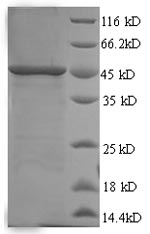
Recombinant Human SMARCB1 is produced in a yeast expression system and covers amino acids 2 to 376 of the protein sequence. An N-terminal 6xHis-tag has been added to help with purification and detection. SDS-PAGE analysis confirms the protein shows greater than 90% purity. This product is for research use only and appears to contain no detectable endotoxin levels.
SMARCB1 acts as a core component of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex and seems to play a crucial role in controlling gene expression by changing chromatin structure. The protein is involved in several cellular processes, including cell cycle control and differentiation. Because of its central position in chromatin remodeling, SMARCB1 has become a major focus for researchers studying gene regulation mechanisms and epigenetic modifications.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Based on the provided information, the recombinant SMARCB1 protein may not be correctly folded or fully bioactive without experimental validation. SMARCB1 is a core component of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, requiring proper folding for its role in protein-protein interactions and nucleosome remodeling. The yeast expression system offers a eukaryotic environment that could support folding and potential post-translational modifications, but the protein is a partial length (2-376aa), missing the C-terminal region (377-385aa). This C-terminal segment may contain functional elements, such as nuclear localization signals or interaction domains, which could impair complete bioactivity. The N-terminal 6xHis tag is relatively small and may not severely interfere with folding, but it could still cause steric hindrance near functional sites. The purity >90% indicates low contaminants, but does not guarantee correct folding. Without validation (e.g., circular dichroism for secondary structure, functional assays with known binding partners), the folding status and bioactivity remain uncertain. Therefore, while the probability of correct folding is moderate due to the eukaryotic system, it is not assured.
1. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
This recombinant SMARCB1 protein can be used in pull-down assays only if it is verified to be correctly folded. The partial sequence (2-376aa) retains key domains but may lack C-terminal functionalities, potentially leading to incomplete or artifactual interactions. If misfolded, pull-down results could yield false positives/negatives. The His-tag enables immobilization, but folding validation (e.g., via binding assays with full-length SMARCB1 partners) is recommended before interaction studies to ensure biological relevance.
2. Antibody Development and Validation
This recombinant SMARCB1 is suitable for antibody generation, but antibody specificity depends on the protein's folding state. If correctly folded, antibodies may recognize native epitopes; if misfolded, they could target non-conformational epitopes, reducing utility for detecting physiological SMARCB1. The His-tag aids purification and assay development, but cross-reactivity with the tag should be controlled. For reliable outcomes, validate antibodies against full-length or native SMARCB1.
3. Structural and Biophysical Characterization
The purified SMARCB1 can be used for structural studies only if correctly folded and with tag removal considerations. The partial length and His-tag may hinder high-resolution structure determination (e.g., by causing heterogeneity in crystallography or NMR). Biophysical techniques (e.g., DLS, AUC) can assess oligomerization and stability, but data interpretation requires folding validation. For meaningful structural insights, use tag-free, full-length protein or confirm folding via spectroscopic methods first.
4. In Vitro Chromatin Remodeling Assays
This recombinant protein is unsuitable for chromatin remodeling assays without bioactivity validation. SMARCB1 requires integration into the SWI/SNF complex for function; the partial length may disrupt complex assembly and nucleosome remodeling activity. If misfolded, assays like nucleosome sliding will yield invalid results. For reliable studies, use full-length, bioactive SMARCB1 and verify activity with positive controls.
5. Biochemical Assay Development
This His-tagged SMARCB1 can serve as a standard for assay development (e.g., quantification or stability tests) independent of folding, as purity >90% supports consistency. However, for functional assays (e.g., measuring enzymatic activities of associated factors), folding and bioactivity must be confirmed. In high-throughput screening, include controls for folding-related artifacts to avoid false interpretations.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
To ensure reliable results, first validate the folding and bioactivity of the recombinant SMARCB1 using techniques such as circular dichroism to confirm secondary structure (expected alpha-helical and beta-sheet content), size-exclusion chromatography to assess oligomeric state, and functional assays (e.g., binding to known SWI/SNF components like BRG1 or nucleosome remodeling assays) to verify activity. If validation fails, consider using full-length SMARCB1 or alternative sources for critical applications. For structural work, remove the His-tag and prioritize homogeneity. In all studies, include appropriate controls (e.g., full-length protein or knockout lysates) to account for potential partial length or folding issues.