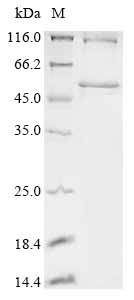
Recombinant human Ankyrin repeat and SOCS box protein 11 (ASB11) production in E. coli starts with cloning the target gene (1-323aa of ASB11) into an expression vector, which is transformed into E. coli cells. The bacteria are cultured under conditions that induce protein expression. Once adequate growth is achieved, the cells are lysed to release the recombinant ASB11 protein. The protein is purified from the cell lysate through affinity chromatography. Protein purity is evaluated using SDS-PAGE, reaching over 85%.
Human ASB11, a member of the ankyrin repeat and suppressor of the cytokine signaling (SOCS) box (ASB) family, has been identified as an endoplasmic reticulum-associated ubiquitin ligase [1]. ASB11 interacts with and promotes the ubiquitination of ribophorin 1, which is involved in the glycosylation of nascent proteins [1]. ASB11 plays a crucial role in the BIK protein ubiquitination process, influencing cell survival and showing promise for anti-cancer strategies [2]. Cul5-ASB11 has been identified as the E3 ligase targeting BIK for ubiquitination and degradation, thereby determining cell fate during cellular stress [2]. Furthermore, ASB11 is a major regulator of human embryonic and adult regenerative myogenesis [3][4]. It exhibits high pan-chordate conservation, indicating fundamental functions in chordate physiology [4].
References:
[1] C. Andresen, S. Smedegaard, K. Sylvestersen, C. Svensson, D. Iglesias-Gato, G. Cazzamaliet al., Protein interaction screening for the ankyrin repeats and suppressor of cytokine signaling (socs) box (asb) family identify asb11 as a novel endoplasmic reticulum resident ubiquitin ligase, Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 289, no. 4, p. 2043-2054, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m113.534602
[2] F. Chen, M. Huang, Y. Lin, C. Ho, S. Lin, H. Chenet al., Bik ubiquitination by the e3 ligase cul5-asb11 determines cell fate during cellular stress, The Journal of Cell Biology, vol. 218, no. 9, p. 3002-3018, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201901156
[3] Y. Li, Uncovering the candidate genes related to sheep body weight using multi-trait genome-wide association analysis, Frontiers in Veterinary Science, vol. 10, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2023.1206383
[4] J. Tee, M. Silva, A. Rygiel, V. Muncan, R. Bink, G. Brinket al., asb11is a regulator of embryonic and adult regenerative myogenesis, Stem Cells and Development, vol. 21, no. 17, p. 3091-3103, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2012.0123