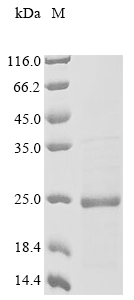
Recombinant Chicken Midkine (RIHB) is produced in E. coli and contains the full-length mature protein spanning amino acids 22 to 142. The protein comes engineered with both an N-terminal 10xHis tag and a C-terminal Myc tag for streamlined purification and detection. SDS-PAGE analysis shows the protein maintains greater than 85% purity, which appears adequate for most research applications. This product is intended for research use only.
Midkine functions as a heparin-binding growth factor that participates in various biological processes. The protein plays what seems to be a crucial role in cell proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis. Its significance likely extends to developmental and repair pathways, making it an important target for scientific studies focused on cellular growth and tissue regeneration.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Chicken Midkine is a heparin-binding growth factor that requires precise folding, proper disulfide bond formation (with five conserved disulfide bonds), and specific tertiary structure for its functional activity in cell growth and differentiation. The E. coli expression system cannot provide the eukaryotic folding environment or oxidative conditions for correct disulfide bond formation. The dual N-terminal 10xHis-tag (∼1 kDa) and C-terminal Myc-tag (∼1.2 kDa) are relatively small but may still interfere with the protein's functional domains and receptor-binding interfaces. While the mature protein region (22-142aa) is complete, the probability of correct folding with functional activity is low without experimental validation of disulfide bond formation.
1. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies Using Pull-Down Assays
This application carries a significant risk without proper folding validation. Midkine interactions with heparin and cell surface receptors require precise tertiary structure and proper disulfide bonding. If correctly folded (verified through heparin-binding assays), the protein may identify physiological interaction partners. If misfolded/unverified, there is a high risk of non-specific binding or failure to replicate genuine receptor interactions.
2. Antibody Development and Validation
This application is highly suitable as antibody development relies on antigenic sequence recognition rather than functional protein folding. The mature protein provides comprehensive epitope coverage for generating antibodies against chicken midkine. The dual tags offer additional epitopes for screening and validation.
3. Comparative Protein Structure and Function Analysis
Meaningful comparative studies require native protein conformation and functional activity. If correctly folded and active (verified), the protein enables valid evolutionary comparisons. If misfolded/inactive (unverified), comparative analyses would yield misleading insights about midkine conservation and divergence across species.
4. ELISA Development and Quantitative Assays
This application is well-suited for developing detection assays. The protein serves as an excellent standard for quantitative midkine detection, as immunoassays depend on epitope recognition rather than functional conformation. The dual tags provide flexible detection options.
5. Cell Culture Supplementation Studies
This application carries a high risk without functional validation. Midkine's biological activity in cell culture requires native conformation and proper receptor binding. If incorrectly folded, the protein will not elicit proper cellular responses and may yield biologically misleading results.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
The E. coli-expressed chicken midkine with dual tags may not be properly folded for functional applications due to the lack of eukaryotic disulfide bond formation machinery. Begin with functional validation using heparin-binding assays and cell-based activity tests to confirm bioactivity before considering Applications 1, 3, and 5. Applications 2 and 4 (antibody development and ELISA) can proceed immediately. If bioactivity is low, consider refolding protocols or use mammalian-expressed midkine for critical functional studies. Always include positive controls with bioactive midkine to validate experimental systems.