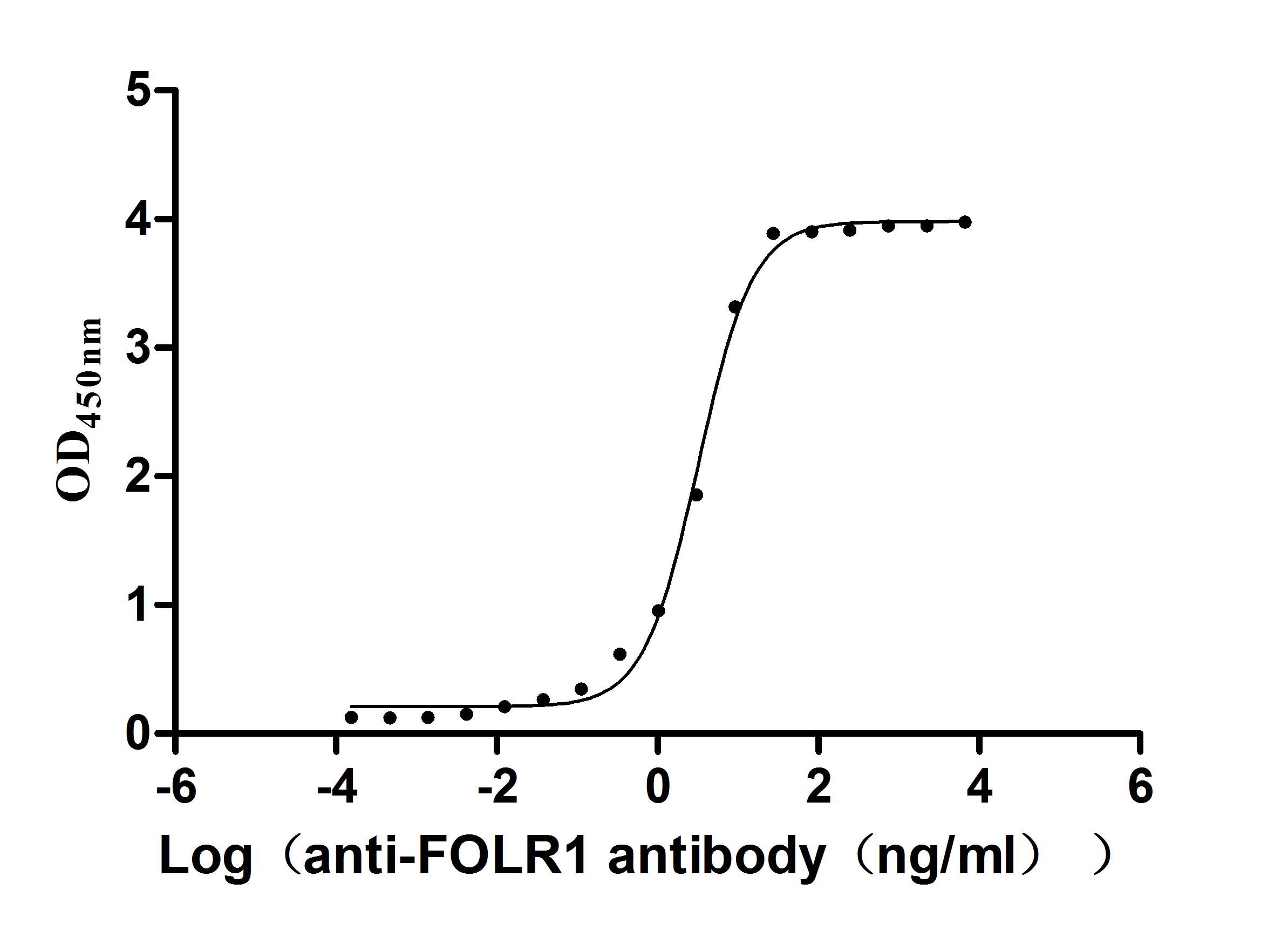
The recombinant Macaca fascicularis FOLR1 protein is an active, high-purity product expressed in mammalian cells to ensure native-like folding and functionality. It includes amino acids 25 to 233 of the original sequence and features a C-terminal 10xHis tag for streamlined purification and assay use. The recombinant FOLR1 protein achieves a purity level above 95%, confirmed by SDS-PAGE. Endotoxin levels are maintained below 1.0 EU/µg, as determined by the LAL method, ensuring compatibility with sensitive biological assays. Functional activity is validated through ELISA, where immobilized FOLR1 at 2 μg/mL binds specifically to the anti-FOLR1 recombinant antibody (CSB-RA008784MA1HU), with an EC50 between 2.900 and 3.544 ng/mL. These properties make it a reliable tool for applications in receptor-ligand studies, antibody screening, and folate pathway research.
The FOLR1 protein, or folate receptor alpha, is a crucial component in cellular functions, particularly in folate transport, which is vital for cellular growth and metabolism. In Macaca fascicularis, this protein has been investigated with various biological processes, particularly its role in reproductive biology, immunity, and disease models.
FOLR1 is integral to folate transport, which is essential for nucleotide synthesis and thereby supports rapid cellular proliferation. This function is particularly significant in the reproductive systems of non-human primates, including M. fascicularis. The protein's expression in the testis is noteworthy, as it supports the spermatogenic process and ensures successful gamete formation. Studies suggest the uniqueness of gene expression programs in the testes of primates, indicating possible adaptations that FOLR1 might have undergone in response to evolutionary pressures [1].
Furthermore, M. fascicularis serves as an important model organism in immunological studies. The expression and function of receptors such as FOLR1 may influence immune responses, including those related to vaccination and disease resistance [2]. For instance, FOLR1 is involved in the cellular uptake of folate, which can modulate immune cell function and proliferation, directly influencing vaccine efficacy and the development of autoimmune diseases [3]. The role of folate is significant due to its involvement in critical immune system interactions and its implications in health and disease.
In addition, M. fascicularis is frequently utilized in biomedical research about human diseases. Their genomic and physiological similarities to humans make them a suitable model for studying various conditions, including cancers, where FOLR1 expression is often altered. Insights into FOLR1's role could enhance therapeutic strategies targeting cancers where this protein is implicated in cell survival and proliferation pathways [4].
References:
[1] A. Boukaba, J. Liu, et al. Ectopic expression of meiotic cohesin generates chromosome instability in cancer cell line. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 119, no. 40, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2204071119
[2] A. Higashino, R. Sakate,.et al. Whole-genome sequencing and analysis of the malaysian cynomolgus macaque (macaca fascicularis) genome. Genome Biology, vol. 13, no. 7, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2012-13-7-r58
[3] R. Campos, E. McDonald, A. Brault, & S. Rossi. Animal models of zika virus sexual transmission. 2021. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.91256
[4] S. Laila, D. Astuti, I. Suparto, E. Handharyani, T. Register, & D. Sajuthi. Atherosclerotic lesion of the carotid artery in indonesian cynomolgus monkeys receiving a locally sourced atherogenic diet. Veterinary Sciences, vol. 9, no. 3, p. 105, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9030105