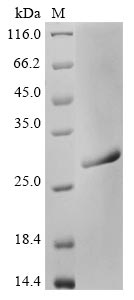
Recombinant Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H from Streptomyces plicatus gets expressed in a yeast system, spanning amino acid region 45-313. This partially expressed protein includes a C-terminal 6xHis-tag, which makes purification and detection straightforward. SDS-PAGE confirms a purity level greater than 90%, suggesting it works well for various research applications that need high-quality reagents.
Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H appears to play a critical role in modifying glycoproteins by cleaving N-linked oligosaccharides. The enzyme seems particularly significant when studying glycoprotein biosynthesis and processing. Researchers often turn to this enzyme for analyzing glycoprotein structures and functions, making it a valuable tool in biochemical research and glycomics.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H (Endo H) is a well-characterized glycosidase that requires precise folding and proper active site formation for its enzymatic activity in cleaving high-mannose and hybrid-type N-glycans. The yeast expression system provides a suitable eukaryotic environment for correct folding and potential glycosylation of this enzyme. The C-terminal 6xHis tag is unlikely to interfere with the catalytic domain and facilitates purification. The partial fragment (45-313aa) likely contains the complete catalytic domain essential for enzymatic function. The probability of correct folding with functional enzymatic activity is high, though experimental validation of deglycosylation activity is recommended.
1. N-linked Glycan Structure Analysis and Deglycosylation Studies
This application is highly suitable. Endo H is widely used for glycan analysis and deglycosylation. The yeast-expressed enzyme with a C-terminal tag is likely fully functional. Validation with standard glycoprotein substrates (e.g., RNase B) is recommended to confirm specific activity before critical experiments.
2. Glycoprotein Mobility Shift Assays and Western Blot Analysis
This application is well-suited for confirming N-glycosylation. The high purity ensures reliable results in mobility shift assays. The enzyme should be tested with control glycoproteins to verify complete deglycosylation capability before analytical use.
3. Preparation of Deglycosylated Protein Standards
This application is suitable but requires optimization. While the enzyme can generate deglycosylated standards, complete removal of the enzyme after reaction is essential to prevent contamination. The His-tag facilitates removal via nickel affinity, but efficiency should be validated.
4. Enzyme Activity and Specificity Studies
This application is highly suitable for biochemical characterization. The recombinant enzyme can be used to determine kinetic parameters (Km, Vmax), pH/temperature optima, and substrate specificity. Comparison with commercial Endo H can validate performance.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This yeast-expressed Endo H with C-terminal His-tag is highly suitable for glycosylation analysis applications due to the appropriate expression system and non-interfering tag placement. Begin with validation using standard glycoprotein substrates (e.g., RNase B for high-mannose glycans) to confirm specific deglycosylation activity. Applications 1, 2, and 4 can proceed once basic activity is verified. Application 3 requires additional optimization to ensure complete enzyme removal after deglycosylation. The partial fragment (45-313aa) should be verified to contain the complete catalytic domain for full functionality.