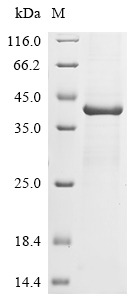
Recombinant Murine polyomavirus Major capsid protein VP1 is expressed in E. coli, covering the full length of the mature protein from amino acids 2 to 373. A C-terminal 6xHis tag is included to help with purification and detection. The protein reaches greater than 85% purity, as confirmed by SDS-PAGE, and works well for research applications. This product is designed for in vitro studies and maintains low endotoxin levels.
The Major capsid protein VP1 appears to be essential for viral capsid assembly in Murine polyomavirus. It likely plays a crucial role in protecting the viral genome, maintaining virus stability, and helping the virus interact with host cells. As a key structural component, VP1 proves valuable for studying viral assembly and pathogenesis, which makes it an important target in virology research.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
The E. coli expression system poses significant risks to proper folding and bioactivity for a complex viral capsid protein like VP1. VP1 must form pentamers and further assemble into virus-like particles (VLPs) through specific interpentamer interactions, disulfide bond formation (e.g., C19–C114), and calcium ion dependency. While E. coli can produce recombinant VP1 that pentamerizes, the system lacks eukaryotic chaperones and may not support native-like disulfide bonding or oligomerization without optimization. The C-terminal His-tag may sterically interfere with the C-terminal arm of VP1, which is critical for invading adjacent pentamers during capsid assembly. While E. coli-derived VP1 can adopt a functional conformation, the absence of validation data means it cannot be assumed to be correctly folded or bioactive. Experimental verification is essential.
1. Viral Capsid Assembly and Structure Studies
This recombinant VP1 protein could be used to study capsid assembly only if its folding and pentamerization are experimentally verified. The full-length sequence contains all domains needed for self-assembly, and the His-tag facilitates purification. However, if the protein is misfolded or improperly oligomerized, in vitro assembly experiments (e.g., using calcium ions) may yield aberrant particles or fail to form VLPs altogether. Techniques like electron microscopy or dynamic light scattering require homogeneous, correctly assembled pentamers for meaningful results. Without validation (e.g., size-exclusion chromatography for pentameric state), data may be misleading.
2. Antibody Development and Immunological Studies
The recombinant VP1 protein is suitable as an immunogen for generating antibodies targeting linear epitopes, as antibody production relies primarily on amino acid sequences rather than native conformation. The high purity (>85%) reduces contamination risks. However, if antibodies are intended to recognize conformational epitopes of native VP1 in viral particles (e.g., for neutralization assays), misfolding of the recombinant protein may result in antibodies that fail to bind authentic virions. The His-tag could also induce tag-specific antibodies, requiring careful screening.
3. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
The His-tagged VP1 can be used technically in pull-down assays to screen for interaction partners (e.g., host receptors or viral proteins like VP2/VP3). However, the biological relevance of interactions depends entirely on correct folding. Misfolding may alter binding interfaces, leading to non-physiological interactions (false positives) or failure to capture genuine partners (false negatives). For example, VP1’s native interaction with sialic acid receptors requires precise tertiary structure. Any identified interactions must be validated using native VP1 from mammalian systems or infection models.
4. Biochemical Characterization and Functional Analysis
This protein can be used for basic biochemical analyses (e.g., thermal stability, protease susceptibility), but results must be interpreted with caution if folding is unverified. Techniques like circular dichroism could assess secondary structure, but data from a misfolded protein would not reflect native VP1 properties. Comparative studies with VP1 from other polyomaviruses require confirmation that both proteins are properly folded to avoid erroneous conclusions about species-specific differences.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
To ensure reliable outcomes, prioritize experimental validation of the protein’s folding and bioactivity before functional applications. Begin with biophysical characterization: use size-exclusion chromatography coupled with multi-angle light scattering (SEC-MALS) to confirm pentameric state (∼210 kDa) and circular dichroism spectroscopy to analyze secondary structure. Then, perform functional assays: test VLP assembly in vitro by adding CaCl₂ and examining particles via electron microscopy, or assess receptor binding using sialylated glycans. If validation succeeds, the protein can be used for the proposed applications with disclosures about tag-related limitations. If validation fails, restrict use to non-conformation-dependent applications (e.g., linear-epitope antibody production).