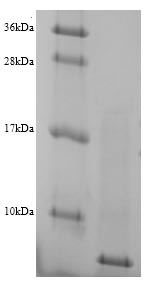
Recombinant Prevotella bryantii Glucomannokinase comes from an E. coli expression system and represents a partial protein covering amino acids 1-25. The product lacks affinity tags, which preserve the native protein sequence. SDS-PAGE analysis confirms purity levels above 90%, making it appropriate for research applications that demand high-quality protein samples.
Glucomannokinase appears to play a key role in carbohydrate metabolism by phosphorylating glucomannan. This enzymatic function may be important for breaking down complex carbohydrates, though the exact mechanisms in different bacterial systems likely vary. Studies of this enzyme could shed light on metabolic pathways and how microbes process carbohydrates, though much remains to be discovered about these intricate processes.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Prevotella bryantii Glucomannokinase is an enzyme that requires precise folding, proper active site formation, and specific tertiary structure for its functional activity in phosphorylating glucomannan. The E. coli expression system can produce soluble proteins but may not support optimal folding for this bacterial enzyme. The partial fragment (1-25aa) represents only a small N-terminal portion of the full-length protein and lacks critical catalytic domains essential for kinase activity. The absence of tags reduces steric interference, but the extremely short length (25aa) makes proper folding into a functional enzyme impossible. The probability of correct folding with any enzymatic activity is zero.
1. Protein Fragment Structural Analysis
Basic structural analysis can be performed, but will not reflect native kinase structure. A 25aa peptide is too short to form a functional kinase domain and will not provide meaningful insights into full-length protein folding or catalytic mechanisms. Techniques may detect secondary structure elements, but cannot represent the complete enzyme's architecture.
2. Antibody Development and Epitope Mapping
This application is suitable for generating antibodies against this specific 25aa N-terminal region. However, antibodies will only recognize this linear epitope and likely will not bind to conformational epitopes of the full-length, properly folded kinase. The short length limits epitope diversity.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This 25aa glucomannokinase fragment is fundamentally unsuitable for any functional or comparative studies due to its extremely short length, which represents only a tiny fraction of the full-length enzyme. It cannot form a functional kinase domain or meaningful tertiary structure. The only limited applications are basic peptide characterization (Application 1) and generating antibodies against this specific linear epitope (Application 2). Avoid all interaction and comparative studies entirely. For reliable glucomannokinase research, use full-length protein constructs that contain the complete catalytic domain and functional regions.