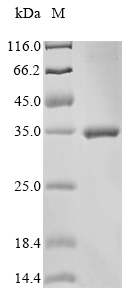
Recombinant Gloydius ussuriensis Thrombin-like enzyme calobin-1 gets expressed in E. coli and spans the full length of the mature protein, covering amino acids 25 to 262. Scientists have engineered the protein with an N-terminal 10xHis tag and a C-terminal Myc tag to make purification and detection more straightforward. SDS-PAGE analysis shows it reaches a purity greater than 85%, which appears suitable for reliable experimental work in research settings.
Thrombin-like enzyme calobin-1 is a serine protease that comes from Gloydius ussuriensis snake venom. The enzyme mimics thrombin's activity by cleaving fibrinogen—a process that plays a crucial role in blood coagulation pathways. Researchers often turn to this enzyme when studying hemostasis and thrombosis, as it may provide insights into blood clotting mechanisms and potential therapeutic applications.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
As a snake venom serine protease, calobin-1 requires precise folding, correct disulfide bond formation, and specific tertiary structure for its functional activity in fibrinogen cleavage. The E. coli expression system cannot provide the necessary eukaryotic oxidative environment for proper disulfide bond formation, which is critical for enzyme stability and activity. The large dual tags may cause significant steric interference with the protein's active site and functional domains. While the protein contains all functional residues, the probability of correct folding with functional enzymatic activity is extremely low without experimental validation.
1. Biochemical Characterization and Enzyme Kinetics Studies
This application carries extreme risk without functional validation. Thrombin-like enzyme activity requires precise active site formation and proper disulfide bonding that E. coli cannot guarantee. If misfolded/inactive (highly probable), kinetic measurements will yield biologically meaningless results. Only if correctly folded and active (requires extensive enzymatic validation) could limited studies be attempted, but tag interference remains a major concern.
2. Antibody Development and Immunological Studies
This application is feasible as antibody development relies on antigenic sequence recognition rather than functional folding. The full-length mature protein provides comprehensive epitope coverage for generating calobin-1-specific antibodies. However, antibodies may primarily target linear epitopes and not recognize conformational epitopes of the native enzyme, limiting their utility for functional studies.
3. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
This application carries a high risk without folding validation. Thrombin-like enzyme interactions with substrates or inhibitors require native conformation. If misfolded (likely), there is a high risk of non-specific binding or tag-mediated artefacts, yielding biologically misleading results. Proper folding and functional validation are essential prerequisites.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This E. coli-expressed calobin-1 with dual tags is unsuitable for most functional studies due to the essential requirements for disulfide bond formation and proper folding that cannot be reliably achieved in this expression system. For reliable calobin-1 research, alternative approaches should be pursued, including using eukaryotic expression systems (e.g., insect or mammalian cells) that support proper oxidative folding, or implementing refolding protocols with extensive activity validation using synthetic substrates or fibrinogen cleavage assays. All applications should include appropriate controls and validation steps to ensure data reliability.