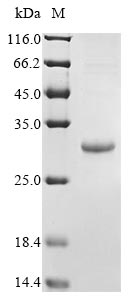
The process of synthesizing recombinant Epstein-Barr virus Secreted protein BARF1 begins with isolating the target gene. This gene encoding the HHV-4 BARF1 (21-221aa) is fused with an N-terminal 6xHis-tag gene and then cloned into an expression vector, which is transformed into E. coli cells. The positive E. coli cells express the recombinant BARF1 protein in the culture medium and are lysed to release these proteins. The collected protein is purified using affinity chromatography. Its purity is greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) secreted protein BARF1 is a viral oncoprotein crucial for EBV-associated malignancies. BARF1 has pleiotropic functions, contributing to cell growth, survival, and immune modulation [1]. It is selectively expressed in latently infected epithelial cancers such as nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) and EBV-positive gastric cancer (EBV-GC) [2]. Despite being an early lytic gene, BARF1 is expressed during epithelial EBV latency, mainly as a secreted protein [3]. BARF1 functions by up-regulating anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and stimulating host cell growth and survival [4]. BARF1 neutralizes hematopoietic colony-stimulating factor 1 (hCSF-1) to achieve immunomodulation [5]. It has been identified as a decoy receptor for macrophage colony-stimulating factors, interfering with macrophage differentiation and activation [6].
References:
[1] E. Hoebe, T. Large, A. Greijer, & J. Middeldorp, Bamhi‐a rightward frame 1, an epstein–barr virus‐encoded oncogene and immune modulator, Reviews in Medical Virology, vol. 23, no. 6, p. 367-383, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1002/rmv.1758
[2] A. Lo, C. Dawson, H. Lung, K. Wong, & Y. Lw, The therapeutic potential of targeting barf1 in ebv-associated malignancies, Cancers, vol. 12, no. 7, p. 1940, 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071940
[3] R. Blanco and F. Aguayo, Role of bamhi-a rightward frame 1 in epstein–barr virus-associated epithelial malignancies, Biology, vol. 9, no. 12, p. 461, 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9120461
[4] E. Seto, L. Yang, J. Middeldorp, T. Sheen, J. Chen, M. Fukayamaet al., Epstein-barr virus (ebv)-encodedbarf1 gene is expressed in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and ebv-associated gastric carcinoma tissues in the absence of lytic gene expression, Journal of Medical Virology, vol. 76, no. 1, p. 82-88, 2005. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.20327
[5] J. Elegheert, N. Bracke, P. Pouliot, I. Gutsche, A. Shkumatov, N. Tarbouriechet al., Allosteric competitive inactivation of hematopoietic csf-1 signaling by the viral decoy receptor barf1, Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, vol. 19, no. 9, p. 938-947, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2367
[6] E. Hoebe, T. Large, N. Tarbouriech, D. Oosterhoff, T. Gruijl, J. Middeldorpet al., Epstein-barr virus-encoded barf1 protein is a decoy receptor for macrophage colony stimulating factor and interferes with macrophage differentiation and activation, Viral Immunology, vol. 25, no. 6, p. 461-470, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1089/vim.2012.0034