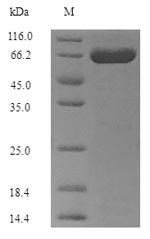
This recombinant Gardnerella vaginalis 5-1 site-specific DNA-methyltransferase (adenine-specific) is expressed in a yeast system and contains the complete protein spanning amino acids 1-525. The protein includes an N-terminal 6xHis-tag for easier purification and detection. With purity levels exceeding 90% as confirmed by SDS-PAGE, this preparation appears well-suited for research applications.
DNA-methyltransferases catalyze the transfer of methyl groups to DNA, usually targeting adenine or cytosine bases. This process may influence gene expression and regulation in ways we're still learning to understand. Since this particular enzyme specifically methylates adenine residues, it could prove useful for investigating epigenetic modifications and how they might affect cellular processes. Research into these mechanisms seems increasingly important for advancing our knowledge of gene regulation and epigenetics.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Based on the provided information, recombinant Gardnerella vaginalis DNA methyltransferase is produced in a yeast expression system as a full-length protein (1-525aa) with an N-terminal 6xHis-tag. DNA methyltransferases are complex enzymes that require precise folding, cofactor binding (SAM), and DNA recognition capability for their catalytic activity. While yeast expression systems provide eukaryotic folding machinery that can support disulfide bond formation and some post-translational modifications, bacterial enzymes may have specific folding requirements that differ from eukaryotic proteins. The full-length nature of the protein increases the probability of correct folding. The small His-tag is unlikely to significantly interfere with enzyme function. Purity >90% by SDS-PAGE indicates good production quality but does not confirm native folding or bioactivity. No validation data (e.g., methylation activity assays, circular dichroism) are provided. Therefore, while the protein has a reasonable chance of being properly folded, its enzymatic activity cannot be confirmed without experimental validation.
1. In Vitro DNA Methylation Assays
Methyltransferase activity requires precise active site formation and cofactor binding; misfolding would render functional studies biologically irrelevant. If correctly folded and functional, this recombinant methyltransferase can be used to study site-specific DNA methylation patterns and kinetics. However, if misfolded or inactive, methylation assays would yield invalid results. The His-tag facilitates purification, but enzymatic activity validation is essential before quantitative studies.
2. Protein-DNA Interaction Studies
DNA recognition depends on native conformation; structural defects would compromise binding specificity studies. If properly folded, the protein can be used in EMSA or surface plasmon resonance to study DNA-binding properties. However, if misfolded, DNA-binding domains may be altered, leading to non-specific binding or failure to recognize genuine recognition sequences.
3. Comparative Enzymology Research
Comparative analyses require native activity to ensure meaningful evolutionary and functional insights. If functionally active, this methyltransferase enables valid comparative studies with other bacterial enzymes. However, activity validation is essential first, as improper folding would make cross-species comparisons misleading.
4. Antibody Development and Validation
Antibody development can proceed without folding validation as it targets linear sequences. This application is suitable, as antibody generation primarily relies on linear epitope recognition. The full-length protein provides comprehensive epitope coverage for producing specific antibodies.
5. Biochemical Characterization Studies
Biochemical studies require a functional enzyme; misfolding invalidates parameter optimization. If correctly folded, the enzyme can be used for biochemical characterization of reaction conditions and kinetic parameters. However, if misfolded, parameter optimization would yield invalid data. The yeast system likely supports proper folding, but activity must be confirmed.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This yeast-expressed full-length methyltransferase has a reasonable probability of proper folding but requires validation before functional applications. The recommended action plan includes: (1) Validate enzymatic activity using DNA methylation assays with appropriate controls; (2) Confirm proper folding through biophysical methods (circular dichroism for secondary structure); (3) For functional studies, include positive controls (known active methyltransferase) and validate activity; (4) Antibody development can proceed immediately; (5) If validation fails, consider bacterial expression systems that may better support bacterial enzyme folding or obtain commercially validated enzyme. Always prioritize activity validation before kinetic or comparative studies to ensure biologically relevant results.