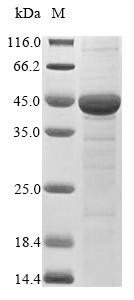
Recombinant Lentinula edodes Peroxidase (mnp2c) is produced in E. coli and includes the complete mature protein sequence from amino acids 21 to 377. The protein carries both an N-terminal 10xHis tag and a C-terminal Myc tag, which makes purification and detection more straightforward. SDS-PAGE analysis confirms the product achieves greater than 85% purity—a level that appears suitable for research applications requiring high-quality protein preparations.
Peroxidases from Lentinula edodes, including mnp2c, seem to play an important role in catalyzing substrate oxidation reactions using hydrogen peroxide. These enzymes are central to lignin breakdown and may have applications in bioremediation and various industrial processes. Studying these enzymes could offer insights into how fungi process nutrients and might contribute to progress in environmental and industrial biotechnology.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Lentinula edodes peroxidase (mnp2c) is a fungal enzyme that requires precise folding, proper heme incorporation, correct disulfide bond formation, and specific tertiary structure for its functional activity in peroxide degradation. The E. coli expression system cannot provide the eukaryotic folding environment, heme incorporation machinery, or oxidative conditions for correct disulfide bond formation required by this complex metalloenzyme. The N-terminal 6xHis-tag may sterically interfere with the protein's active site and substrate-binding domains. While the full-length protein (1-343aa) contains all functional domains, the probability of correct folding with functional peroxidase activity is extremely low without experimental validation of heme incorporation and enzymatic activity.
1. Biophysical Characterization Studies
Basic biophysical analysis can be performed, but will not reflect native peroxidase structure. Techniques like circular dichroism spectroscopy may assess secondary structure content but cannot verify heme incorporation or functional folding. The His-tag may dominate the protein's physical properties, and results will describe an apo-protein rather than the functional holo-enzyme.
2. Antibody Development and Validation
This application is highly suitable as antibody development relies on antigenic sequence recognition rather than functional enzymatic activity. The full-length protein provides comprehensive epitope coverage for generating peroxidase-specific antibodies. The high purity (>85%) ensures minimal contamination-related issues during immunization protocols.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
The E. coli-expressed peroxidase with His-tag is unlikely to be properly folded for functional applications due to the essential requirements for heme incorporation that cannot be met in this expression system. Application 1 (Biophysical Characterization) provides only basic physical characterization of the apo-protein and cannot verify functional folding. Application 2 (antibody development) can proceed immediately as it doesn't require functional protein conformation. For reliable peroxidase research requiring enzymatic activity, use fungal expression systems that support proper heme incorporation and post-translational modifications, or consider in vitro heme reconstitution protocols with extensive functional validation.