptor-Ligand Interaction Analysis
The protein is suitable for binding studies but the Fc-induced dimerization may enhance avidity effects, potentially distorting true monomeric affinity measurements. The relatively high ED₅₀ (μg/ml range) suggests moderate binding affinity compared to some high-affinity receptor-ligand pairs. Researchers should include monomeric EFNA4 controls and validate binding kinetics with full-length proteins to ensure physiological relevance.
3. Cell Adhesion and Migration Assays
While the protein can be used for adhesion studies, the Fc-mediated dimerization creates non-physiological clustering that may produce exaggerated adhesion or repulsion responses compared to membrane-anchored ephrins. The soluble nature prevents natural membrane presentation, altering the spatial constraints important for Eph-ephrin-mediated repulsive guidance. Researchers should confirm findings with membrane-bound EFNA4 expression systems.
4. Antibody Development and Validation
This protein serves as a good antigen, but the Fc and His tags may dominate immune responses, reducing antibodies against EFNA4-specific epitopes. Antibodies may recognize artificial conformations created by the dimeric tag. The partial sequence lacks C-terminal GPI-anchor region epitopes. Comprehensive validation requires testing against full-length, membrane-associated EFNA4.
5. Functional ELISA Development
The protein is suitable for ELISA development, but the dimeric nature may enhance apparent affinity through avidity effects. The ED₅₀ should be re-established for each specific assay format. Assays may overestimate binding strength compared to physiological monomeric interactions. Validation with monomeric EFNA4 constructs is recommended for accurate quantification.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This mammalian-expressed human EFNA4 partial protein (26-171aa) with a C-terminal His-Fc tag is a functional binding reagent, but its dimeric nature and lack of membrane anchoring domain significantly limit its applicability for physiological Eph-ephrin signaling studies. The moderate binding affinity (ED₅₀ ~1.5 μg/ml) suggests it's suitable for qualitative binding studies but requires careful interpretation for quantitative applications. For immediate use: employ it at 1-10 μg/ml based on the ED₅₀ for binding assays, but always include monomeric controls to distinguish true affinity from avidity effects. For signaling studies, this dimeric protein may cause exaggerated clustering responses - validate key findings with full-length membrane-bound EFNA4. For adhesion/migration assays, the Fc tag enables easy surface coating but creates non-physiological presentation - supplement with cellular overexpression of full-length EFNA4. For antibody development, use this protein for immunization, but screen clones against GPI-anchored full-length EFNA4. The mammalian expression ensures proper glycosylation, which is crucial for Eph-ephrin interactions, but the artificial dimerization and soluble nature limit physiological relevance. Always include appropriate controls for tag-mediated artifacts and consider that Eph-ephrin signaling normally requires precise membrane presentation and clustering control that this reagent cannot replicate.